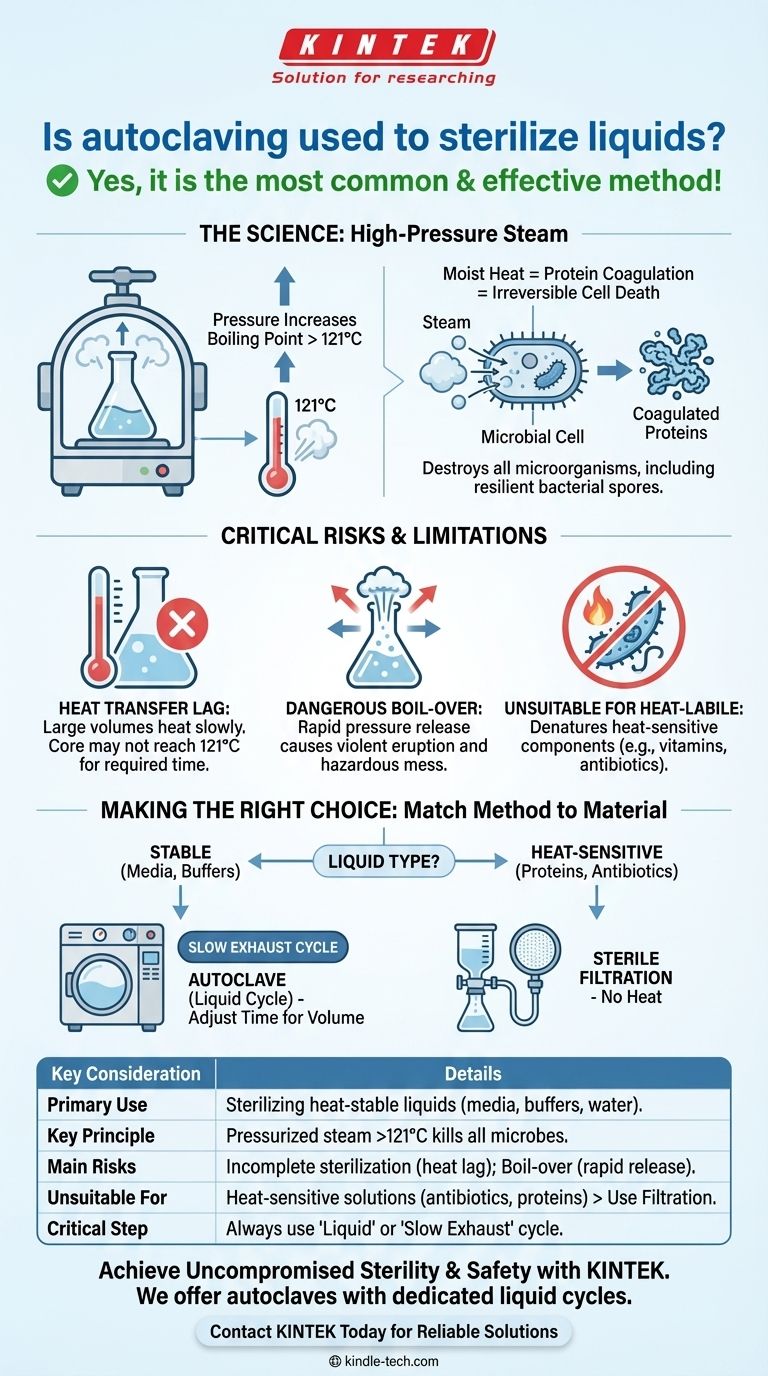
Yes, autoclaving is the most common and effective method for sterilizing liquids like microbiological media, buffers, and water. The process uses high-pressure steam to raise the temperature of the liquid well above the boiling point, ensuring the complete destruction of all microorganisms, including resilient bacterial spores.
The core challenge in autoclaving liquids is not the method's effectiveness, but ensuring proper procedure. Unlike solid instruments, liquids heat slowly and unevenly, creating a significant risk of incomplete sterilization or dangerous boil-over if not handled with precise protocols.

The Science of Liquid Sterilization by Autoclave
To use an autoclave safely and effectively for liquids, it is essential to understand the principles at work. The process is a careful manipulation of pressure and temperature.
Overcoming the Boiling Point
Under normal atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C (212°F), a temperature insufficient to kill heat-resistant endospores. An autoclave is a sealed chamber that increases internal pressure.
According to the laws of physics, raising the pressure on a liquid increases its boiling point. This allows the water within the liquid being sterilized to reach temperatures of 121°C or higher without boiling away.
The Power of Moist Heat
The key to an autoclave's effectiveness is pressurized steam, a form of moist heat. Steam is an incredibly efficient vehicle for heat transfer.
When this high-temperature moisture penetrates microbial cells, it causes the coagulation of essential proteins. This process is irreversible, permanently disabling their functions and leading to cell death.
Eliminating All Microbial Life
The combination of temperatures above boiling and the rapid heat transfer of steam is lethal to all forms of microbial life.
This includes not just active bacteria, fungi, and viruses, but also the highly-resistant endospores that can survive boiling and many chemical disinfectants. This makes autoclaving the gold standard for achieving true sterility.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Risks
While powerful, autoclaving liquids carries specific risks and limitations that are not present when sterilizing solid goods. Ignoring them can lead to failed sterilization or serious accidents.
The Challenge of Heat Transfer Lag
The most common point of failure is heat transfer lag. Liquids, especially in large volumes, heat up very slowly. The outside of the flask may be at 121°C, but the center of the liquid can remain at a much lower temperature for a significant portion of the cycle.
If the core of the liquid never reaches the target sterilization temperature for the required duration, microorganisms will survive. This is why longer cycle times are required for larger liquid volumes.
The Danger of Boil-over
At the end of a sterilization cycle, the autoclave chamber contains a liquid heated well above its normal boiling point. If the pressure is released too quickly, the liquid will erupt in violent boiling.
This phenomenon, known as boil-over, can cause a sudden loss of volume, create a hazardous mess inside the autoclave, and pose a severe burn risk to the operator. It can also cause bottles to crack or shatter.
Not All Liquids Are Suitable
Autoclaving is a high-heat process. It is completely unsuitable for heat-labile (heat-sensitive) solutions.
Components such as some vitamins, antibiotics, and proteins will be denatured or destroyed by the high temperatures. For these liquids, an alternative method like sterile filtration is necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your sterilization is both successful and safe, you must match the method to the material and follow the correct protocol.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing stable buffers or culture media: Autoclaving is the definitive method. Always use a "liquid" or "slow exhaust" cycle and increase the cycle time for volumes larger than one liter to compensate for heat lag.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive solutions: Do not autoclave. Use sterile filtration to remove microorganisms without using heat, thereby preserving the integrity of your solution's components.
Ultimately, understanding the physics of pressurized steam is the key to achieving reliable and safe sterilization for your liquids.
Summary Table:
| Key Consideration | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Sterilizing heat-stable liquids (media, buffers, water). |
| Key Principle | Pressurized steam raises liquid temperature above 121°C to kill all microbes, including spores. |
| Main Risks | Incomplete sterilization from heat lag; dangerous boil-over from rapid pressure release. |
| Unsuitable For | Heat-sensitive solutions (antibiotics, proteins), which require sterile filtration. |
| Critical Step | Always use a 'Liquid' or 'Slow Exhaust' cycle to prevent boil-over. |
Achieve Uncompromised Sterility and Safety in Your Lab
Sterilizing liquids requires precision and the right equipment to avoid contamination and accidents. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, providing autoclaves designed with dedicated liquid cycles for safe, effective sterilization of your culture media and buffers.
Let our experts help you select the perfect autoclave for your laboratory's specific needs. Contact KINTEK today to ensure your liquid sterilization protocols are both reliable and safe.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- What experimental conditions do stainless steel autoclaves provide for PCT-A leaching? Optimize Phosphate Glass Testing
- What role does an autoclave play in the acid treatment for microalgae disruption? Unlock High-Yield Cell Pretreatment
- What is the primary function of a laboratory autoclave in the pre-treatment of medical plastic waste for liquid fuel?
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK



















