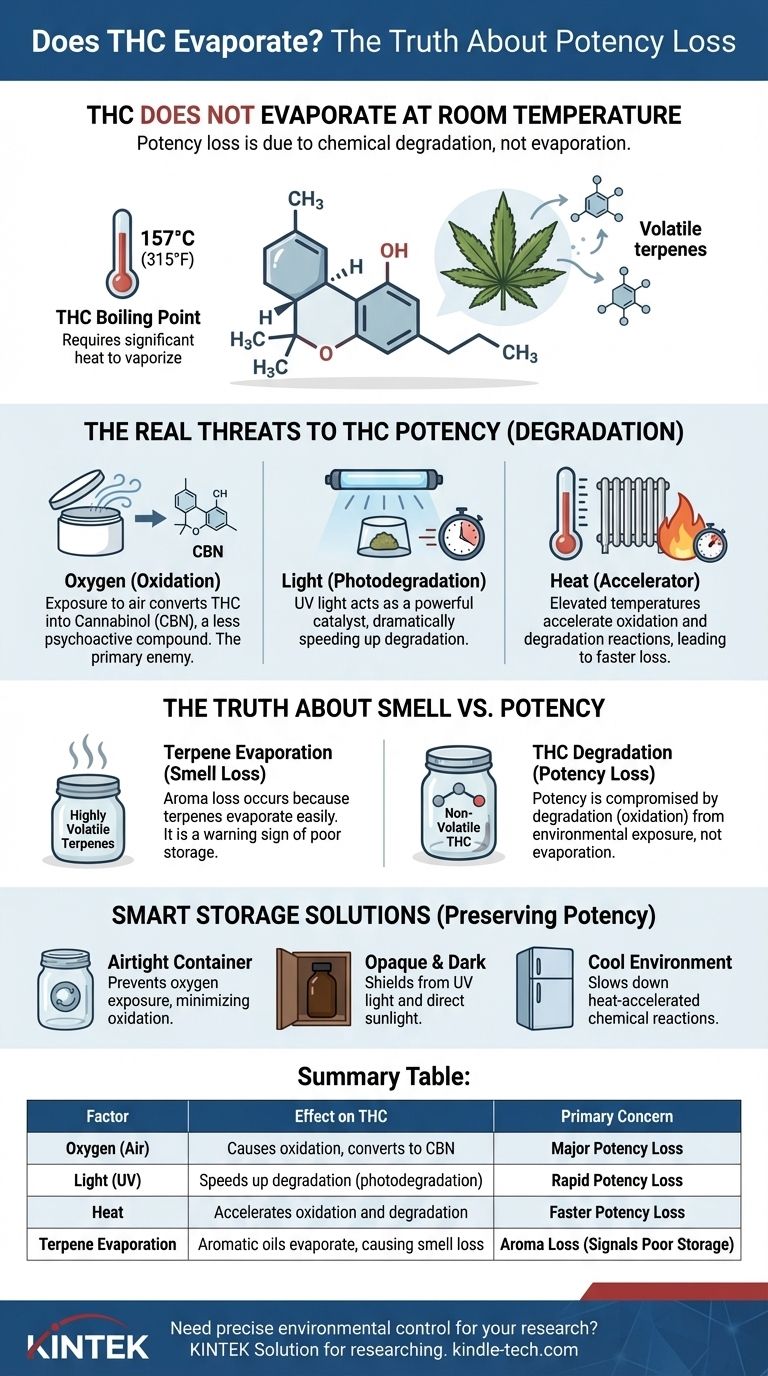
At room temperature, THC effectively does not evaporate. Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is a heavy, oily compound with a very high boiling point, meaning it does not naturally turn into a gas under normal conditions. The loss of potency in cannabis products over time is not due to evaporation, but rather to chemical degradation from exposure to the environment.
The core issue isn't THC "evaporating" into the air, but rather it breaking down into a less psychoactive compound. Your primary concerns for preserving potency are not preventing evaporation, but shielding the product from air, light, and heat.

Why THC Is Not a Volatility Risk
The Chemistry of Evaporation
Evaporation occurs when a liquid turns into a gas at a temperature below its boiling point. Substances that do this readily, like water or alcohol, are considered volatile.
THC, however, is not volatile. It is a large, heavy cannabinoid molecule that prefers to stay in a solid or liquid state at room temperature.
THC's High Boiling Point
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which it rapidly turns into a vapor. Water boils at 100°C (212°F).
In contrast, THC's boiling point is approximately 157°C (315°F). It simply will not turn into a vapor unless subjected to significant, direct heat, such as during vaporization or smoking.
The Real Threats to THC Potency
If THC isn't evaporating, why do cannabis products lose their effectiveness? The answer is degradation, a chemical change driven by three main environmental factors.
1. Oxygen (Oxidation)
Exposure to air is the primary enemy of THC. Oxygen in the atmosphere causes a process called oxidation, which slowly transforms THC into Cannabinol (CBN).
CBN has very mild psychoactive effects compared to THC. This conversion is the single largest contributor to potency loss in stored cannabis.
2. Light (Photodegradation)
UV light acts as a powerful catalyst that dramatically speeds up the degradation of THC.
Leaving cannabis flower or concentrates exposed to direct sunlight, or even significant indoor lighting, will accelerate the conversion of THC to CBN and degrade the product rapidly.
3. Heat
While room-temperature heat won't cause evaporation, elevated temperatures (like those in a hot car or near a radiator) act as an accelerator for oxidation.
Heat provides the energy needed for these chemical reactions to occur more quickly, leading to faster potency loss.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Smell vs. Potency
A common point of confusion is the loss of smell, which many people mistake for a loss of potency. It's crucial to distinguish between the two.
The Evaporation of Terpenes
The distinct smell of cannabis comes from terpenes, which are lightweight, aromatic oils. Unlike THC, terpenes are highly volatile and evaporate easily at room temperature.
When you open a container of cannabis, the aroma you smell is from evaporating terpenes, not THC.
Why This Distinction Matters
An old product that has lost its smell has definitely lost its terpenes. Because the conditions that cause terpenes to evaporate (air exposure) also cause THC to oxidize, a loss of smell is often a warning sign that potency has also been compromised.
However, losing smell does not directly equal losing potency. You are losing one set of compounds (terpenes) to evaporation and another (THC) to chemical degradation.
How to Apply This to Your Product
Your preservation strategy should focus on controlling the environment to prevent degradation.
- If your primary focus is long-term storage of flower or edibles: Use an airtight, opaque container (like a glass jar in a dark cabinet) and store it in a cool, dark place.
- If your primary focus is preserving the potency of oils or concentrates: Ensure the container is sealed tightly immediately after each use and stored away from any light or heat source.
- If your primary focus is minimizing odor: An airtight container is non-negotiable. This practice not only traps the smell from evaporating terpenes but also provides the oxygen-free environment needed to protect THC.
By controlling its environment, you gain direct control over your product's potency and lifespan.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on THC | Primary Concern |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen (Air) | Causes oxidation, converting THC to less potent CBN. | Major Potency Loss |
| Light (UV) | Speeds up degradation (photodegradation). | Rapid Potency Loss |
| Heat | Accelerates oxidation and degradation reactions. | Faster Potency Loss |
| Terpene Evaporation | Lightweight aromatic oils evaporate, causing smell loss. | Aroma Loss (Signals Poor Storage) |
Need precise environmental control for your research or product development? KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables designed for accurate, stable, and controlled conditions. Whether you are studying cannabinoid stability or developing new products, our solutions help you achieve reliable results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect equipment for your lab's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What is the delta 20 rule of evaporation? Master Safe and Effective Spraying
- What is the widely used boat made of in thermal evaporation? Choosing the Right Material for High-Purity Deposition
- Do cannabinoids evaporate? How to Preserve Potency and Prevent Degradation
- How does a molybdenum evaporation source function in H2S for MoS2 synthesis? Master Reactive Film Deposition

