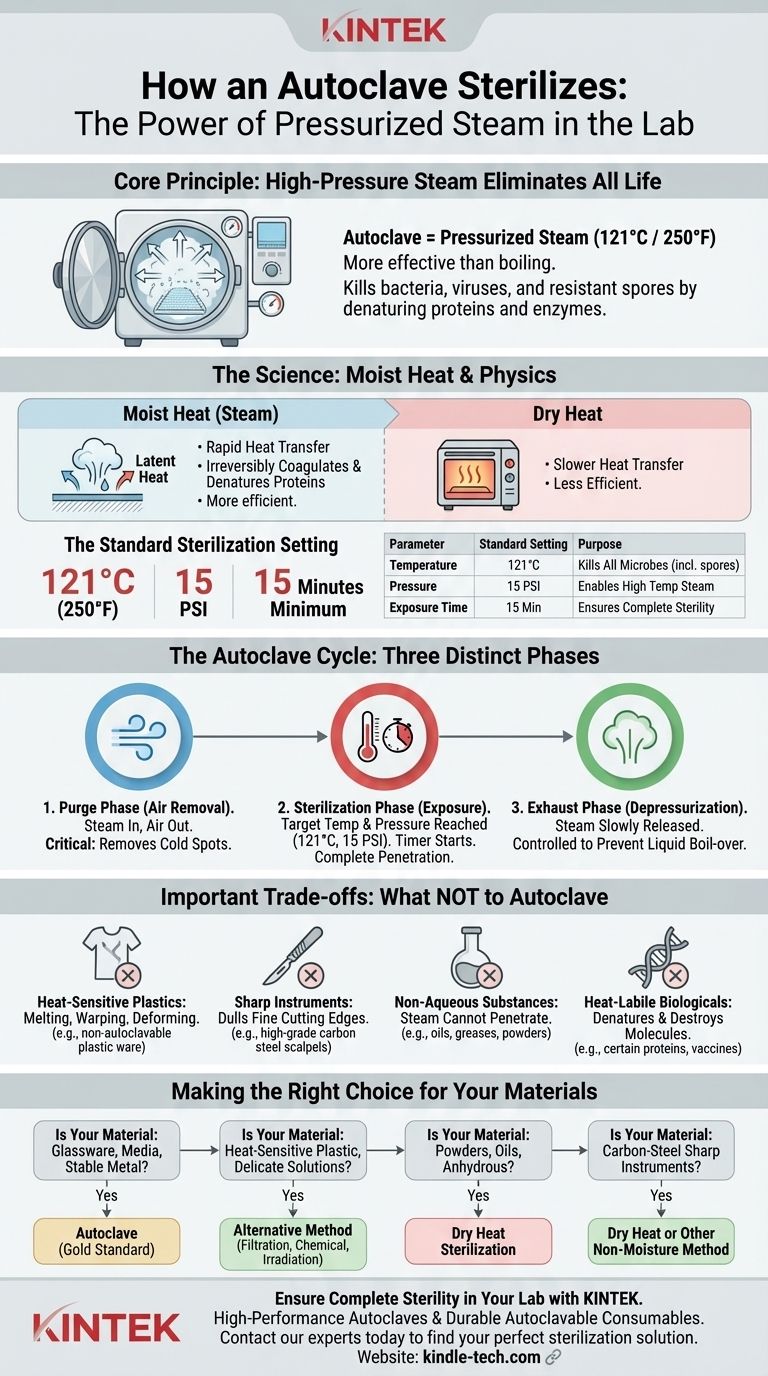
At its core, an autoclave uses high-pressure steam to sterilize laboratory equipment. This process is far more effective than simple boiling because the pressure allows the steam to reach temperatures (typically 121°C or 250°F) that are high enough to kill not just bacteria and viruses, but also their highly resistant spores. The moist heat rapidly denatures the essential proteins and enzymes of microorganisms, rendering them non-functional and ensuring complete sterility.
The key to understanding an autoclave is recognizing that it's not just about heat; it's about using pressurized steam to eliminate all air and force lethal temperatures into every crevice of the items being sterilized. Knowing which materials can withstand this intense process is just as critical as knowing how to operate the machine.

The Principle of Moist Heat Sterilization
The effectiveness of an autoclave hinges on a simple principle of physics: the temperature of steam increases as pressure increases. This controlled environment is uniquely capable of destroying all forms of microbial life.
Why Steam is More Effective Than Dry Heat
Moist heat is a significantly more efficient method of heat transfer than dry heat. The steam condenses on cooler surfaces, releasing latent heat and rapidly raising the item's temperature.
This process irreversibly coagulates and denatures the structural proteins and enzymes within microorganisms. Without these vital components, the microbes cannot survive or reproduce.
The Standard for Sterilization: 121°C at 15 PSI
The most common and universally accepted setting for autoclaving is a temperature of 121°C (250°F) under a pressure of 15 pounds per square inch (PSI).
A minimum exposure time of 15 minutes at this temperature and pressure is sufficient to kill even the most heat-resistant bacterial spores, which are often used as biological indicators to validate the sterilization process.
The Three Phases of an Autoclave Cycle
A standard autoclave cycle is a precisely controlled process consisting of three distinct phases. Understanding each phase is essential for ensuring a successful sterilization run.
Phase 1: The Purge Phase (Air Removal)
After the door is sealed, the autoclave begins pumping steam into the chamber. This incoming steam displaces the cooler, heavier air, forcing it out through an exhaust vent.
Removing all air is the most critical step. Pockets of trapped air can create "cold spots" that prevent the steam from reaching the items, leading to a failed sterilization cycle.
Phase 2: The Sterilization (Exposure) Phase
Once all air has been purged, the exhaust valve closes. The continued injection of steam causes the temperature and pressure inside the chamber to rise to the desired setpoint (e.g., 121°C and 15 PSI).
The timer for the sterilization cycle begins only after the chamber reaches this target. The load is held at this temperature and pressure for the programmed duration, ensuring complete penetration of the steam and killing of all microbes.
Phase 3: The Exhaust Phase (Depressurization)
After the exposure time is complete, the exhaust valve opens, and steam is slowly released from the chamber. This allows the internal pressure to return to ambient levels safely.
This phase must be controlled, especially for liquid loads, to prevent liquids from boiling over violently due to the sudden drop in pressure.
Understanding the Trade-offs: What Not to Autoclave
An autoclave is a powerful tool, but it is not suitable for all materials. Using it improperly can destroy valuable equipment and substances.
Heat-Sensitive Materials
Many common plastics will melt, warp, or deform under the high temperatures of an autoclave. Always verify that a plastic item is marked as "autoclavable." Similarly, many chemical solutions and compounds will degrade or break down when exposed to excessive heat.
Sharp Instruments
While stainless steel surgical tools are frequently autoclaved, high-grade carbon steel scalpels, scissors, and blades should not be. The combination of high heat and moisture will dull their fine cutting edges, rendering them useless.
Non-Aqueous Substances
An autoclave is ineffective for sterilizing oily substances, greases, or powders. Since these materials are anhydrous (water-repelling), the steam cannot penetrate them to provide moist heat, making sterilization unreliable. Dry heat sterilization is the correct method for these items.
Heat-Labile Biologicals
Certain high-protein solutions, serums, vaccines, and enzymes are sensitive to heat (heat-labile). The temperatures inside an autoclave will denature and destroy these molecules, negating their biological activity. These materials typically require sterilization by filtration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Materials
To use an autoclave effectively, you must match the sterilization method to the material you are processing.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing glassware, microbiological media, or heat-stable metal instruments: The autoclave is your gold standard for achieving complete sterility.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive plastics or delicate solutions: You must use an alternative method like sterile filtration, chemical sterilization, or irradiation.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing powders, oils, or anhydrous items: An autoclave is ineffective; dry heat sterilization is the appropriate and necessary choice.
- If your primary focus is preserving the sharpness of carbon-steel instruments: Avoid the autoclave and consider dry heat or other methods that do not rely on moisture.
By understanding both the power and the limitations of autoclaving, you can ensure the absolute integrity of your work and maintain a safe, effective laboratory environment.
Summary Table:
| Key Autoclave Sterilization Parameter | Standard Setting | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 121°C (250°F) | Kills all microbes, including resistant spores. |
| Pressure | 15 PSI | Enables steam to reach the required high temperature. |
| Minimum Exposure Time | 15 minutes | Ensures complete sterilization of the entire load. |
Ensure Complete Sterility in Your Lab with KINTEK
Autoclaving is critical for a safe and effective laboratory, but using the right equipment and consumables is just as important. Whether you need to sterilize glassware, media, or instruments, KINTEK provides the reliable autoclaves and autoclavable labware you can trust.
Let KINTEK support your laboratory's sterilization needs:
- High-Performance Autoclaves: Achieve consistent, validated sterilization cycles.
- Durable Autoclavable Consumables: From pipette tips to glassware, our products withstand the high-pressure steam environment.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect sterilization solution for your specific requirements and ensure the integrity of your work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- Can autoclave sterilize liquid? Master Safe and Effective Liquid Sterilization
- Is a UV sterilizer as good as an autoclave? The Critical Difference Between Sterilization and Disinfection
- What are the considerations for autoclave? Ensure Sterilization Success and Safety
- Why is autoclave done for 15 minutes? The Science Behind Sterilization Cycles
- What is the protocol for autoclave machine? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe Sterilization



















