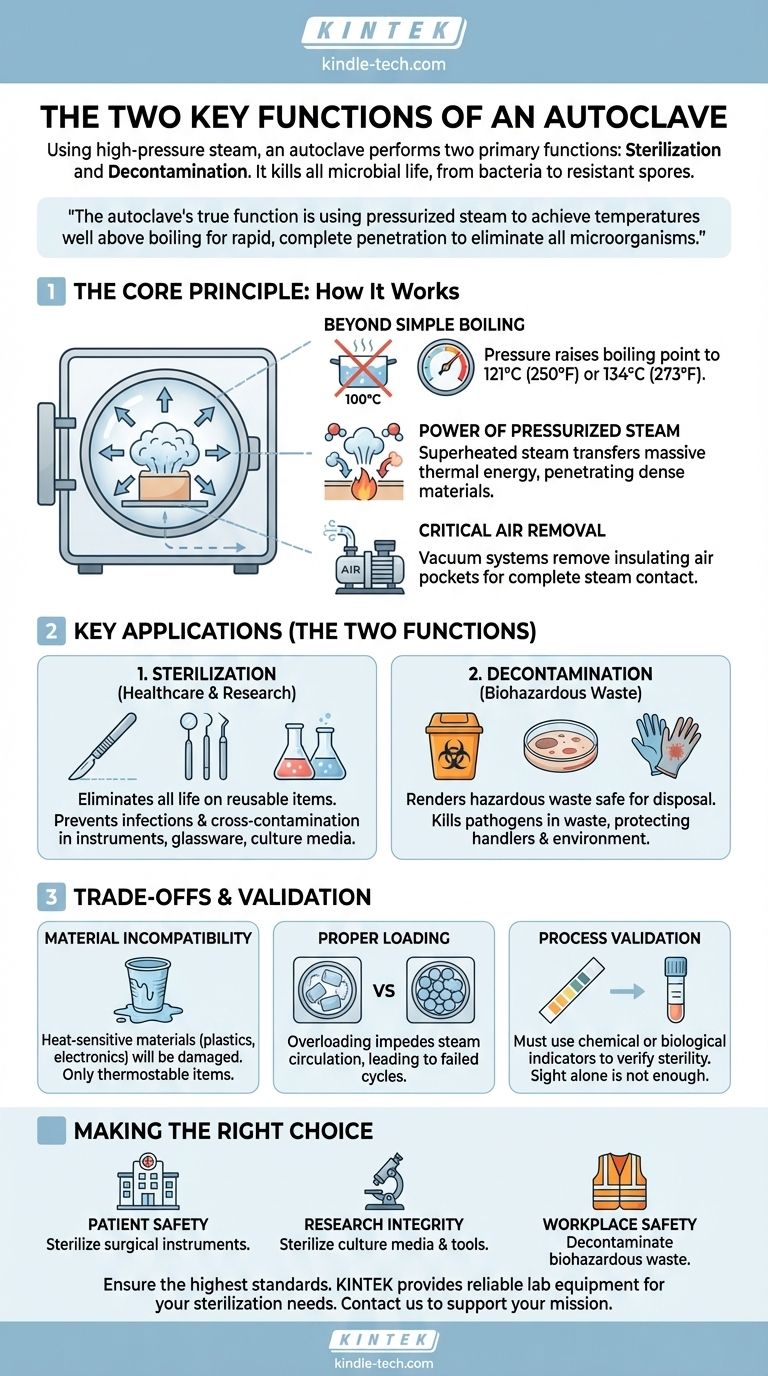
At its core, an autoclave performs two primary, related functions: the sterilization of materials and the decontamination of waste. It achieves this by using high-pressure steam to kill all forms of microbial life, from simple bacteria to highly resistant spores, ensuring that instruments are safe for use and that hazardous waste is rendered inert before disposal.
The autoclave's true function is not merely heating objects, but using pressurized steam to achieve temperatures well above boiling, ensuring rapid and complete penetration to eliminate all microorganisms. This principle of moist heat sterilization is the gold standard for applications where absolute sterility is non-negotiable.

The Core Principle: How an Autoclave Achieves Sterility
To understand an autoclave's function, you must first grasp why it is far more effective than simply boiling something in water. The process relies on a fundamental principle of physics.
Beyond Simple Boiling
Water boils at 100°C (212°F) at standard atmospheric pressure. While this temperature can kill many active bacteria, it is often insufficient to eliminate highly resistant bacterial spores.
An autoclave is a sealed pressure chamber. By increasing the pressure inside the chamber, it raises the boiling point of water, allowing the steam to reach much higher temperatures, typically 121°C (250°F) or 134°C (273°F).
The Power of Pressurized Steam
This superheated steam is the active sterilizing agent. When it makes contact with cooler items in the chamber, it condenses rapidly back into water, releasing a massive amount of thermal energy.
This process transfers heat far more efficiently than dry air, allowing the lethal temperature to penetrate dense materials, wrapped instrument packs, and the internal surfaces of hollow devices. This ensures that even the most protected microbes are destroyed.
The Critical Role of Air Removal
For steam to be effective, it must displace all the air within the chamber and inside the items being sterilized. Trapped pockets of air act as an insulating barrier, creating "cold spots" that prevent steam from making contact and sterilizing the surface.
Most modern autoclaves incorporate a vacuum system to actively remove air from the chamber before the steam is introduced, guaranteeing complete and uniform steam penetration.
Key Applications Across Industries
The autoclave's functions are critical in any environment where microbial contamination poses a risk.
Sterilization in Healthcare and Research
The most common function is the sterilization of reusable equipment. This includes surgical instruments, dental tools, and other medical devices to prevent patient-to-patient transmission of infections.
In laboratory settings, autoclaves are used to sterilize glassware, metal equipment, and liquid solutions like culture media. This prevents cross-contamination that would invalidate research results.
Decontamination of Biohazardous Waste
The second major function is rendering hazardous materials safe for disposal. This is often referred to as decontamination or rendering waste inert.
Items such as used petri dishes, single-use medical devices, contaminated gloves, and other biological waste are autoclaved to kill all pathogens before they are discarded as ordinary trash, protecting waste handlers and the environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, an autoclave is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is crucial for safe and effective operation.
Material Incompatibility
The combination of high heat, steam, and pressure will damage or destroy many materials.
Heat-sensitive plastics will melt, sharp surgical instruments can become dull, and sensitive electronics will be destroyed. Autoclaves are only suitable for thermostable materials like stainless steel, certain types of glass, and specific heat-resistant polymers.
The Importance of Proper Loading
An autoclave's effectiveness depends entirely on steam contacting every surface. Overloading the chamber or packing items too densely will impede steam circulation.
This can lead to failed sterilization cycles where items appear processed but still harbor live microorganisms, creating a significant safety risk.
Process Validation is Non-Negotiable
You cannot confirm sterility by sight alone. Each cycle must be monitored with chemical indicators (which change color at a specific temperature) or biological indicators (vials containing highly resistant spores).
A successful test on these indicators is the only way to prove that the autoclave achieved the necessary conditions for sterilization.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific application of an autoclave's functions directly relates to a primary safety or operational goal.
- If your primary focus is patient safety: You must use the autoclave to sterilize all reusable surgical and medical instruments that contact sterile body tissue to prevent infections.
- If your primary focus is research integrity: You must sterilize all culture media, glassware, and instruments to eliminate outside microbes and ensure your experimental results are valid.
- If your primary focus is workplace and public safety: You must use the autoclave to decontaminate all biohazardous waste before it leaves your facility, neutralizing potential pathogens.
Ultimately, the autoclave is an indispensable tool of control, ensuring safety and reliability in any scientific or medical endeavor.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Purpose | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Sterilization | Eliminates all microbial life on reusable items. | Surgical instruments, lab glassware, culture media. |
| Decontamination | Renders biohazardous waste safe for disposal. | Used petri dishes, contaminated gloves, medical waste. |
Ensure the highest standards of safety and sterility in your laboratory.
An autoclave is a critical piece of equipment for any lab that handles biological materials. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables to meet your exact sterilization and decontamination needs. Our expertise ensures you get the right solution for your applications, from research integrity to workplace safety.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's mission with the right equipment and service.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of autoclave in microbiology lab? Achieve Sterile Conditions with 121°C
- What criteria must be followed when loading the autoclave to help ensure sterility will be achieved? Master the Key to Reliable Sterilization
- What are the settings for autoclave sterilization? Ensure Reliable Sterility with Proper Parameters
- Why is it important to use the autoclave to sterilize laboratory tools? Ensure Complete Sterility for Reliable Results
- What instruments are used in autoclave sterilization? A Guide to Validating Sterility with Confidence



















