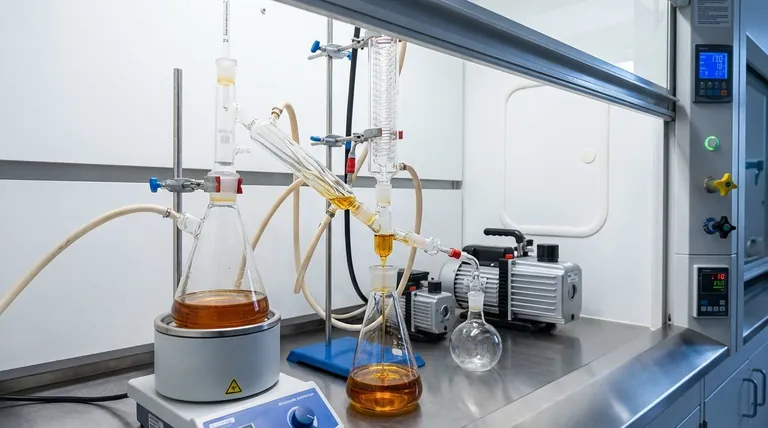
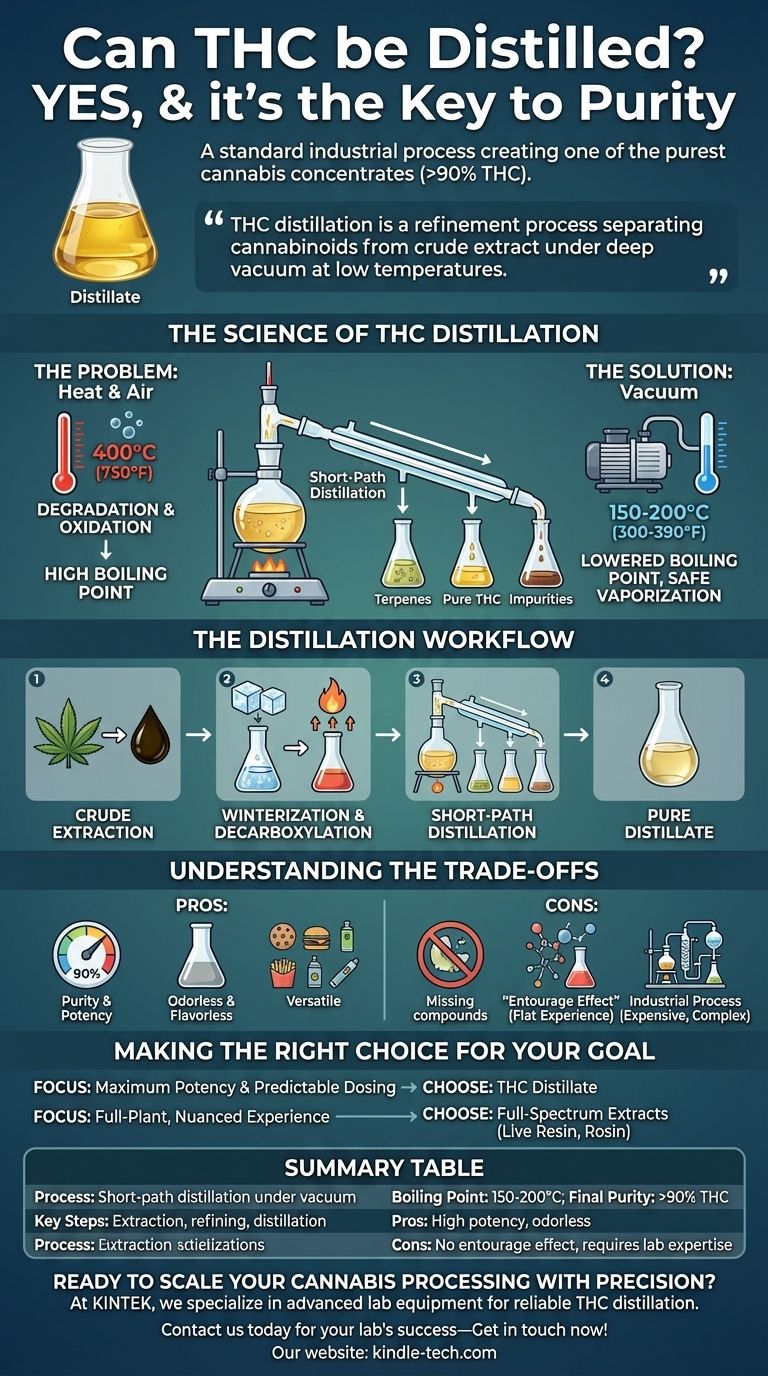
Yes, THC can be distilled, and it is a standard industrial process used to create one of the purest cannabis concentrates available. This technique, known as fractional or short-path distillation, isolates THC from other plant compounds by leveraging differences in their boiling points. The final product is a thick, translucent oil called "distillate," which can achieve purity levels exceeding 90% THC.
THC distillation is a refinement process that separates cannabinoids from crude cannabis extract. It works by heating the oil under a deep vacuum, which allows the THC to vaporize at a low temperature, leaving behind lipids, chlorophyll, and other impurities.

The Science of THC Distillation
To understand how THC is distilled, you first need to grasp the core principle: different compounds turn into vapor at different temperatures. Distillation exploits this to separate a desired compound from a mixture.
The Problem with Heat and Air
At normal atmospheric pressure, THC has a very high boiling point of over 400°C (750°F). Heating it to this temperature would destroy the molecule completely. The presence of oxygen also causes rapid degradation, or oxidation, at high temperatures.
The Solution: Vacuum
The entire process is performed under a deep vacuum. Lowering the pressure inside the distillation apparatus dramatically lowers the boiling point of all compounds. Under vacuum, THC can be vaporized at a much safer and more manageable temperature, typically between 150-200°C (300-390°F).
This allows the THC to be gently separated from less volatile substances like waxes, plant material, and other non-psychoactive compounds, as well as from more volatile compounds like terpenes.
The Distillation Workflow
Creating THC distillate is a multi-step process that begins long before the actual distillation occurs. It requires specialized laboratory equipment and significant technical expertise.
Step 1: Crude Extraction
First, cannabinoids are extracted from the raw cannabis plant using a solvent like CO2, ethanol, or a hydrocarbon. The result is a dark, unrefined "crude oil" that contains THC, other cannabinoids, terpenes, fats, and chlorophyll.
Step 2: Winterization and Decarboxylation
The crude oil must be refined. It is first "winterized" by mixing it with ethanol and freezing it. This causes undesirable fats, lipids, and waxes to solidify so they can be filtered out. The oil is then gently heated in a process called decarboxylation to convert the raw, non-psychoactive THCA into the active THC.
Step 3: Short-Path Distillation
The refined oil is placed into a heated flask connected to a condenser and collection flasks, all under vacuum. As the oil is heated, the most volatile compounds (terpenes) vaporize first and can be collected separately. As the temperature rises, the THC vaporizes, travels a "short path" to the condenser, and cools back into a pure liquid, dripping into a separate collection flask. Heavier impurities are left behind.
Understanding the Trade-offs
THC distillate is a powerful and versatile product, but its unique properties come with distinct compromises.
Pro: Purity and Potency
The primary benefit of distillate is its extremely high concentration of THC. This makes it one of the most potent cannabis products on the market, ideal for users seeking a strong effect from a small amount.
Pro: Odorless and Flavorless
The distillation process removes all the plant's native terpenes, which are responsible for its aroma and flavor. This makes the resulting oil completely neutral, allowing manufacturers to use it in edibles without any cannabis taste or to add specific terpene blends back in for customized vape cartridges.
Con: Loss of the "Entourage Effect"
The main drawback is the removal of those same terpenes and minor cannabinoids (like CBD, CBG, or CBN). Many believe these compounds work synergistically with THC in an "entourage effect," creating a more nuanced and well-rounded experience. The high from pure distillate is often described as "flat" or one-dimensional compared to full-spectrum extracts.
Con: Industrial and Inaccessible
This is not a do-it-yourself process. It requires expensive, fragile glassware, high-powered vacuum pumps, and a deep understanding of organic chemistry to perform safely and effectively.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a cannabis product depends entirely on what you want to achieve. Distillation creates a product with a specific set of characteristics that may or may not align with your needs.
- If your primary focus is maximum potency and predictable dosing: THC distillate is the ideal choice, especially for edibles and vape pens where a neutral, high-purity base is desired.
- If your primary focus is a full-plant, nuanced experience: You should opt for "full-spectrum" extracts like live resin, rosin, or solventless hash oil, which preserve the natural terpenes and minor cannabinoids.
Ultimately, understanding the difference between isolated purity and a complete chemical profile is the key to navigating the modern cannabis market.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Process | Short-path distillation under vacuum |
| Boiling Point (Under Vacuum) | 150-200°C (300-390°F) |
| Final Purity | >90% THC |
| Key Steps | Crude extraction, winterization, decarboxylation, distillation |
| Pros | High potency, odorless/flavorless, versatile for products |
| Cons | Loss of entourage effect, requires lab equipment/expertise |
Ready to Scale Your Cannabis Processing with Precision?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed for reliable THC distillation. Our solutions help you achieve the purity and consistency your customers demand, whether you're producing distillate for vapes, edibles, or other high-value products.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can support your lab's success—Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Customizable Laboratory High Temperature High Pressure Reactors for Diverse Scientific Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is the standard autoclave temperature set to 121? The Science of Effective Sterilization
- What are examples of autoclave in microbiology? Essential Sterilization for Lab Safety & Accuracy
- What are the disadvantages of autoclave in microbiology? Key Limitations for Lab Safety
- What is the size of the autoclave? Choose the Right Capacity for Your Lab
- What equipment is used for laboratory sterilization? A Guide to Autoclaves, Ovens & Filtration


















