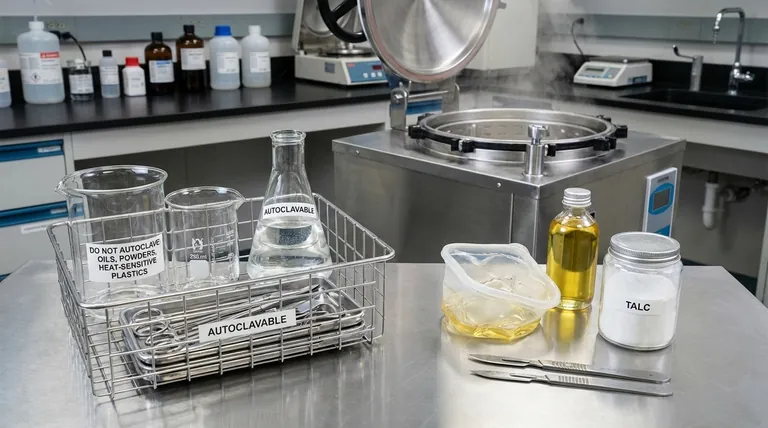
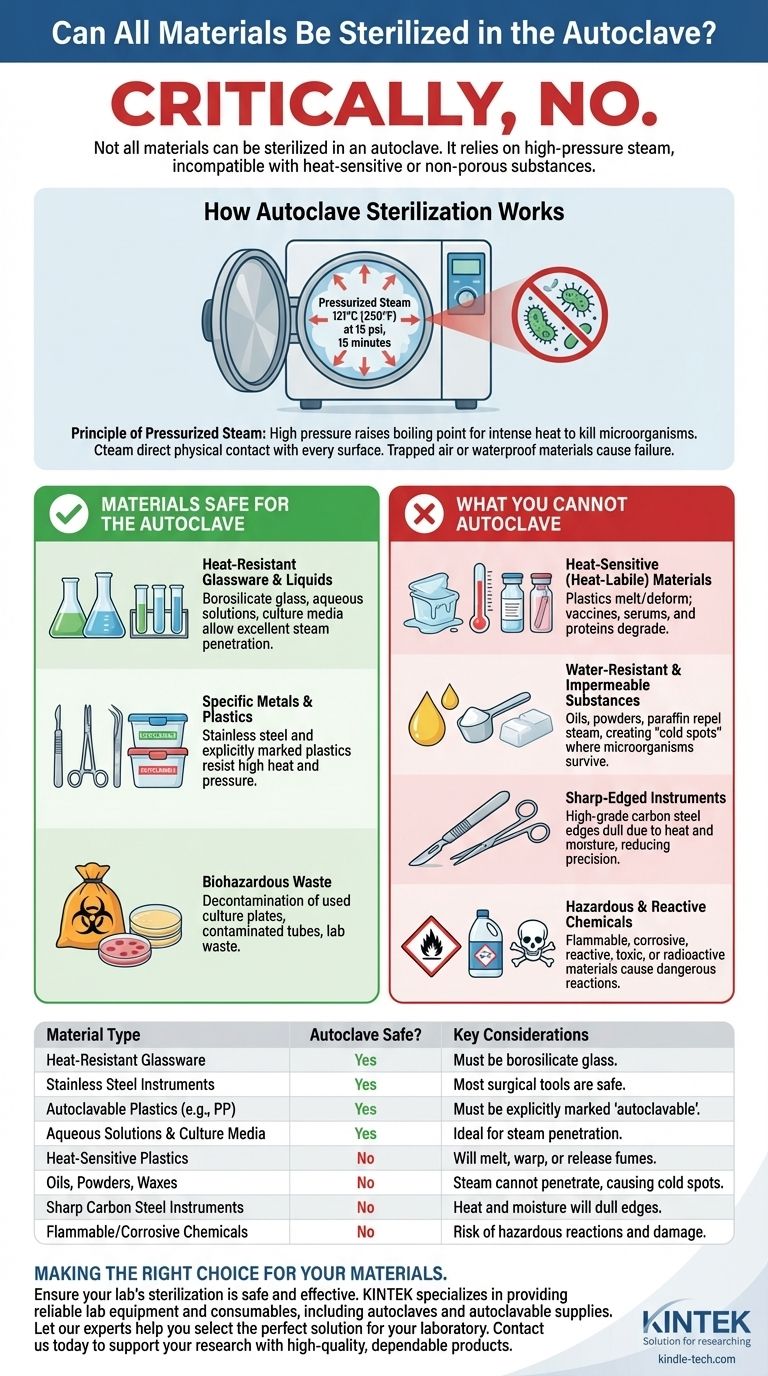
Critically, no, not all materials can be sterilized in an autoclave. An autoclave relies on high-pressure steam to kill microorganisms, making it fundamentally incompatible with any substance that is damaged by high temperatures or cannot be penetrated by water vapor. Using it incorrectly can result in melted equipment, ineffective sterilization, or even hazardous chemical reactions.
The suitability of a material for autoclave sterilization depends entirely on its ability to withstand high temperatures (typically 121°C) and allow for direct contact with pressurized steam. Anything that melts, degrades, repels water, or is chemically reactive is not a candidate for this method.

How Autoclave Sterilization Works
The Principle of Pressurized Steam
An autoclave is a pressure chamber that uses pressurized steam to sterilize its contents. By increasing the pressure, it raises the boiling point of water, allowing the steam to reach temperatures far higher than it could in an open environment.
The standard for sterilization is reaching 121°C (250°F) at 15 psi of pressure and holding those conditions for at least 15 minutes. This combination of intense heat and moisture efficiently denatures the proteins in microorganisms, rendering them sterile.
The Critical Role of Steam Penetration
For sterilization to be successful, steam must make direct physical contact with every surface of the item. If air is trapped or a material is waterproof, the steam cannot transfer its heat effectively, and sterilization will fail. This principle is the primary reason why certain materials are excluded.
Materials Safe for the Autoclave
Heat-Resistant Glassware and Liquids
Autoclaves are ideal for sterilizing autoclave-resistant glassware (like borosilicate glass), aqueous solutions, water, and many types of culture media. These materials easily tolerate the high temperatures and allow for excellent steam penetration.
Specific Metals and Plastics
Most surgical instruments made of stainless steel are perfectly safe to autoclave. However, you must only use plastics that are explicitly marked as "autoclavable," such as polypropylene (PP) and some polycarbonates (PC). These are engineered to resist the high heat and pressure without melting or warping.
Biohazardous Waste
A common and critical use for autoclaves is the decontamination of biohazardous waste before disposal. This includes used culture plates, contaminated tubes, and other laboratory waste that must be rendered non-infectious.
Understanding the Limitations: What You Cannot Autoclave
Heat-Sensitive (Heat-Labile) Materials
This is the largest category of excluded items. Many plastics will melt, deform, or release hazardous fumes. Furthermore, delicate biological solutions like certain vaccines, serums, or proteins (e.g., urea) will degrade and lose njihov effectiveness in the intense heat.
Water-Resistant and Impermeable Substances
You cannot autoclave oils, powders, or paraffin-embedded tissues. Because these materials are waterproof or water-resistant, steam cannot penetrate them to provide the necessary heat for sterilization. This creates "cold spots" where microorganisms survive.
Sharp-Edged Instruments
While many instruments are safe, high-grade carbon steel surgical instruments like scalpels and some scissors should not be autoclaved. The extreme heat and moisture can dull their fine cutting edges, reducing their precision and useful life.
Hazardous and Reactive Chemicals
Never place flammable, corrosive, reactive, toxic, or radioactive materials in an autoclave. The high-pressure, high-heat environment can cause dangerous reactions. Common household bleach, for example, is highly corrosive and will damage the autoclave chamber and release hazardous fumes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Materials
To ensure safety and efficacy, your decision must be based on the material's fundamental properties. Use these guidelines to make a clear choice.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing stable aqueous solutions or approved glassware: The autoclave is the most effective and reliable method.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive liquids or biologicals: You must use an alternative like sterile filtration.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing plastics or instruments: Always verify they are explicitly rated as "autoclavable" to prevent damage to both the item and the equipment.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing oils, powders, or flammable/corrosive chemicals: The autoclave is never the correct tool; you must use other methods like dry heat sterilization or chemical treatment.
Understanding these core principles is the key to achieving successful sterilization while protecting your materials and equipment.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Autoclave Safe? | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Heat-Resistant Glassware | Yes | Must be borosilicate glass. |
| Stainless Steel Instruments | Yes | Most surgical tools are safe. |
| Autoclavable Plastics (e.g., PP) | Yes | Must be explicitly marked 'autoclavable'. |
| Aqueous Solutions & Culture Media | Yes | Ideal for steam penetration. |
| Heat-Sensitive Plastics | No | Will melt, warp, or release fumes. |
| Oils, Powders, Waxes | No | Steam cannot penetrate, causing cold spots. |
| Sharp Carbon Steel Instruments | No | Heat and moisture will dull edges. |
| Flammable/Corrosive Chemicals | No | Risk of hazardous reactions and damage. |
Ensure your lab's sterilization is safe and effective. Choosing the right method is critical for protecting your valuable equipment and samples. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables, including autoclaves and autoclavable supplies, to meet your specific sterilization needs.
Let our experts help you select the perfect solution for your laboratory. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your research with high-quality, dependable products.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- What is the function of laboratory autoclaves in SCWR research? Predict Material Compatibility and Corrosion Kinetics
- What are the advantages of using an autoclave equipped with a stirring device for molten salt testing? Dynamic Accuracy
- What role does an autoclave play in the acid treatment for microalgae disruption? Unlock High-Yield Cell Pretreatment
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK



















