In essence, an autoclave destroys bacteria by using high-pressure steam to fatally damage their internal structures. This process elevates the temperature far beyond the boiling point of water, and the immense energy transferred by the condensing steam causes the microbes' essential proteins and enzymes to coagulate and denature, rendering them non-functional and leading to cell death.
The autoclave's power lies not just in high heat, but in the efficiency of moist heat. Pressurized steam penetrates microbial cells far more effectively than dry air, ensuring the rapid and irreversible breakdown of the proteins necessary for life.
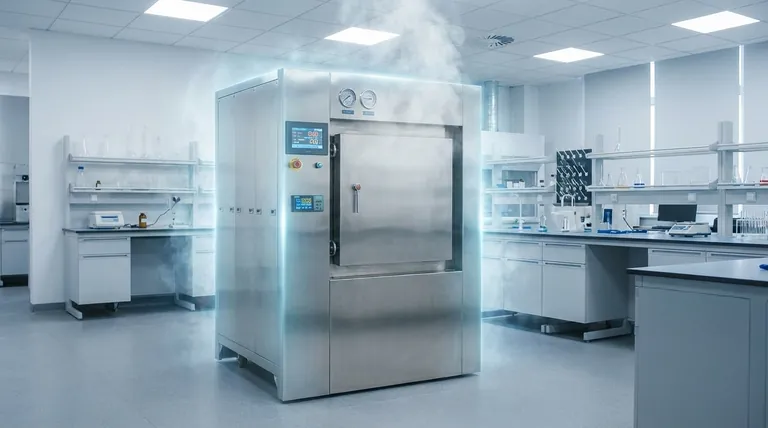

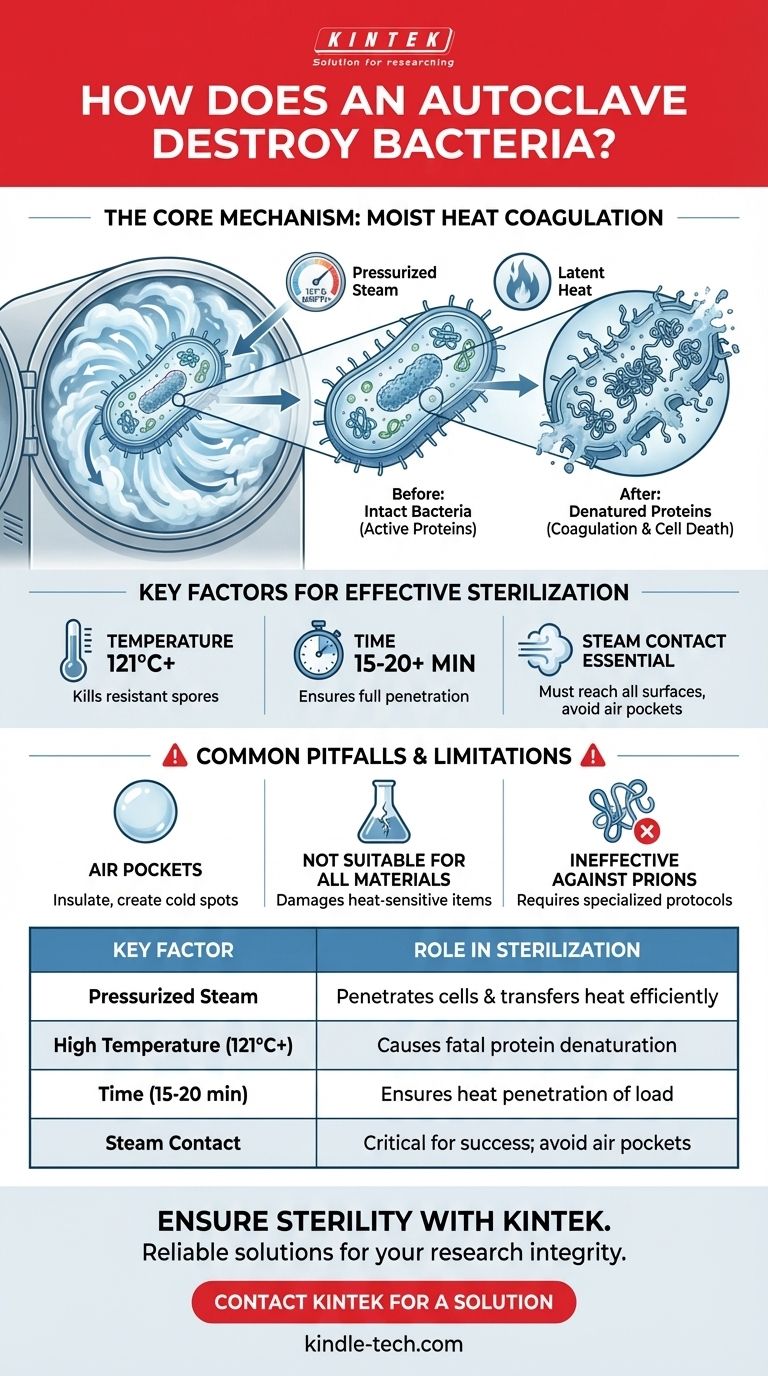
The Core Mechanism: Moist Heat Coagulation
To understand why autoclaving is the gold standard for sterilization, we must first distinguish it from simply heating something in an oven. The key difference is the presence of pressurized steam, which fundamentally changes how thermal energy is delivered.
The Role of Pressurized Steam
Under normal atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C (212°F). An autoclave is a pressure chamber that increases the pressure, allowing water to exist as steam at much higher temperatures, typically 121°C (250°F) or higher.
This superheated steam is the active sterilizing agent. It carries a massive amount of thermal energy.
How Steam Transfers Heat with Extreme Efficiency
When this high-temperature steam makes contact with cooler items inside the autoclave, it immediately condenses back into water. This phase change releases a large amount of latent heat directly onto the surface of the microorganisms.
This method is far more efficient at transferring heat than dry air. It ensures that every surface the steam touches is rapidly brought to the lethal sterilization temperature.
The Fatal Blow: Protein Denaturation
This intense, rapid heat transfer causes irreversible coagulation and denaturation of the bacteria's structural proteins and essential enzymes.
Think of it like cooking an egg white. The heat causes the liquid proteins to become a solid, opaque mass. This change in structure is permanent. Once a microbe's proteins are denatured, its cellular machinery breaks down completely, and the organism dies.
Key Factors for Effective Sterilization
Achieving sterility isn't just about turning the machine on. Three factors—time, temperature, and steam contact—are codependent and critical for success.
Achieving the Right Temperature
The standard temperature for most general sterilization is 121°C. This temperature is proven to be effective at killing not just bacteria but also highly resistant bacterial endospores.
The Importance of Time
Sterilization is not instantaneous. The items inside the autoclave must be held at the target temperature for a minimum duration, typically 15-20 minutes or longer, depending on the size and nature of the load. This ensures the heat fully penetrates the entire load and kills all microorganisms present.
Ensuring Complete Steam Contact
This is the most common point of failure. If steam cannot reach a surface, that surface will not be sterilized. This is why proper loading of an autoclave is absolutely critical.
Common Pitfalls and Limitations
While incredibly effective, the autoclave process is not infallible and has clear limitations that every user must understand to avoid sterilization failure.
The Risk of Air Pockets
Air is a poor conductor of heat and acts as an insulator. If air gets trapped in a container, a coiled tube, or within a densely packed load, it can create a "cold spot" that the steam cannot penetrate, leaving microorganisms alive.
Not Suitable for All Materials
The combination of high heat, pressure, and moisture will destroy or damage many materials. This includes heat-sensitive plastics, delicate electronics, corrosive materials, and many chemical solutions.
Ineffectiveness Against Prions
Standard autoclave cycles are effective against bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores. However, they are not considered sufficient to inactivate prions—the misfolded proteins responsible for diseases like Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD). Prion decontamination requires more aggressive chemical and thermal protocols.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure successful sterilization, you must align your procedure with the nature of the items being processed.
- If your primary focus is routine lab media or glassware: Prioritize proper loading techniques to eliminate air pockets and ensure steam can circulate freely around every item.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing complex instruments: Ensure items are fully disassembled and cleaned beforehand so that steam can contact every internal and external surface.
- If your primary focus is process validation and safety: Always use appropriate chemical or biological indicators within your loads to provide definitive proof that sterilization conditions were met.
Ultimately, understanding the interplay of steam, temperature, and time transforms the autoclave from a simple machine into a reliable and indispensable tool for ensuring sterility.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Role in Sterilization |
|---|---|
| Pressurized Steam | Penetrates cells and transfers heat efficiently. |
| High Temperature (121°C+) | Causes fatal protein denaturation and coagulation. |
| Time (15-20 min) | Ensures heat fully penetrates the entire load. |
| Steam Contact | Critical for reaching all surfaces; air pockets cause failure. |
Ensure your lab's sterility and safety with reliable autoclaves from KINTEK.
As a leading provider of laboratory equipment, KINTEK understands that precise and effective sterilization is non-negotiable for your research and testing integrity. Our autoclaves are designed to deliver the critical combination of high-pressure steam, temperature, and time needed to destroy even the most resistant bacteria and spores, protecting your samples, media, and personnel.
Whether you are processing routine lab glassware, complex instruments, or sensitive media, we have solutions tailored to your specific needs. Contact us today to find the perfect autoclave for your laboratory and achieve guaranteed sterility.
Contact KINTEK for a Sterilization Solution
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory high-pressure autoclave sterilizer necessary? Ensure Accuracy in Antibacterial Research
- What is the most efficient method of sterilization? Match the Right Method to Your Materials
- Is a sterilizer the same as an autoclave? Understand the Critical Differences for Your Lab
- What should be autoclaved in a lab? A Guide to Safe and Effective Sterilization
- What type of sterilizer is used for sterilizing liquids? Choose the Right Method for Your Lab
- What is the role of the Bowie-Dick-Test in waste decontamination? Focus on Lab Efficiency & Compliance
- What are the advantages of using an autoclave equipped with a stirring device for molten salt testing? Dynamic Accuracy
- Which of the following is not safe to be autoclaved? Avoid These Dangerous Materials



















