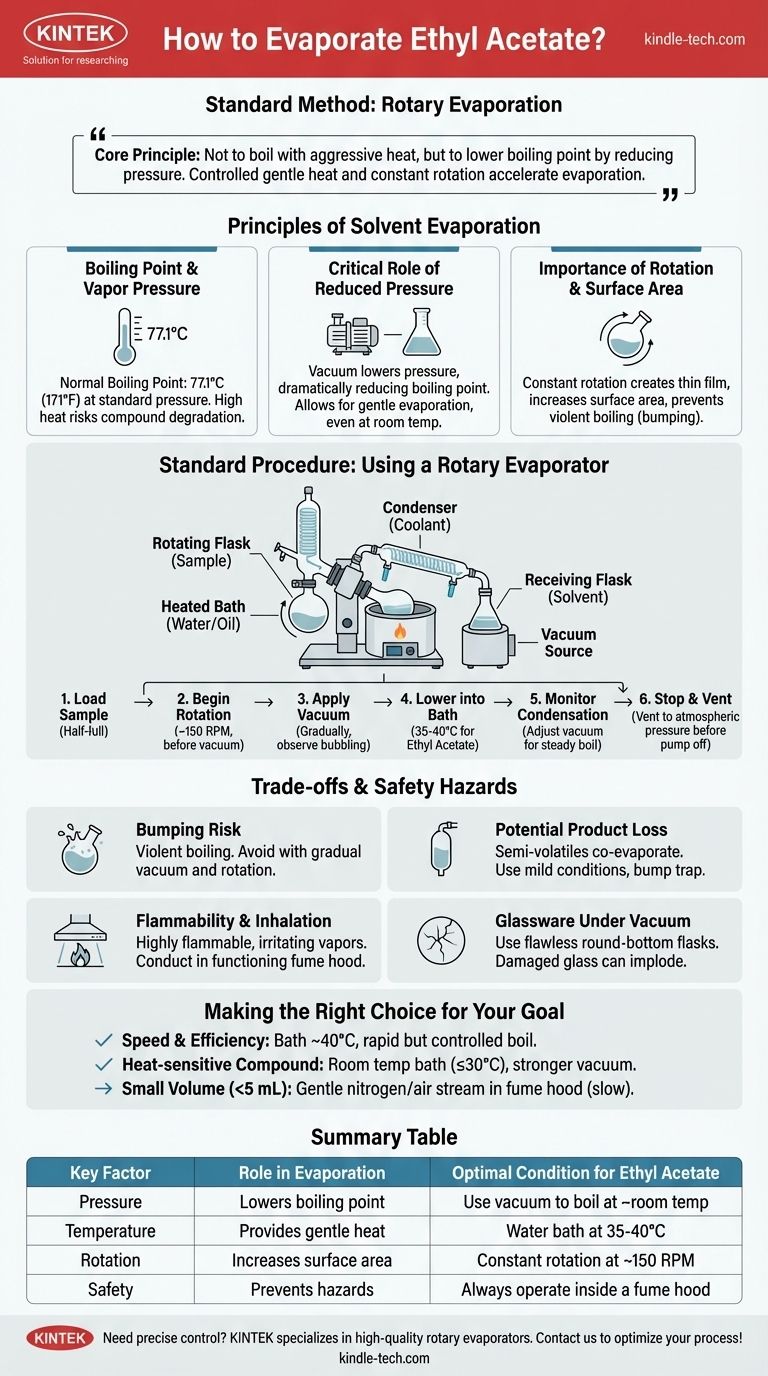
To evaporate ethyl acetate, the most effective and standard laboratory method is rotary evaporation. This technique combines gentle heating with reduced pressure and rotation, which lowers the solvent's boiling point and increases its surface area, allowing for rapid and controlled removal without damaging the dissolved compound.
The core principle is not to boil ethyl acetate with aggressive heat, but to lower its boiling point significantly by reducing pressure. Controlled, gentle heat and constant rotation are then used to accelerate this low-temperature evaporation safely and efficiently.

The Principles Behind Solvent Evaporation
To properly remove a solvent like ethyl acetate, you must understand the interplay of temperature, pressure, and surface area. Mastering these factors gives you precise control over the process.
Boiling Point and Vapor Pressure
Ethyl acetate has a normal boiling point of 77.1°C (171°F) at standard atmospheric pressure. This is the temperature at which its vapor pressure equals the pressure of the surrounding atmosphere, allowing it to turn into a gas.
Attempting to boil it at this temperature can be slow and may risk degrading heat-sensitive compounds you wish to isolate.
The Critical Role of Reduced Pressure
The boiling point of a liquid is directly dependent on the ambient pressure. By using a vacuum pump to lower the pressure inside a sealed system, you can dramatically lower the boiling point of ethyl acetate.
For example, at a moderate vacuum, ethyl acetate can boil at room temperature or even lower, allowing for gentle evaporation.
The Importance of Rotation and Surface Area
Constantly rotating the flask creates a thin, uniform film of the solution on the inner surface. This dramatically increases the surface area available for evaporation.
This rotation also provides agitation, which ensures even heating and prevents violent boiling, a phenomenon known as "bumping."
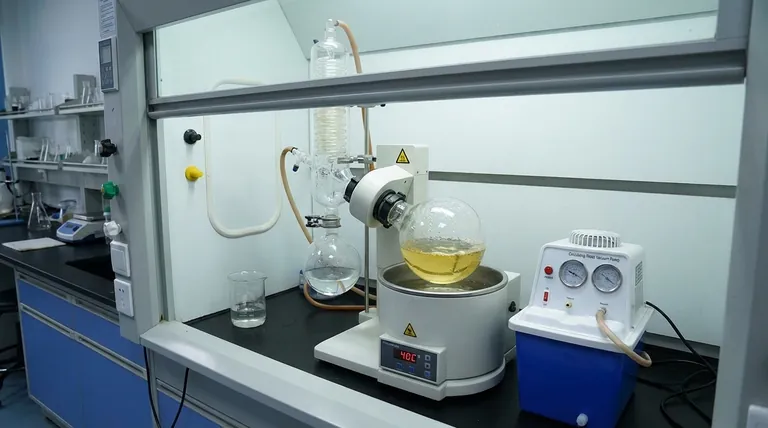
Standard Procedure: Using a Rotary Evaporator
The rotary evaporator, or "rotovap," is the standard piece of equipment designed to leverage these principles for efficient solvent removal.
Key Components
A standard rotovap setup includes a rotating flask containing your sample, a heated water or oil bath, a condenser with circulating coolant, a receiving flask to collect the condensed solvent, and a connection to a vacuum source.
A Step-by-Step Guide
- Load Your Sample: The flask should be no more than half-full to prevent splashing into the condenser.
- Begin Rotation: Start the motor to begin rotating the flask (e.g., ~150 RPM). This must be done before applying vacuum.
- Apply Vacuum: Gradually apply the vacuum. You will see bubbling as dissolved air is removed, followed by the solvent beginning to boil.
- Lower into Bath: Once the system is under a stable vacuum, lower the rotating flask into the pre-heated water bath, typically set to 35-40°C for ethyl acetate.
- Monitor Condensation: Observe the solvent condensing on the cold coil and dripping into the receiving flask. Adjust the vacuum to maintain a steady, non-violent rate of boiling.
- Stop and Vent: Once evaporation is complete, stop the rotation, and carefully vent the system to slowly return it to atmospheric pressure before turning off the vacuum pump.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety Hazards
While efficient, rotary evaporation requires careful attention to avoid common pitfalls and ensure safety.
The Risk of "Bumping"
Bumping is the violent, uncontrolled boiling of a liquid. It can happen if the vacuum is applied too quickly or without rotation, causing you to lose your valuable product into the condenser.
Always apply vacuum gradually and ensure the flask is rotating smoothly before you begin heating.
Potential Product Loss
If your desired compound is semi-volatile, it can co-evaporate with the ethyl acetate. To prevent this, use the mildest conditions possible (lower temperature, less vacuum) and consider using a bump trap between the flask and the rotovap.
Flammability and Inhalation Risks
Ethyl acetate is highly flammable and its vapors are irritating. The entire procedure must be conducted inside a functioning fume hood.
The condenser's purpose is not only to recover solvent but also to prevent flammable vapors from reaching the vacuum pump and being exhausted into the lab. Ensure your coolant is circulating and cold before you start.
Glassware Under Vacuum
Only use round-bottom flasks or specialized evaporating flasks that are free of cracks, scratches, or chips. Damaged glassware can implode under vacuum, posing a significant safety risk.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal conditions depend on the stability of your compound and your desired speed.
- If your primary focus is speed and efficiency: Use a rotary evaporator with a bath temperature around 40°C and adjust the vacuum to achieve a rapid but controlled boil.
- If your primary focus is isolating a heat-sensitive compound: Keep the water bath at room temperature (or no higher than 30°C) and rely on a stronger vacuum to remove the solvent.
- If you are removing a very small volume (<5 mL) without a rotovap: You can gently blow a stream of dry nitrogen or air over the surface of the liquid in a fume hood, but be aware this is much slower and less controlled.
By understanding and controlling the relationship between pressure and temperature, you can remove ethyl acetate with precision and confidence.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Role in Evaporation | Optimal Condition for Ethyl Acetate |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure | Lowers boiling point | Use vacuum to boil at ~room temperature |
| Temperature | Provides gentle heat | Water bath at 35-40°C |
| Rotation | Increases surface area | Constant rotation at ~150 RPM |
| Safety | Prevents hazards | Always operate inside a fume hood |
Need precise control for your solvent evaporation? KINTEK specializes in high-quality rotary evaporators and lab equipment designed for safety and efficiency. Our experts can help you select the perfect system for your laboratory's needs. Contact us today to optimize your ethyl acetate removal process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a rotavap? Achieve Gentle, Efficient Solvent Removal for Your Lab
- Why is biochar production a carbon-neutral process? It's Actually a Powerful Carbon-Negative Tool
- What is the advantage of sputtering? Achieve Superior, High-Purity Thin Films from Any Material
- Are electric arc furnaces efficient? Unlocking Modern Steelmaking's Power and Flexibility
- Is it possible to make fuel from plastic? Turn Waste into Valuable Energy
- How does heat treating affect the strength of a metal? A Guide to Tailoring Metal Properties
- Does water bath evaporate? Yes, and here’s how to control it effectively.
- What are the advantages of using a laboratory vacuum filtration system for the recovery of graphene powders?



















