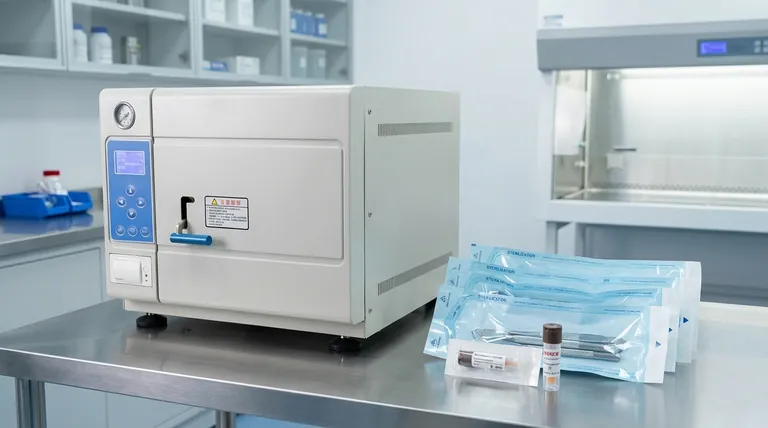
Contrary to common belief, there is no fixed expiration date for an autoclaved item. The modern, accepted standard is that sterility is not determined by time but by specific events. An item remains sterile indefinitely until its protective barrier is compromised.
The core principle to understand is event-related sterility. This means a properly sterilized and packaged item is considered sterile until an event—such as a tear in the packaging, exposure to moisture, or improper handling—occurs that compromises its barrier.

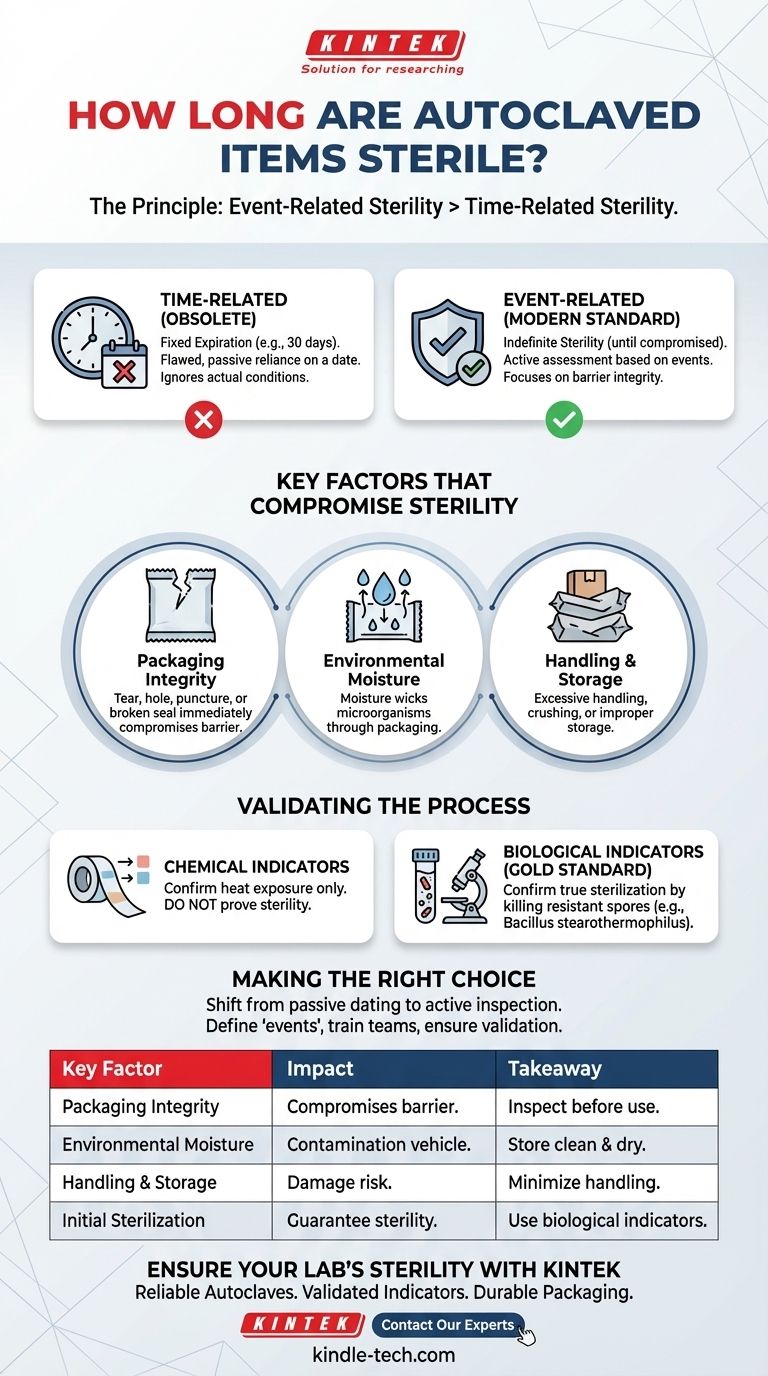
The Principle: Event-Related vs. Time-Related Sterility
Historically, facilities assigned arbitrary expiration dates (e.g., 30 days, 6 months) to sterilized packs. This practice is now considered obsolete because it fails to account for the actual conditions that lead to contamination.
What is Event-Related Sterility?
Event-related sterility is a scientific practice that relies on the quality of the packaging material, storage conditions, and handling methods. The item's sterility is maintained as long as its protective barrier remains intact.
This approach requires active assessment rather than passive reliance on a calendar date. Before use, every package must be inspected for signs of compromise.
Why Time-Based Dating is Unreliable
A time-based system is inherently flawed. A package dropped on a wet floor is contaminated within seconds, regardless of its "expiration date."
Conversely, a properly wrapped and stored package can remain sterile for years. Relying on a date can create a false sense of security and lead to the use of contaminated items or the wasteful re-sterilization of perfectly safe ones.
Key Factors That Compromise Sterility
An "event" is any action or condition that breaches the microbial barrier of a sterilized package. Understanding these events is the key to maintaining sterility.
Packaging Integrity
This is the most critical factor. Any tear, hole, puncture, or broken seal immediately renders the item non-sterile. Compression or creasing of the package can also create micro-tears that allow contaminants to enter.
Environmental Moisture
Moisture is a vehicle for microorganisms. If a sterilized pack becomes wet, it effectively wicks bacteria and other microbes through the packaging material, contaminating the contents. Packages must be stored in a clean, dry environment with controlled humidity.
Handling and Storage
Excessive or improper handling increases the risk of damage. Items should be handled as little as possible. Storage shelves must be clean, and packs should not be stacked so tightly that they are crushed or abraded.
Validating the Initial Sterilization Process
While storage is crucial, none of it matters if the item wasn't properly sterilized in the first place. This requires a robust validation process for your autoclave.
The Role of Chemical Indicators
Chemical indicators, like autoclave tape, change color when exposed to certain temperatures. However, they only confirm that the item has been through a heat cycle. They do not prove that the conditions necessary for sterilization (the correct temperature, for the required duration, with proper steam penetration) were met.
The Gold Standard: Biological Indicators
The only way to confirm true sterilization is with a biological indicator. These typically contain spores of a highly resistant bacterium, such as Bacillus stearothermophilus.
These spores are far more difficult to kill than common pathogens. If your autoclave cycle can kill these resilient spores, it provides a high degree of confidence that all other potential contaminants have been eliminated. As a best practice, this validation should be performed regularly (e.g., monthly) and for each type of load.
The Importance of Load-Specific Validation
An autoclave's effectiveness can vary dramatically based on the contents. A dense, heavy load or a large volume of liquid requires a different cycle than hollow, lightweight instruments. Each type of container and load configuration must be validated to ensure steam is penetrating and sterilizing effectively.
Making the Right Choice for Your Protocol
Implementing an event-related sterility protocol requires a shift in mindset from passive dating to active inspection and quality control.
- If your primary focus is establishing a new protocol: Define and document what constitutes a contaminating "event" in your facility and establish clear inspection criteria for all sterilized packages.
- If your primary focus is team training: Emphasize that every team member is responsible for inspecting the integrity of a package immediately before opening it.
- If your primary focus is safety and compliance: Ensure your autoclave validation records, using biological indicators, are meticulously maintained and that your event-related sterility policy is clearly written and accessible.
Ultimately, sterility is an active process you control, not a passive state determined by a calendar.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Impact on Sterility | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| Packaging Integrity | Any tear, hole, or broken seal compromises sterility. | Always inspect packaging before use. |
| Environmental Moisture | Moisture wicks microbes through packaging, causing contamination. | Store in a clean, dry environment. |
| Handling & Storage | Rough handling or tight stacking can damage packaging. | Minimize handling and ensure proper storage. |
| Initial Sterilization | Without proper validation, sterility cannot be guaranteed. | Use biological indicators for validation. |
Ensure Your Lab's Sterility with KINTEK
Proper sterilization is critical for accurate results and safety. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable autoclaves, validated biological indicators, and durable packaging materials designed to maintain sterility.
Our products help you:
- Achieve and confirm true sterilization with biological indicators
- Protect your instruments with high-quality, tear-resistant packaging
- Maintain compliance with industry standards
Don't leave your lab's safety to chance. Contact our sterilization experts today for a consultation on the right equipment and protocols for your specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the uses of autoclave in laboratory equipment? Ensure Sterile Conditions for Your Research
- What is cycle time as related to autoclaving? Master the Full Process for Effective Sterilization
- Which autoclave is used in microbiology lab? Gravity Displacement vs. Pre-Vacuum Explained
- What are the three components of autoclaving? Master the Phases for Perfect Sterilization
- What equipment is used for laboratory sterilization? A Guide to Autoclaves, Ovens & Filtration



















