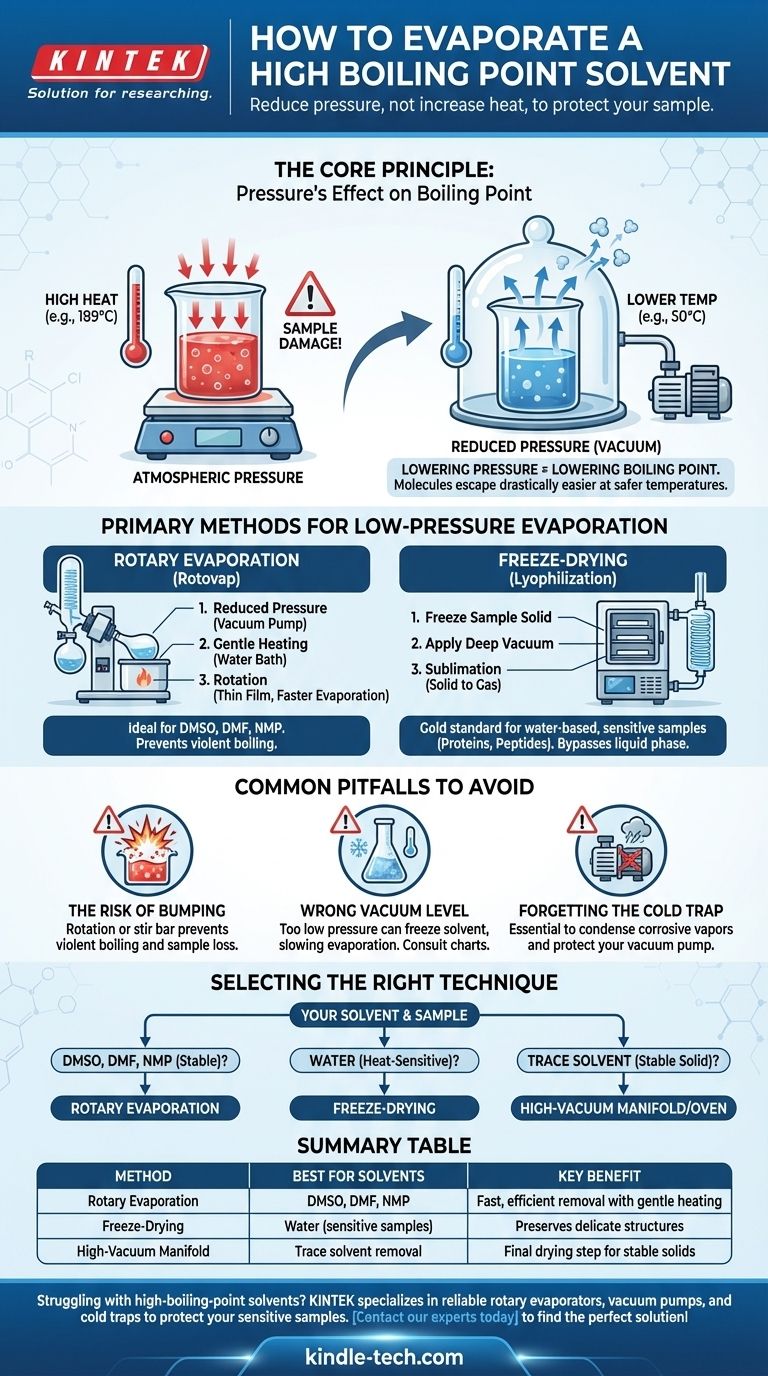
Evaporating a high-boiling-point solvent is a common laboratory challenge where simply adding more heat is often counterproductive and can destroy your sample. The solution is not to force the evaporation with high temperatures, but to change the environment by significantly reducing the pressure. This lowers the solvent's boiling point, allowing it to vaporize gently and efficiently at a much safer, lower temperature.
The core principle is this: instead of fighting the solvent's high boiling point with destructive heat, you change the rules of the game. By applying a vacuum, you make it drastically easier for solvent molecules to escape, enabling rapid evaporation at or near room temperature.
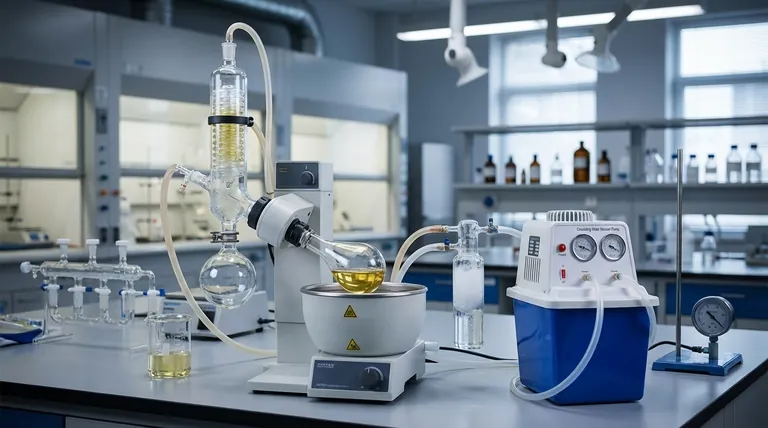

The Core Principle: Pressure's Effect on Boiling Point
To effectively remove a high-boiling-point solvent, you first have to understand the physics at play. The process is entirely governed by the relationship between temperature, pressure, and the physical state of the solvent.
What Defines a Boiling Point?
A liquid boils at the temperature where its vapor pressure—the pressure exerted by its gaseous form—equals the pressure of the environment surrounding it.
At sea level, water boils at 100°C because that is the temperature at which its vapor pressure equals standard atmospheric pressure (~760 torr).
The Pressure-Temperature Relationship
The key insight is that if you can lower the environmental pressure, you also lower the temperature required for the solvent to boil.
Think of it as removing a heavy lid from a container. With less pressure pushing down on the liquid's surface, its molecules can escape into the gas phase far more easily and with less energy (heat).
Why This Protects Your Sample
Many chemical compounds, especially complex organic molecules or biological materials, are thermally sensitive.
Applying the high heat needed to boil something like DMSO (boiling point: 189°C) at atmospheric pressure would almost certainly cause decomposition, side reactions, or polymerization, destroying your final product. Low-pressure evaporation avoids this entirely.
Primary Methods for Low-Pressure Evaporation
Labs use specialized equipment designed to exploit the pressure-temperature relationship. The two most common methods are rotary evaporation and lyophilization.
The Rotary Evaporator ("Rotovap")
A rotary evaporator is the most common workhorse for this task. It efficiently removes solvents by combining three actions simultaneously.
- Reduced Pressure: A vacuum pump lowers the pressure inside the system.
- Gentle Heating: A water bath provides a controlled, low level of heat to the flask.
- Rotation: Spinning the flask spreads the sample into a thin film, dramatically increasing the surface area for faster evaporation and preventing violent boiling (bumping).
This method is ideal for removing common high-boiling-point organic solvents like DMSO, DMF, and NMP.
Freeze-Drying (Lyophilization)
For the most sensitive samples, especially those in water, freeze-drying is the gold standard. This process bypasses the liquid phase completely.
First, the sample is frozen solid. Then, a very deep vacuum is applied. Under these conditions, the frozen solvent sublimates—turning directly from a solid into a gas—which is then captured by an extremely cold condenser.
This technique is essential for preserving the structure of delicate materials like proteins, peptides, and nanoparticles that would be damaged by any amount of heat or the physical stress of conventional evaporation.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While powerful, these techniques require proper execution to be effective and safe. Understanding the potential issues is critical for success.
The Risk of "Bumping"
Under vacuum, a liquid can sometimes superheat and boil explosively in a phenomenon called bumping. This can cause you to lose a significant portion of your sample into the condenser.
The rotation of a rotovap is the primary defense against bumping. For static vacuum systems, adding a stir bar can help.
Choosing the Right Vacuum Level
More vacuum is not always better. If the pressure is too low, you can accidentally freeze your solvent in the flask (a common problem with water on a rotovap), which dramatically slows evaporation.
Always consult a vapor pressure chart or nomograph for your specific solvent to find the optimal temperature and pressure settings.
The Cold Trap is Non-Negotiable
A cold trap—a condenser chilled with dry ice/acetone or liquid nitrogen—must always be placed between your apparatus and the vacuum pump.
Solvent vapors are highly corrosive and will destroy the oil and internal components of an unprotected pump. The cold trap condenses these vapors into a liquid or solid, saving you from a very expensive repair.
Selecting the Right Technique for Your Solvent
Your choice of method depends entirely on the solvent you are removing and the sensitivity of your compound.
- If your solvent is DMSO, DMF, or NMP: A rotary evaporator connected to a suitable vacuum pump and protected by a cold trap is the industry-standard method.
- If your solvent is water and your sample is highly heat-sensitive (e.g., a protein): Freeze-drying (lyophilization) is the superior choice to preserve its delicate structure.
- If you are removing final, trace amounts of solvent from a stable solid: A high-vacuum manifold (Schlenk line) or a vacuum oven can be used for the final drying step after bulk removal.
Mastering pressure control is the key to efficiently isolating your pure compound without compromise.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For Solvents | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Rotary Evaporation | DMSO, DMF, NMP | Fast, efficient removal with gentle heating |
| Freeze-Drying | Water (for sensitive samples) | Preserves delicate structures like proteins |
| High-Vacuum Manifold | Trace solvent removal | Final drying step for stable solids |
Struggling with high-boiling-point solvents? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable rotary evaporators, vacuum pumps, and cold traps to ensure your sensitive samples are protected during evaporation. Our expertise helps laboratories like yours achieve pure, undamaged compounds efficiently. Contact our experts today to find the perfect evaporation solution for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- Vacuum Cold Mounting Machine for Sample Preparation
People Also Ask
- How does a water circulating vacuum pump operate? Discover the Efficient Liquid Piston Principle
- Why is a water circulating vacuum pump suitable for handling flammable or explosive gases? Inherent Safety Through Isothermal Compression
- What is the importance of a vacuum pump for Schottky hybrid interfaces? Achieve Atomic-Level Purity and Bonding
- What are the advantages of a water circulating vacuum pump? Superior Durability for Demanding Lab Environments
- What types of gases can a water circulating vacuum pump handle? Safely Manage Flammable, Condensable & Dirty Gases



















