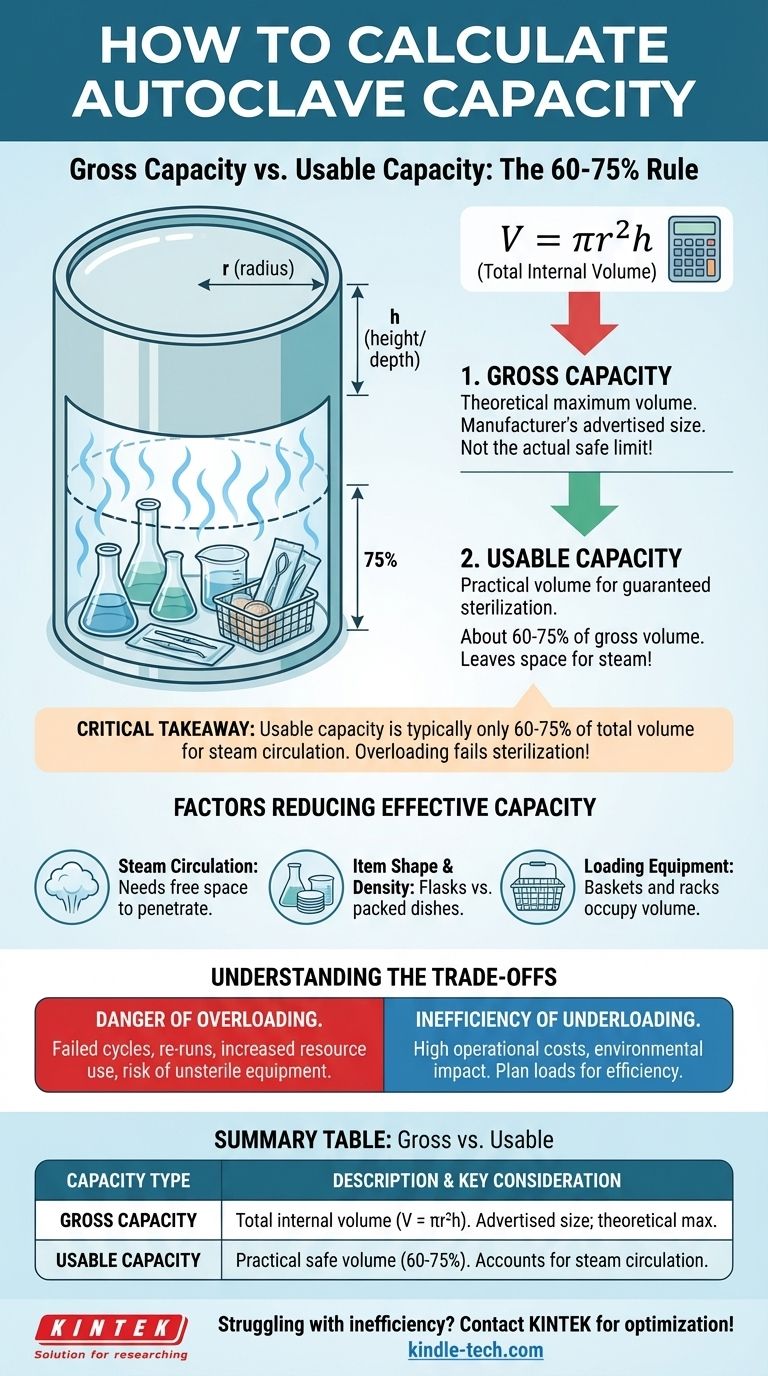
To calculate an autoclave's capacity, you find the volume of its cylindrical chamber using the formula V = πr²h, where 'r' is the radius and 'h' is the height or depth of the chamber. However, this theoretical maximum, known as gross capacity, is very different from the actual amount of material you can safely and effectively sterilize, which is called the usable capacity.
The most critical takeaway is that an autoclave's "usable capacity" is typically only 60-75% of its total calculated volume. Focusing solely on the chamber's dimensions without accounting for loading requirements and steam circulation will lead to inefficient use and failed sterilization cycles.
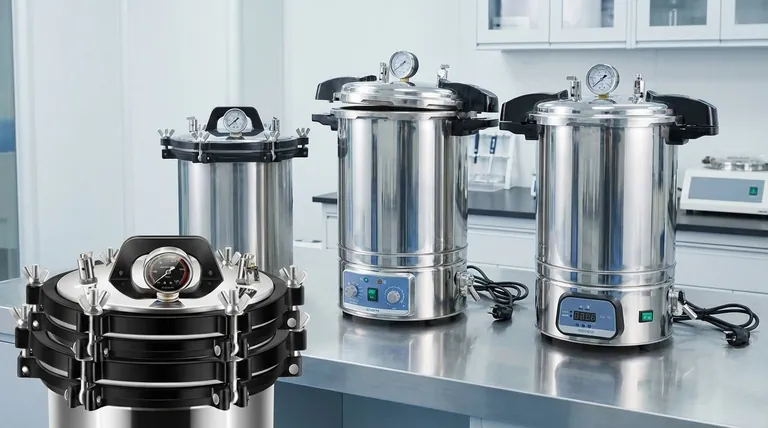

Gross Capacity vs. Usable Capacity
The number a manufacturer advertises is the gross capacity. Your success in the lab depends on understanding the usable capacity.
Step 1: Calculate the Gross Chamber Volume
First, determine the total internal volume of the autoclave chamber. Most laboratory autoclaves have a cylindrical chamber.
Measure the internal radius (from the center to the side wall) and the depth or height of the chamber in centimeters.
Use the standard formula for the volume of a cylinder: Volume = π × (radius)² × height. The result will be in cubic centimeters (cm³), which you can convert to liters by dividing by 1,000.
Step 2: Estimate the Realistic Usable Capacity
Usable capacity is the practical volume you can fill while guaranteeing a successful sterilization cycle. It is always less than the gross capacity.
A reliable industry guideline is the 75% rule. For effective sterilization, you should not load items into more than 75% of the chamber's gross volume. For dense loads like waste, this may be even lower.
This space is not wasted; it is essential for the steam to circulate and penetrate every surface of the load. Without this free space, you create cold spots where microorganisms can survive.
Factors That Reduce Your Effective Capacity
Simply knowing the 75% guideline is not enough. You must understand the physical constraints that dictate how you load the chamber.
Steam Circulation is Non-Negotiable
The fundamental principle of steam sterilization is direct contact. Every surface of every item must be exposed to high-temperature, high-pressure steam for a specific duration.
If items are packed too tightly together or are touching the chamber walls, the steam cannot circulate freely. This creates air pockets or insulated "cold spots" that will not reach sterilization temperature, completely invalidating the cycle.
Item Shape and Container Choice
The type of items you are sterilizing dramatically impacts loading density.
A chamber filled with media bottles or flasks leaves significant empty space between each container. A load of petri dishes can be stacked more densely, but still requires space around the stacks. A bag of biohazardous waste is an irregular shape that prevents other items from being loaded efficiently alongside it.
Required Loading Equipment
Remember to account for the volume taken up by baskets, racks, or solid-bottomed containers. These items are necessary for safe and organized loading, but they occupy a portion of the usable volume before you even add your materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing autoclave use is a balance between throughput and efficacy. Misunderstanding this balance leads to common and costly errors.
The Danger of Overloading
The most common mistake is overloading the chamber to save time. This is a false economy.
An overloaded cycle is very likely to fail. This forces you to re-run the entire load, doubling the time, energy, and water consumption while putting your research or processes on hold. More importantly, it creates the risk of using improperly sterilized equipment.
The Inefficiency of Underloading
Conversely, consistently running very small loads in a large autoclave is inefficient. It consumes a disproportionate amount of energy and water for the amount of material being processed.
While less dangerous than overloading, chronic underloading increases operational costs and environmental impact. Planning your workflow to consolidate loads is key to efficient operation.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your approach to capacity depends on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is purchasing a new autoclave: Calculate your typical load volume, including racks, then multiply by 1.5 to 2.0 to find the minimum gross capacity you should be looking for.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput with an existing unit: Map out your loads based on item type and apply the 75% rule to create standardized loading patterns that guarantee success.
- If your primary focus is ensuring sterilization efficacy: Always prioritize leaving adequate space (at least 1-2 inches) between all items and the chamber walls over maximizing the number of items per cycle.
Ultimately, treating your autoclave's usable capacity as a firm operational limit, not a guideline to be pushed, is the key to safe, efficient, and reliable sterilization.
Summary Table:
| Capacity Type | Description | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Gross Capacity | Total internal chamber volume (V = πr²h) | Manufacturer's advertised size; theoretical maximum |
| Usable Capacity | Practical volume for safe, effective sterilization | Typically 60-75% of gross volume; accounts for steam circulation |
Struggling with autoclave inefficiency or failed cycles? KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables. Our experts can help you select the right autoclave for your lab's specific needs and ensure you maximize its usable capacity for safe, reliable sterilization every time. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and optimize your lab's workflow!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the pressure of autoclave at 121 C? The Key to Effective Steam Sterilization
- What is the purpose of the autoclave incubator? Master the Sterilization vs. Incubation Workflow
- Do autoclaves use a lot of electricity? Managing Energy Costs in Your Sterilization Process
- How is temperature controlled in autoclave? Master the Link Between Pressure and Sterilization
- What is the temperature of a low autoclave? The Critical Minimum for Sterilization
- How do you use autoclave in microbiology? A Guide to Absolute Sterilization for Lab Safety
- What is the alternative method of sterilization for culture media if autoclaving is not suitable? Protect Heat-Sensitive Components
- Is an autoclave a medical device? Understanding Regulatory Classification and Intended Use



















