In short, autoclaves are checked through regular calibration and biological indicator tests to verify their effectiveness, and maintained through routine cleaning and inspection of their physical components. This dual approach ensures both the safety of the operator and the integrity of the sterilization process.
The core principle of autoclave management is that consistent, documented verification is just as critical as physical maintenance. You must not only keep the machine clean and functional but also prove it is achieving the required conditions for sterilization.

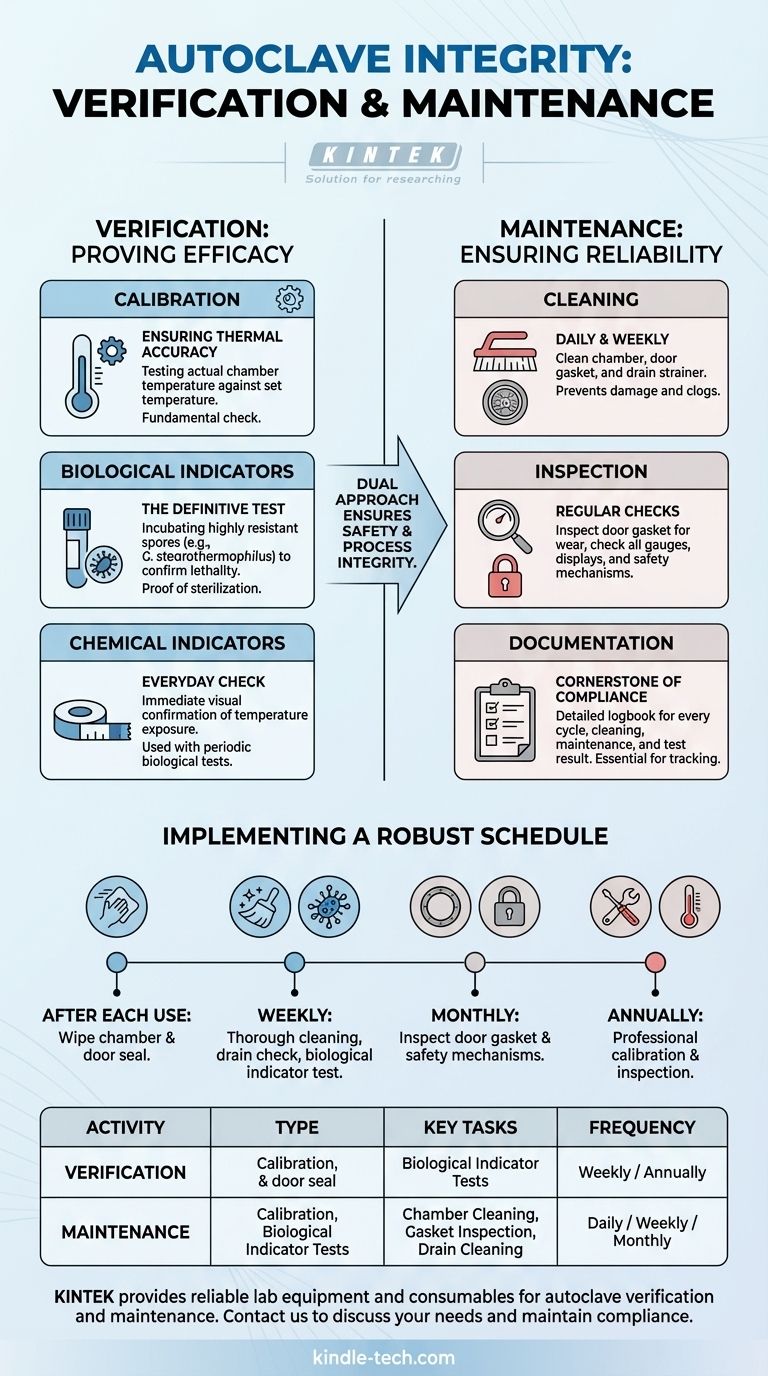
The Pillars of Autoclave Integrity
An effective autoclave management program is built on two distinct but equally important activities: verification (confirming it works) and maintenance (keeping it in working order).
Verification: Proving Sterilization Efficacy
Verification is the process of gathering data to prove the autoclave is reaching the necessary temperature and pressure to achieve sterilization.
Calibration: Ensuring Thermal Accuracy
Calibration involves testing the actual temperature inside the autoclave chamber against the temperature set on the control panel. This is a fundamental check to ensure the machine is performing as the manufacturer intended.
A technician uses a calibrated temperature probe to confirm that a setting of 121°C actually results in a chamber temperature of 121°C. Without this, you are operating on an assumption, not a fact.
Biological Indicators: The Definitive Test
While calibration confirms temperature, biological indicators confirm lethality. These are vials or strips containing highly resistant bacterial spores (like Geobacillus stearothermophilus).
After a cycle, these indicators are incubated. If the spores show no growth, it provides definitive proof that the autoclave's conditions—steam, temperature, and time—were sufficient to kill the most resistant microorganisms.
Chemical Indicators: The Everyday Check
Chemical indicators, such as autoclave tape, change color when exposed to specific temperatures. They are placed on every load to provide immediate, visual confirmation that the load has been processed.
However, they do not prove sterilization was successful; they only show that the necessary temperature was reached. They should always be used in conjunction with periodic biological indicators.
Maintenance: Ensuring Physical Reliability
Routine maintenance prevents equipment failure, ensures safety, and extends the life of the unit.
Daily and Weekly Cleaning
The autoclave chamber and door gasket must be cleaned regularly. Debris, spills, or mineral buildup can damage the chamber, prevent the door from sealing properly, and compromise the entire process.
The chamber drain strainer should also be removed and cleaned to prevent clogs that could impede steam flow and cycle completion.
Inspection of Components
Regularly inspect the door gasket for any signs of cracking or wear, as a faulty seal is a common point of failure. Check that all gauges and displays are functioning and easy to read.
Documentation: The Cornerstone of Compliance
A detailed logbook is non-negotiable. Every cycle, cleaning, maintenance activity, calibration, and test result must be recorded. This log is the primary record of the autoclave's performance and is essential for troubleshooting and regulatory audits.
Responding to Common Problems
Even well-maintained equipment can experience issues. A prepared response is key.
Handling a Spill
If a spill of biological or chemical material occurs inside the chamber, you must not operate the unit until it is safely cleaned.
First, wait for the autoclave to cool completely to room temperature. Then, use an appropriate spill kit and personal protective equipment to contain and clean the material. All waste must be disposed of according to your laboratory's biohazardous material protocols.
Finally, document the entire incident and the clean-up procedure in the autoclave logbook before returning the unit to service.
Implementing a Robust Maintenance Schedule
A proactive schedule removes guesswork and ensures nothing is overlooked.
- After Each Use: Wipe down the chamber and door seal to remove any debris or moisture.
- Weekly: Perform a more thorough cleaning of the chamber and remove and clean the drain strainer. Run a test cycle with a biological indicator to verify efficacy.
- Monthly: Inspect the door gasket for wear and check all safety mechanisms, like the door lock and pressure relief valve, for proper function.
- Annually: Schedule a professional service for a full inspection and temperature/pressure calibration. This service should also include checking all electrical and mechanical components.
By integrating these verification and maintenance tasks into a consistent schedule, you ensure your autoclave remains a reliable and safe asset.
Summary Table:
| Activity Type | Key Tasks | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Verification | Calibration, Biological Indicator Tests | Weekly / Annually |
| Maintenance | Chamber Cleaning, Gasket Inspection, Drain Cleaning | Daily / Weekly / Monthly |
Ensure your lab's autoclave is operating safely and effectively. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment, including autoclaves, and the consumables needed for their verification and maintenance. Our expertise helps laboratories maintain compliance and achieve consistent sterilization results. Contact us today to discuss your autoclave needs and keep your processes running smoothly.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory high-pressure autoclave sterilizer necessary? Ensure Accuracy in Antibacterial Research
- What role does an autoclave play in the acid treatment for microalgae disruption? Unlock High-Yield Cell Pretreatment
- What role does a laboratory autoclave play in the separation of lignin? High-Purity Extraction for Biomass Research
- What is the function of laboratory autoclaves in SCWR research? Predict Material Compatibility and Corrosion Kinetics
- What role does an autoclave play in remediation experiments? Ensure Precision by Eliminating Biological Noise



















