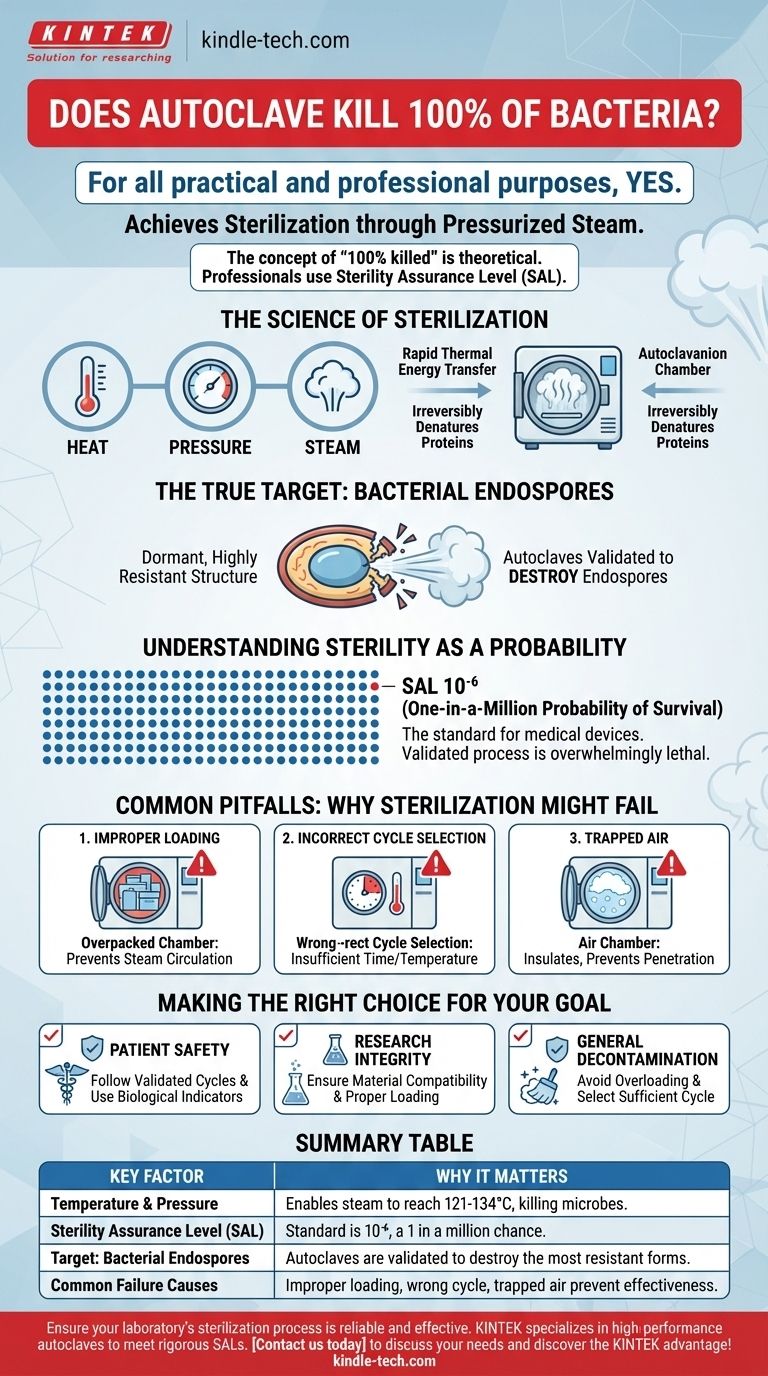
For all practical and professional purposes, yes. A properly functioning and correctly operated autoclave achieves sterilization, which is the complete elimination or destruction of all forms of microbial life, including bacteria. It uses pressurized steam to reach high temperatures that irreversibly denature essential proteins and enzymes within microorganisms, effectively killing them.
The concept of "100% killed" is a theoretical absolute. In scientific and medical fields, sterilization is defined by a Sterility Assurance Level (SAL), which represents the statistical probability of a single microorganism surviving—typically a one-in-a-million chance. An autoclave is designed to meet and exceed this rigorous standard.

The Science of Sterilization
How Autoclaves Achieve Destruction
An autoclave does not simply use dry heat; its effectiveness comes from a combination of heat, pressure, and steam.
Pressurizing the chamber allows the steam to reach temperatures far above the normal boiling point of water (e.g., 121°C or 134°C). This high-temperature, moisture-saturated steam is extremely effective at transferring thermal energy.
This energy rapidly penetrates materials and coagulates the structural proteins and enzymes within any microorganism. This process is irreversible and lethal, disrupting all essential life functions.
The True Target: Bacterial Endospores
The real benchmark for any sterilization process isn't killing simple bacteria, but destroying bacterial endospores.
Endospores are dormant, highly resistant structures produced by certain bacteria (like Geobacillus or Clostridium) to survive extreme conditions. They can withstand heat, radiation, and chemicals that would kill ordinary bacteria.
An autoclave cycle is specifically designed and validated to be powerful enough to eliminate these resilient endospores, ensuring that less-resistant microbes are also destroyed.
Understanding Sterility as a Probability
Professionals don't speak in terms of "100%." They use the Sterility Assurance Level (SAL).
An SAL of 10⁻⁶ is the standard for medical devices. This means there is a one-in-a-million probability that a single microorganism survived the process on a given item.
This probabilistic approach acknowledges that you cannot physically prove the absence of every single microbe. Instead, you validate a process that is so overwhelmingly lethal that the chance of failure is infinitesimally small and professionally acceptable.
Common Pitfalls: Why Sterilization Might Fail
Achieving the required SAL depends entirely on the correct operation of the autoclave. Failure is almost always due to human error or improper maintenance, not a flaw in the underlying principle.
Improper Loading
Items must be loaded to allow for free circulation of steam.
Overpacking the chamber or using sealed, inappropriate containers prevents steam from penetrating the load and reaching every surface, creating cold spots where microbes can survive.
Incorrect Cycle Selection
Different materials require different cycles. A cycle designed for solid metal instruments will not effectively sterilize liquids or porous materials like surgical gowns.
Using the wrong cycle (e.g., insufficient time, temperature, or pressure) is a primary cause of sterilization failure.
Trapped Air
Air is an insulator and the enemy of steam sterilization. If air is not properly removed from the chamber and the items within it, it prevents deep steam penetration.
This is why modern autoclaves have pre-vacuum cycles to actively remove air before injecting steam, ensuring no insulating air pockets remain.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure effective sterilization, your focus should be on the process and validation, not just the machine itself.
- If your primary focus is patient safety in a medical or dental setting: You must strictly follow validated cycles for specific instruments and use biological indicators (vials of endospores) regularly to prove the process is working.
- If your primary focus is research integrity: You must ensure the materials you are sterilizing are compatible with the heat and pressure, and that your loading technique allows steam to penetrate complex lab equipment or media.
- If your primary focus is general decontamination: Ensure you are not overloading the machine and that you are selecting a cycle with sufficient time and temperature to handle the bioburden you are treating.
Ultimately, a properly validated and operated autoclave provides the highest level of sterility assurance required for critical applications.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Why It Matters for Sterilization |
|---|---|
| Temperature & Pressure | Enables steam to reach 121°C-134°C, denaturing proteins and killing microbes. |
| Sterility Assurance Level (SAL) | Standard is 10⁻⁶, a one-in-a-million chance a microbe survives. |
| Target: Bacterial Endospores | Autoclaves are validated to destroy even the most resistant bacterial forms. |
| Common Failure Causes | Improper loading, incorrect cycle selection, or trapped air prevent effective sterilization. |
Ensure your laboratory's sterilization process is reliable and effective. KINTEK specializes in high-performance autoclaves and lab equipment designed to meet the rigorous Sterility Assurance Levels required in medical, dental, and research settings. Our experts can help you select the right autoclave for your specific needs, ensuring patient safety and research integrity. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory's sterilization requirements and discover the KINTEK advantage!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
People Also Ask
- Why is it important to use the autoclave to sterilize laboratory tools? Ensure Complete Sterility for Reliable Results
- What is the pressure of autoclave at 121 C? The Key to Effective Steam Sterilization
- What is cycle time as related to autoclaving? Master the Full Process for Effective Sterilization
- What are the settings of autoclave in microbiology? Achieve Guaranteed Sterility for Your Lab
- What precautions should be taken when using an autoclave in the laboratory? A Guide to Safe Sterilization



















