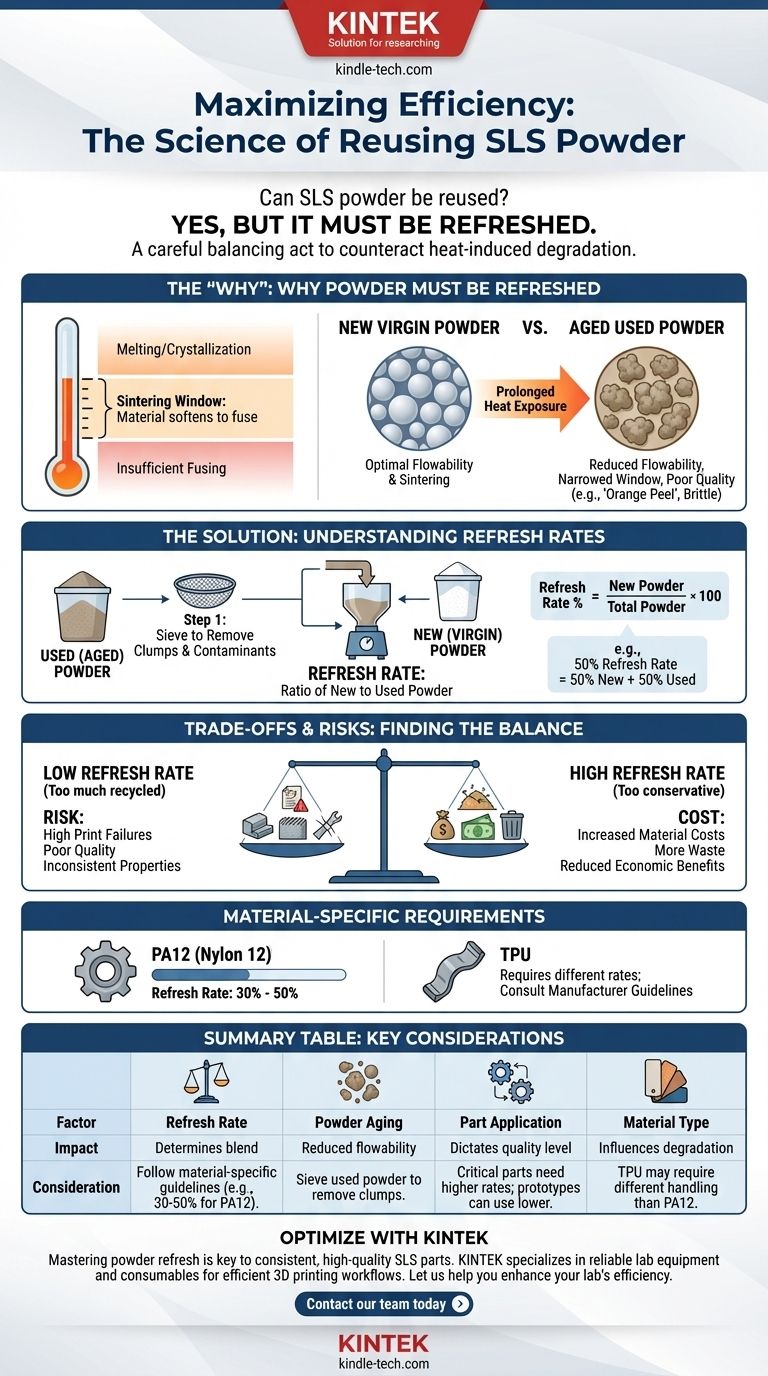
Yes, but it must be done correctly. Reusing unsintered powder from a Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) print job is not just possible—it is a standard and essential practice for making the technology economically viable. However, you cannot simply reuse the old powder as-is. It must be "refreshed" by mixing it with a specific ratio of new, virgin powder to ensure the quality and mechanical properties of your next print.
Reusing SLS powder is a careful balancing act. The goal is to counteract the heat-induced degradation of the used powder by blending it with new material, a process defined by a "refresh rate." Get this ratio wrong, and you risk compromising the integrity of your parts.

Why Powder Must Be "Refreshed," Not Just Reused
To understand powder reuse, you must first understand what happens to all the powder in the build chamber during a print, not just the powder that becomes the part.
The "Sintering Window"
Every SLS material has a specific temperature range known as the sintering window. This is the narrow band of temperatures where the material is soft enough to fuse together when hit by the laser but not so hot that it melts or crystallizes on its own. The entire build chamber is held at a high temperature just below this window.
The Problem of Heat Exposure
The unsintered powder that surrounds your part—often called "cake"—doesn't remain pristine. It sits at an elevated temperature for the entire duration of the print, which can be many hours or even days.
This prolonged heat exposure, while not enough to fully sinter it, causes the powder to age. The polymer chains in the particles begin to change, and some particles may even lightly fuse together.
How Aging Degrades Powder Quality
Aged powder has different properties than new, virgin powder.
- Reduced Flowability: Aged particles become less spherical and clump together, preventing the recoater blade from spreading a smooth, dense layer of powder for the next layer of the print.
- Narrowed Sintering Window: The material's thermal properties shift, making it more difficult to process consistently.
- Poor Part Quality: Using overly-aged powder leads to a common defect known as "orange peel," where the part surface is rough and uneven. It can also result in parts that are more brittle and have lower mechanical strength.
The Solution: Understanding and Using Refresh Rates
The industry-standard solution to powder degradation is to refresh the used material by mixing it with new powder.
What is a Refresh Rate?
A refresh rate is the required ratio of new (virgin) powder to used (aged) powder in a mix. For example, a 50% refresh rate means your mix is 50% new powder and 50% used powder.
This process introduces fresh, un-aged particles back into the system, effectively diluting the degraded powder and restoring the mix's overall quality and processability.
The Refreshing Process
The process is straightforward but requires care. First, the entire block of used powder is removed from the printer. The finished parts are excavated, and the remaining loose powder is collected.
This used powder is then sieved to filter out any clumps, partially sintered chunks, or other contaminants. Finally, it is carefully weighed and blended with the correct amount of virgin powder to achieve the desired refresh rate.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Choosing a refresh rate is a strategic decision that balances cost against quality.
The Risk of a Low Refresh Rate
Using too much recycled powder (a low refresh rate) is a common mistake driven by a desire to minimize costs. This significantly increases the risk of print failures, "orange peel" surfaces, and parts with poor, inconsistent mechanical properties. The money saved on material is quickly lost on failed prints and unusable parts.
The Cost of a High Refresh Rate
Conversely, being too conservative with an unnecessarily high refresh rate (e.g., 70-80% new powder) increases material costs and generates more waste. This undermines the primary economic and environmental benefits of reusing powder in the first place.
Material-Specific Requirements
There is no universal refresh rate. Different materials age differently. For example, a standard PA12 (Nylon 12) often uses a refresh rate between 30% and 50%. More flexible materials like TPU may require different rates due to their unique thermal properties. Always start with the recommendation from your material manufacturer.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To implement a safe and effective reuse strategy, align your refresh rate with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum part quality and performance: Strictly follow the material manufacturer's recommended refresh rate, typically around 50%, to ensure the highest consistency and best mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is cost reduction for non-critical prototypes: You can experiment with slightly lower refresh rates (e.g., 30-40%), but you must implement rigorous quality control to monitor for any decline in surface finish or part strength.
- If you are new to SLS printing: Always begin with the manufacturer's official guidelines. Deviating without a deep understanding of your machine and material is a recipe for failed prints and frustration.
Mastering your powder reuse strategy is fundamental to succeeding with SLS technology and achieving both cost-effective and high-quality production.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Reuse Strategy | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Refresh Rate | Determines blend of new vs. used powder | Follow material-specific guidelines (e.g., 30-50% for PA12) |
| Powder Aging | Causes reduced flowability and poor sintering | Sieve used powder to remove clumps before blending |
| Part Application | Dictates required quality level | Critical parts need higher refresh rates; prototypes can use lower rates |
| Material Type | Influences degradation rate | TPU may require different handling than PA12 |
Optimize Your SLS Powder Management with KINTEK
Mastering your powder refresh rate is key to achieving consistent, high-quality SLS parts while controlling costs. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables that support efficient 3D printing workflows. Whether you need precision sieves for powder preparation or expert advice on material handling, we are here to help.
Let us help you enhance your lab's efficiency and part quality. Contact our team today to discuss your specific SLS powder management needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Electrode Polishing Material for Electrochemical Experiments
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Customizable XRD Sample Holders for Diverse Research Applications
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a laboratory autoclave in the pre-treatment of medical plastic waste for liquid fuel?
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- What are the advantages of using an autoclave equipped with a stirring device for molten salt testing? Dynamic Accuracy
- What experimental conditions do stainless steel autoclaves provide for PCT-A leaching? Optimize Phosphate Glass Testing
- What role does an autoclave play in the acid treatment for microalgae disruption? Unlock High-Yield Cell Pretreatment



















