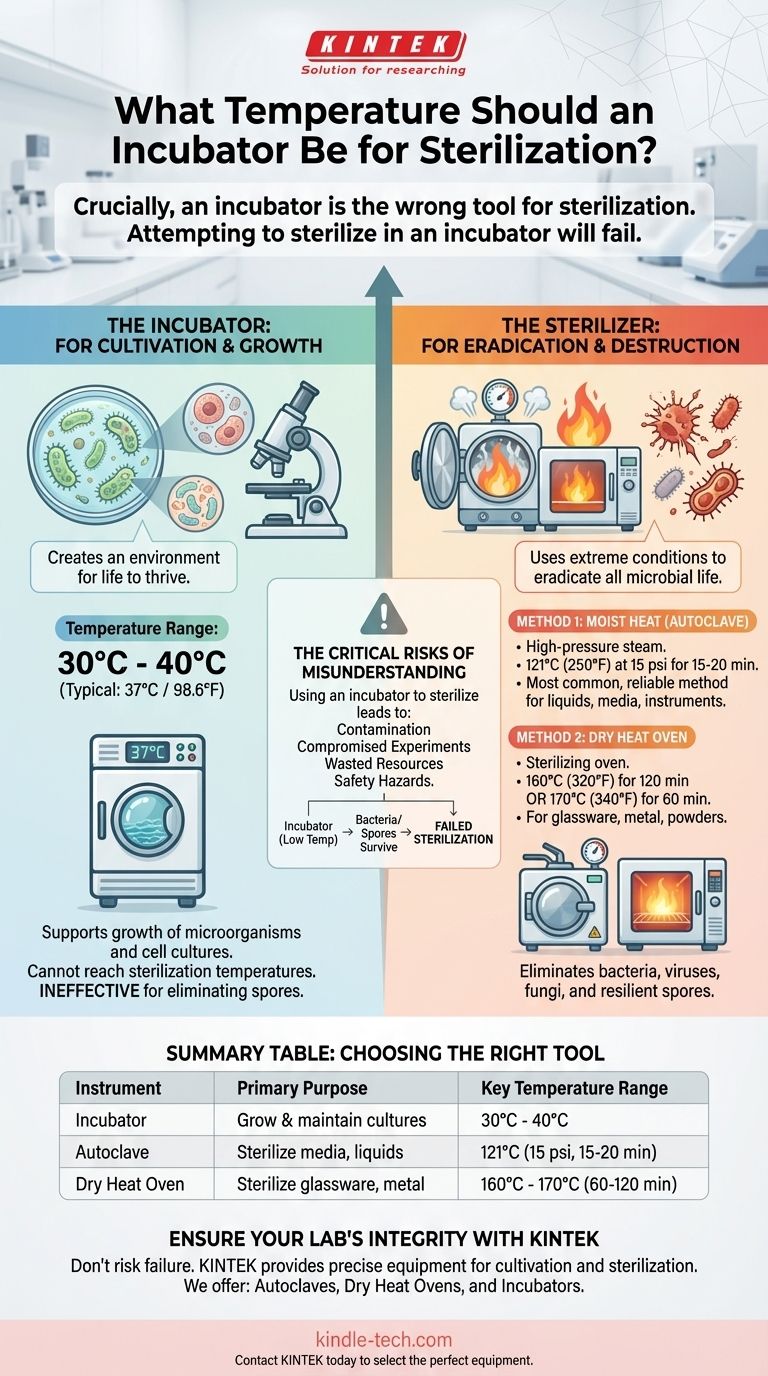
Crucially, an incubator is the wrong tool for sterilization. An incubator is designed to grow and maintain biological cultures, while a sterilizer is designed to destroy them. Attempting to sterilize in an incubator will fail and lead to contamination. For true sterilization, you must use a dedicated device like a dry heat oven or an autoclave.
The core principle to understand is that incubators create an environment for life to thrive, typically between 30°C and 40°C. Sterilizers use extreme conditions—such as dry heat at 170°C or pressurized steam at 121°C—to eradicate all forms of microbial life.

Incubators vs. Sterilizers: A Fundamental Difference
To ensure the integrity of your work, you must use the correct instrument for the job. The functions of an incubator and a sterilizer are diametrically opposed.
The Purpose of an Incubator: Cultivation
An incubator provides a controlled, stable environment to promote the growth of microorganisms or cell cultures.
Its key function is to maintain a specific, consistent temperature, often around 37°C (98.6°F) for mammalian cells or common bacteria. Most incubators cannot even reach temperatures above 80-100°C, which is far below any effective sterilization threshold.
The Purpose of a Sterilizer: Eradication
Sterilization is a process that eliminates or deactivates all forms of life, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and especially resilient bacterial spores.
This requires extreme conditions that incubators are not built to create. Using an incubator for this purpose is not a matter of it being less effective; it is completely ineffective.
Correct Temperatures for True Sterilization
Sterilization is achieved using specific equipment designed to reach and hold validated temperatures for a required duration. The two most common methods in a laboratory setting are dry heat and moist heat.
Method 1: Dry Heat Sterilization
This method uses a sterilizing oven, which is appropriate for materials that can withstand high temperatures but may be damaged by moisture, such as glassware, metal instruments, and powders.
The common standard is exposing items to 170°C (340°F) for at least 60 minutes or 160°C (320°F) for at least 120 minutes.
Method 2: Moist Heat Sterilization (Autoclaving)
An autoclave is the most common and reliable method for general laboratory sterilization. It uses high-pressure steam to penetrate and kill microbes far more efficiently than dry heat.
The universally accepted standard for autoclaving is 121°C (250°F) at 15 psi of pressure for a minimum of 15-20 minutes, though larger loads may require longer cycle times.
The Critical Risks of Misunderstanding
Confusing incubation with sterilization is a significant procedural error that carries serious consequences for your results and safety.
Why You Cannot Sterilize in an Incubator
An incubator's maximum temperature is insufficient to kill heat-resistant microorganisms.
Most importantly, it cannot eliminate bacterial spores, which are dormant, highly protected structures that can survive boiling and require the extreme temperatures of an autoclave or dry heat oven to be destroyed.
The Consequences of Failed Sterilization
If you use an incubator in an attempt to sterilize, your equipment, media, or instruments will remain contaminated.
This will lead to compromised experiments, wasted resources, and unreliable data. In a clinical or diagnostic setting, it can pose a direct safety hazard.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Always match your equipment to the specific biological outcome you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is to grow and maintain cell or bacterial cultures: Use a laboratory incubator set to the optimal growth temperature for your specific organism (e.g., 37°C).
- If your primary focus is to sterilize heat-stable, moisture-sensitive items like glassware: Use a dry heat sterilizing oven at 160°C to 170°C.
- If your primary focus is to sterilize most laboratory media, liquids, and instruments: Use an autoclave, which applies pressurized steam at 121°C.
Choosing the right instrument is the first and most critical step in achieving a successful and valid scientific outcome.
Summary Table:
| Instrument | Primary Purpose | Key Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Incubator | Grow and maintain cultures | 30°C - 40°C (e.g., 37°C) |
| Autoclave (Moist Heat) | Sterilize media, liquids, instruments | 121°C (250°F) for 15-20 min |
| Dry Heat Oven | Sterilize glassware, metal, powders | 160°C - 170°C for 60-120 min |
Ensure Your Lab's Integrity with the Right Equipment
Don't risk contamination and failed experiments by using the wrong instrument. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise, reliable laboratory equipment you need for both cultivation and sterilization.
We offer:
- Autoclaves for effective, reliable steam sterilization.
- Dry Heat Ovens for sterilizing moisture-sensitive items.
- Incubators for maintaining optimal culture conditions.
Let our experts help you select the perfect equipment for your specific application.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss your lab's needs and ensure your protocols are built on a foundation of accuracy and safety.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
People Also Ask
- What role does an autoclave play in remediation experiments? Ensure Precision by Eliminating Biological Noise
- What role does an autoclave play in the acid treatment for microalgae disruption? Unlock High-Yield Cell Pretreatment
- What extreme conditions does a laboratory autoclave simulate? Testing Wear Resistance of Nuclear Fuel Cladding
- Are there any specific types of contamination that an autoclave cannot remove? Understanding the Limits of Steam
- Why is a laboratory high-pressure autoclave sterilizer necessary? Ensure Accuracy in Antibacterial Research



















