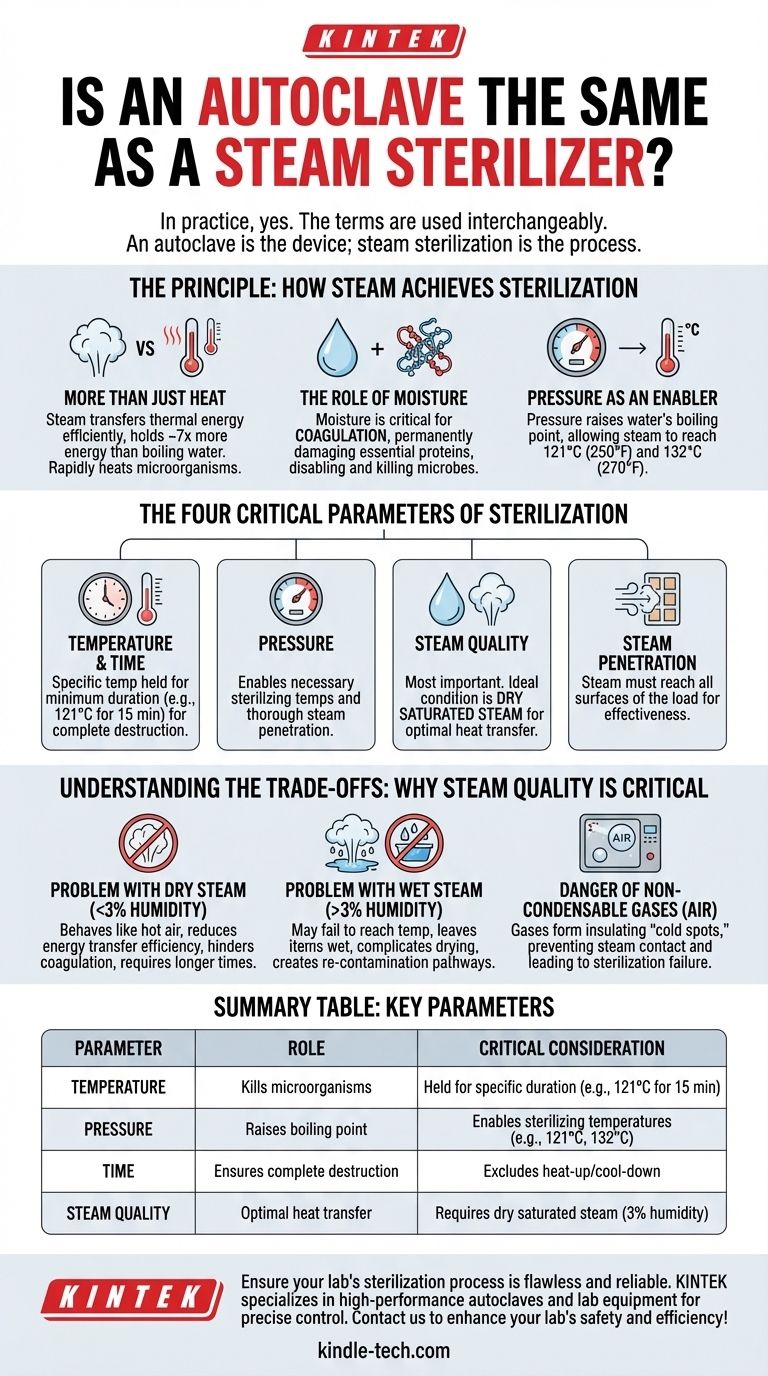
In practice, yes. The terms "autoclave" and "steam sterilizer" are used interchangeably to describe a device that uses pressurized steam to eliminate microorganisms. An autoclave is the specific name for the chamber that performs steam sterilization, which is the name of the process itself.
While the terms effectively refer to the same thing, the critical distinction lies not in the name but in the method. Understanding why steam is used and the precise conditions required for it to work is the key to grasping the principle of sterilization.
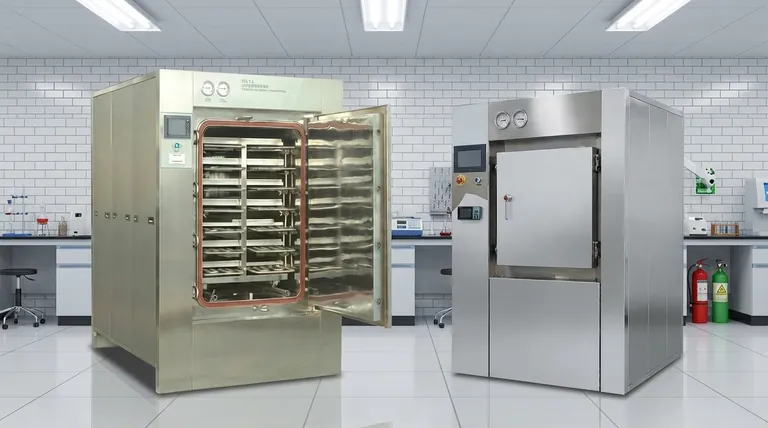

The Principle: How Steam Achieves Sterilization
An autoclave is far more than a simple pressure cooker. It is a precision instrument that leverages the unique physical properties of steam to destroy even the most resilient microorganisms, including bacterial spores.
More Than Just Heat
Steam is an incredibly efficient agent for transferring thermal energy. It contains vastly more energy than boiling water at the same temperature—in fact, steam at 100°C holds nearly seven times the energy of water at 100°C. When this steam contacts a cooler item, it rapidly transfers this energy, heating the cells of microorganisms far more effectively than hot air ever could.
The Role of Moisture
The effectiveness of steam sterilization is not just about heat, but also about moisture. The moisture present in the steam is critical for a process called coagulation, where it permanently damages the essential proteins that microbes need to survive and reproduce. This process effectively disables and kills them.
Pressure as an Enabler
The primary role of pressure inside an autoclave is to raise the boiling point of water. This allows the steam to reach temperatures far higher than 100°C (212°F). The most common sterilization temperatures, 121°C (250°F) and 132°C (270°F), are only achievable under pressure.
The Four Critical Parameters of Sterilization
For steam sterilization to be successful, four parameters must be precisely controlled. A failure in any one of these can lead to an incomplete or ineffective cycle.
Temperature & Time
A specific temperature must be achieved and held for a minimum duration to ensure all microorganisms are killed. For example, a cycle might run at 121°C for at least 15 minutes, not including the initial heat-up and final cool-down phases.
Pressure
As noted, pressure is the mechanism used to achieve the necessary sterilizing temperatures. It ensures that steam can thoroughly penetrate the load being sterilized.
Steam Quality
This is arguably the most important and nuanced parameter. The ideal condition is dry saturated steam, which holds the maximum possible energy without containing excessive liquid water. This ensures optimal heat transfer.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Steam Quality is Critical
Deviations from ideal steam quality can compromise the entire sterilization process. Both overly wet and overly dry steam introduce significant problems that can lead to failure.
The Problem with Dry Steam
When steam is "superheated" or has too little moisture (less than 3% humidity), it behaves more like hot air. This drastically reduces its ability to transfer energy efficiently and hinders the protein coagulation necessary to kill microbes, ultimately requiring longer sterilization times.
The Problem with Wet Steam
Conversely, steam with too much moisture (more than 3% humidity) can also cause issues. It may fail to reach the required temperature at a given pressure and can leave sterilized items wet. This dampness not only complicates drying but can also create pathways for re-contamination after the cycle is complete.
The Danger of Non-Condensable Gases
Air or other gases that don't condense like steam can get trapped in the autoclave chamber. These gases can form insulating "cold spots" on the items being sterilized, preventing steam from making direct contact and leading to a complete sterilization failure in those areas.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Understanding these principles is about ensuring a reliable and effective outcome every time. It shifts the focus from the machine's name to the integrity of the process itself.
- If your primary focus is reliability and consistency: Ensure your process uses dry saturated steam and meticulously controls the four key parameters of time, temperature, pressure, and steam quality.
- If your primary focus is avoiding sterilization failure: Pay close attention to steam quality, as issues with overly wet steam, dry steam, or non-condensable gases are the most common sources of error.
Ultimately, mastering sterilization comes from understanding that the autoclave is the tool, but pressurized steam is the agent that does the critical work.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Role in Sterilization | Critical Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Kills microorganisms | Must be held for a specific duration (e.g., 121°C for 15 min) |
| Pressure | Raises boiling point of water | Enables steam to reach sterilizing temperatures (e.g., 121°C, 132°C) |
| Time | Ensures complete microbial destruction | Cycle duration excludes heat-up and cool-down phases |
| Steam Quality | Optimal heat transfer and protein coagulation | Requires dry saturated steam (3% humidity) for maximum efficiency |
Ensure your lab's sterilization process is flawless and reliable. KINTEK specializes in high-performance autoclaves and lab equipment designed to deliver precise temperature, pressure, and steam quality control. Our solutions help laboratories achieve consistent, effective sterilization, preventing costly failures and contamination risks. Contact us today to find the perfect autoclave for your specific needs and enhance your lab's safety and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is the primary purpose of an autoclave in the preparation of media for the biological leaching of uranium?
- Why is a 24-hour hydrothermal treatment in an autoclave necessary for BMO nanosheets? Unlock Superior Photocatalysis
- What experimental conditions do stainless steel autoclaves provide for PCT-A leaching? Optimize Phosphate Glass Testing
- How does an autoclave ensure the reliability of experimental results? Achieving a Sterile Baseline for Lab Research
- What role does an autoclave play in remediation experiments? Ensure Precision by Eliminating Biological Noise



















