Yes, autoclaving is the gold standard and most reliable method for sterilizing the vast majority of surgical instruments. This process uses high-pressure, saturated steam to reach temperatures that are lethal to all forms of microbial life, including highly resistant bacterial spores. However, successful sterilization is not as simple as placing an instrument inside; it is a meticulous process where every step, from cleaning to loading, is critical for ensuring patient safety and preserving the life of the instrument.
The core challenge isn't if you should autoclave surgical instruments, but how to do so correctly. Effective sterilization and instrument longevity depend entirely on rigorous pre-cleaning, proper loading techniques, and selecting the correct cycle parameters.

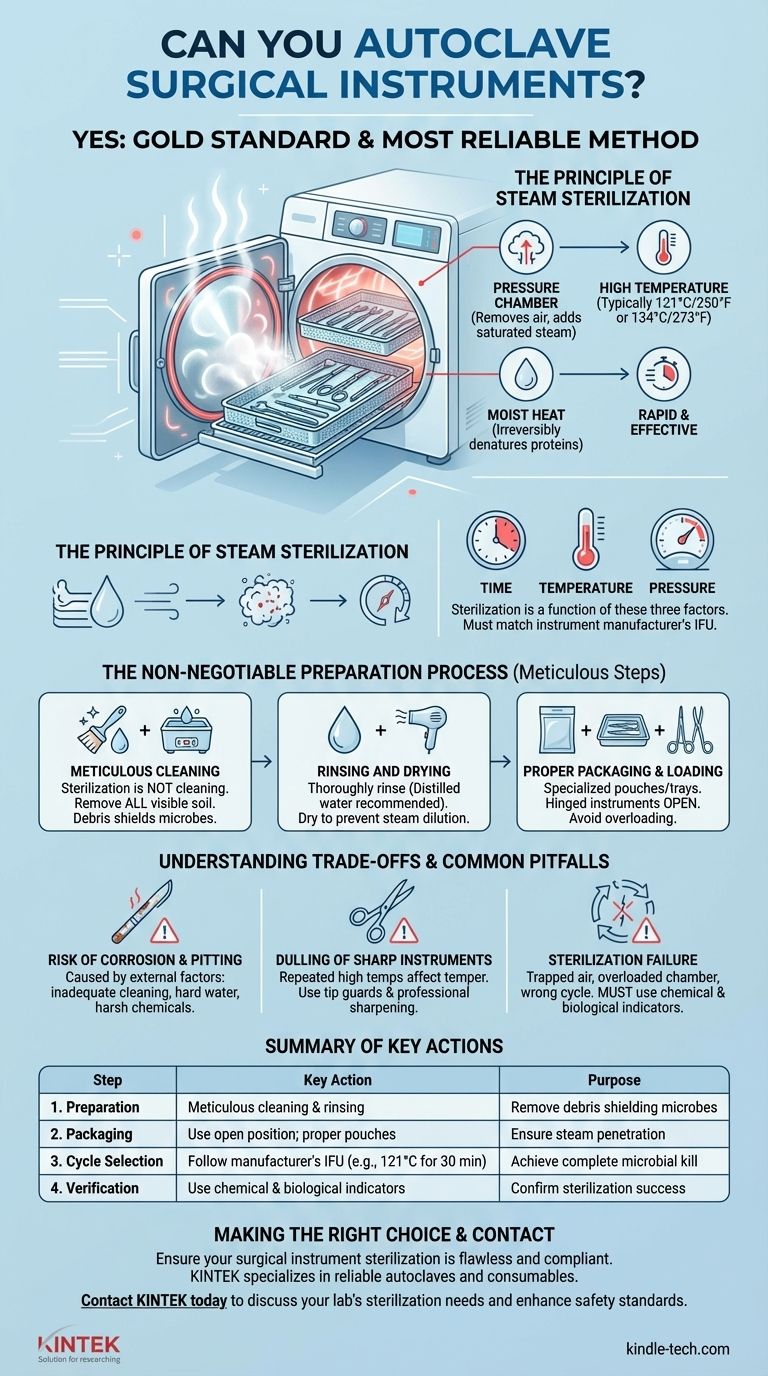
The Principle of Steam Sterilization
How an Autoclave Works
An autoclave is essentially a highly controlled pressure chamber. It works by removing air and replacing it with saturated steam.
By increasing the pressure inside the chamber, the autoclave can achieve steam temperatures far above the boiling point of water (typically 121°C or 134°C), which is necessary for sterilization.
Why Steam is So Effective
Moist heat is exceptionally effective at destroying microorganisms. The hot, condensing steam rapidly transfers thermal energy to every surface of an instrument, irreversibly denaturing the essential proteins that microbes need to survive.
This method is significantly faster and more effective at a lower temperature than dry heat sterilization.
The Critical Variables: Time, Temperature, and Pressure
Sterilization is a function of these three interconnected factors. A typical gravity displacement cycle runs at 121°C (250°F) for at least 30 minutes. A more modern pre-vacuum cycle can achieve sterilization at 134°C (273°F) in as little as 4 minutes.
The chosen cycle must match the instrument manufacturer's recommendations.
The Non-Negotiable Preparation Process
Step 1: Meticulous Cleaning
Sterilization is not cleaning. Any organic debris left on an instrument—such as blood, tissue, or saline—can shield microorganisms from the steam, leading to sterilization failure.
Instruments must first be thoroughly cleaned, either manually with appropriate brushes or in an ultrasonic cleaner, to remove all visible soil.
Step 2: Rinsing and Drying
After cleaning, instruments must be rinsed thoroughly. Using distilled or deionized water for the final rinse is highly recommended, as minerals in tap water can cause spotting, staining, and corrosion over time.
Drying instruments before packaging prevents the steam from being diluted, ensuring its efficacy.
Step 3: Proper Packaging and Loading
Instruments should be placed in specialized sterilization pouches, trays, or containers designed to allow steam penetration while maintaining sterility after the cycle.
Hinged instruments like hemostats or scissors must be placed in the open position. Multi-part instruments should be disassembled to ensure steam reaches every component.
Finally, avoid overloading the autoclave chamber. Packs should be arranged to allow for free circulation of steam around every single item.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Risk of Corrosion and Pitting
Rust and corrosion on stainless steel instruments are almost always caused by external factors, not the autoclaving process itself. The primary culprits are inadequate cleaning (residual organic matter), improper rinsing (mineral deposits from hard water), or exposure to harsh chemicals.
Dulling of Sharp Instruments
Repeated exposure to high temperatures can, over a long period, affect the temper of metal and dull the sharp edges of instruments like scissors and osteotomes.
Proper handling, using protective tip guards, and adhering to a professional sharpening schedule can mitigate this.
Sterilization Failure
The most significant risk is a failed cycle. This can result from air pockets trapped within the chamber (common in gravity displacement autoclaves), an overloaded chamber, improper packaging, or selecting the wrong cycle.
This is why process verification is not optional. Both chemical indicators (which change color) and biological indicators (spore tests) must be used regularly to confirm that every cycle achieves complete sterilization.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is routine sterilization of robust instruments: Your priority must be an unwavering commitment to the multi-step cleaning process and avoiding the temptation to overload the autoclave.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing delicate or microsurgical instruments: Always consult the manufacturer’s instructions for use (IFU), use protective instrument trays, and ensure they are not crushed by heavier items.
- If your primary focus is ensuring absolute safety and compliance: Implement a strict and documented protocol for using chemical indicators in every pack and conducting regular biological indicator (spore) tests to validate your autoclave’s performance.
A disciplined and informed approach to autoclaving is the bedrock of patient safety and effective surgical practice.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Meticulous cleaning & rinsing | Remove debris that can shield microbes |
| 2. Packaging | Use open position; proper pouches | Ensure steam penetration to all surfaces |
| 3. Cycle Selection | Follow manufacturer's IFU (e.g., 121°C for 30 min) | Achieve complete microbial kill |
| 4. Verification | Use chemical & biological indicators | Confirm sterilization success |
Ensure your surgical instrument sterilization is flawless and compliant. Proper autoclaving is critical for patient safety and instrument longevity. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable laboratory autoclaves and consumables designed for the rigorous demands of surgical settings.
Our experts can help you select the right equipment and establish validated sterilization protocols. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your lab's sterilization needs and enhance your surgical practice's safety standards.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
People Also Ask
- What is the primary purpose of an autoclave in the preparation of media for the biological leaching of uranium?
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- How should solid materials in bags be prepared for decontamination? Master Steam Penetration for Safe Sterilization
- What role does an autoclave play in remediation experiments? Ensure Precision by Eliminating Biological Noise
- Why is the prevention of air entrapment critical for the autoclave sterilization process? Ensure 100% Sterility Today



















