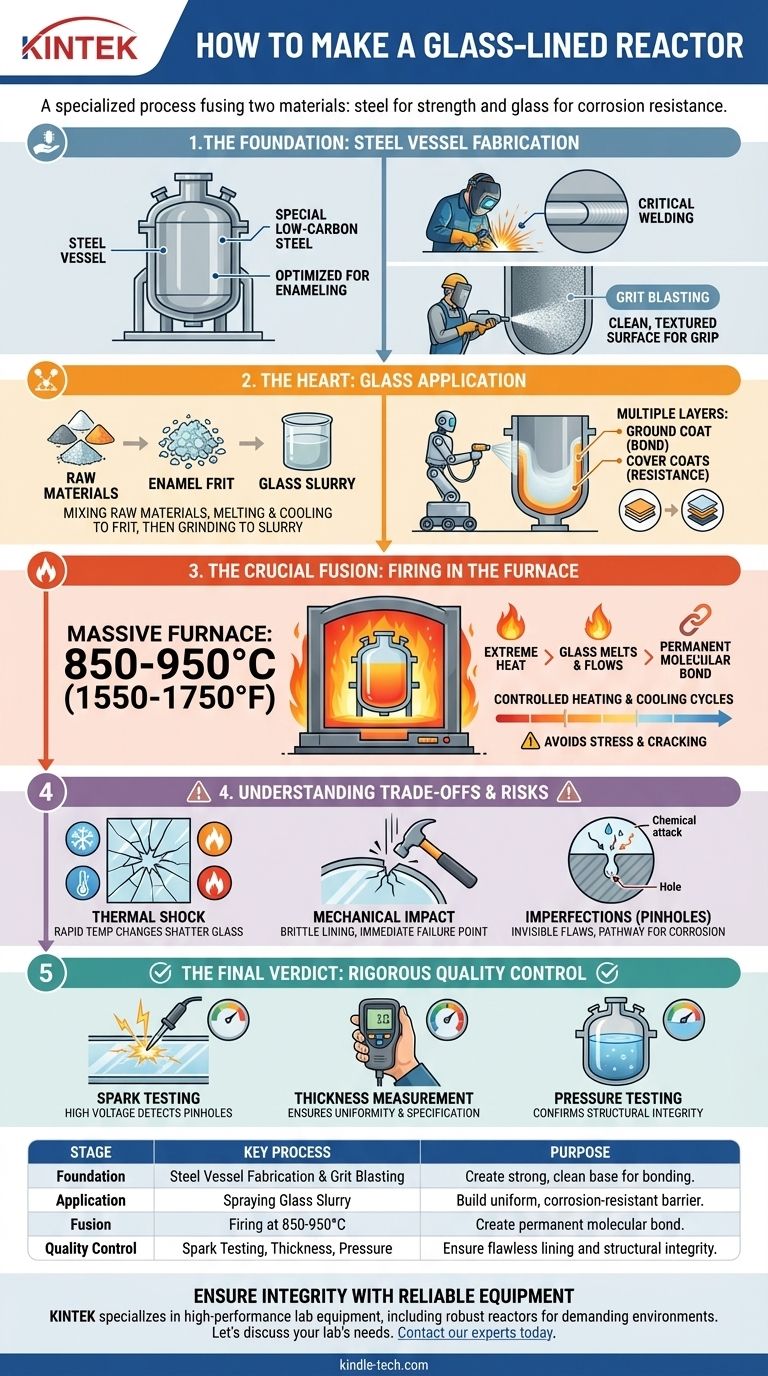
Manufacturing a glass-lined reactor is a highly specialized process that fuses two fundamentally different materials to create a single, high-performance piece of equipment. It involves fabricating a purpose-built steel vessel, meticulously preparing its interior surface, applying a proprietary glass slurry in multiple layers, and then firing the entire unit in a massive furnace at over 800°C to create a permanent, molecular bond between the glass and steel.
The core challenge is not simply coating steel with glass, but creating a composite material that leverages the structural strength of steel and the supreme corrosion resistance of glass. The quality and reliability of the final reactor depend entirely on the precision and control executed at every stage of this complex process.

The Foundation: Steel Vessel Fabrication
The process begins long before any glass is applied. The quality of the steel vessel itself dictates the final integrity of the lining.
Selecting the Right Steel
The choice of steel is critical. Special low-carbon steel is used because its composition is optimized for the enameling process, promoting a strong chemical bond with the glass ground coat during firing.
The Critical Role of Welding
All welds on the interior of the vessel must be perfectly smooth, non-porous, and free of sharp edges. Any imperfection in a weld creates a stress point where the glass lining is likely to fail under thermal or mechanical pressure.
Creating the Ideal Surface
Before any coating, the vessel's interior is subjected to grit blasting. This high-pressure process scours the steel, removing any impurities and creating a clean, textured surface profile that is ideal for the glass to physically grip onto.
The Heart of the Process: Glass Application
This stage is where the corrosion-resistant barrier is built. The specific formulation of the glass is often a closely guarded trade secret.
Crafting the Enamel Frit
Raw materials like silica, various metallic oxides, and other minerals are mixed and melted to form molten glass. This is then rapidly cooled, shattering it into a material called frit. This frit is the base ingredient for the lining.
Applying the Glass Slurry
The frit is ground into a fine powder and mixed with water and other agents to create a liquid suspension, or slurry. This slurry is sprayed onto the prepared steel surface in multiple, thin, uniform layers. A dark-colored "ground coat" is always applied first to create the primary bond, followed by several "cover coats" that provide the final thickness and chemical resistance.
The Crucial Fusion: Firing in the Furnace
This is the most critical and visually dramatic step, where the separate materials are transformed into a single, integrated unit.
The Science of the Molecular Bond
The coated vessel is moved into a colossal furnace and heated to between 850-950°C (1550-1750°F). At this extreme temperature, the glass particles melt, flow together to form a seamless layer, and chemically react with the steel surface. This creates an incredibly strong fusion bond.
The Importance of Controlled Cycles
This firing process is repeated for each layer of glass. Both the heating and cooling cycles are precisely controlled. Cooling too quickly would induce immense stress in the glass, causing it to crack and fail.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Failure Points
A glass-lined reactor is a remarkable piece of engineering, but its composite nature creates specific vulnerabilities that are essential to understand.
The Risk of Thermal Shock
The single greatest enemy of a glass lining is thermal shock. Rapid, localized changes in temperature cause the steel and glass to expand or contract at different rates, which can easily shatter the glass lining.
The Danger of Mechanical Impact
While strong against corrosion, the glass lining is inherently brittle. Dropping a tool or any sharp impact on the interior surface can chip or crack the lining, creating an immediate failure point.
Imperfections: Pinholes and Discontinuities
Even with a perfect process, microscopic flaws like pinholes or bubbles can occur. These tiny imperfections are invisible to the naked eye but can become pathways for corrosive chemicals to attack the steel substrate.
The Final Verdict: Rigorous Quality Control
Because the integrity of the lining is paramount, every finished reactor undergoes a battery of non-destructive tests before it can be certified for use.
Spark Testing for Integrity
The most important test is the spark test. A high-voltage (thousands of volts) probe is passed over the entire glass surface. Electricity will not pass through intact glass, but it will create a visible spark if it finds even a microscopic pinhole or crack, instantly revealing any breach in the lining.
Verifying Lining Thickness
An electronic gauge is used to measure the thickness of the glass lining across the entire vessel. This ensures the lining meets the required specification and is applied uniformly, with no thin spots that could wear prematurely.
Pressure Testing the Vessel
Finally, the completed reactor is hydrostatically tested. It is filled with water and pressurized to well above its designed operating pressure to confirm the structural integrity of the steel fabrication and all its welds.
How This Knowledge Empowers You
Understanding the manufacturing process is key to specifying, operating, and maintaining this critical equipment effectively.
- If your primary focus is procurement: Ask potential suppliers about their specific welding procedures, steel sourcing, and quality control documentation, particularly their spark testing protocol.
- If your primary focus is operations: Recognize that thermal shock is the biggest operational risk and enforce strict, gradual protocols for all heating and cooling cycles.
- If your primary focus is maintenance: Always use non-sparking, soft tools inside the reactor and never allow any mechanical impact on the glass surface.
By understanding how a glass-lined reactor is born, you become an informed stakeholder, better equipped to ensure its safety, reliability, and long service life.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Foundation | Steel Vessel Fabrication & Grit Blasting | Create a strong, clean, textured base for bonding. |
| Application | Spraying Glass Slurry (Ground & Cover Coats) | Build a uniform, corrosion-resistant barrier. |
| Fusion | Firing at 850-950°C | Create a permanent molecular bond between glass and steel. |
| Quality Control | Spark Testing, Thickness Measurement, Pressure Testing | Ensure the lining is flawless and the vessel is structurally sound. |
Ensure the integrity of your critical processes with reliable equipment. The complex manufacturing of a glass-lined reactor underscores the need for precision and quality. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including robust reactors designed for demanding laboratory environments. Our expertise ensures you get durable, safe, and efficient solutions tailored to your specific needs.
Let's discuss how our equipment can enhance your lab's safety and productivity. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Beaker and Lids
People Also Ask
- How does a high-pressure reactor demonstrate its value in accelerated aging? Predict Catalyst Durability Fast
- What is the contribution of a hydrothermal reactor to graded pore construction? Precision Templates for TAS
- What roles do autoclaves play in MFI zeolite synthesis? Master Hydrothermal Crystalline Growth
- What is the purpose of using high-purity argon gas in a high-pressure reactor? Ensure Precise Corrosion Test Data
- What is the purpose of using a high-temperature hydrothermal reactor? Enhance Iodine@Activated Carbon Cathode Synthesis



















