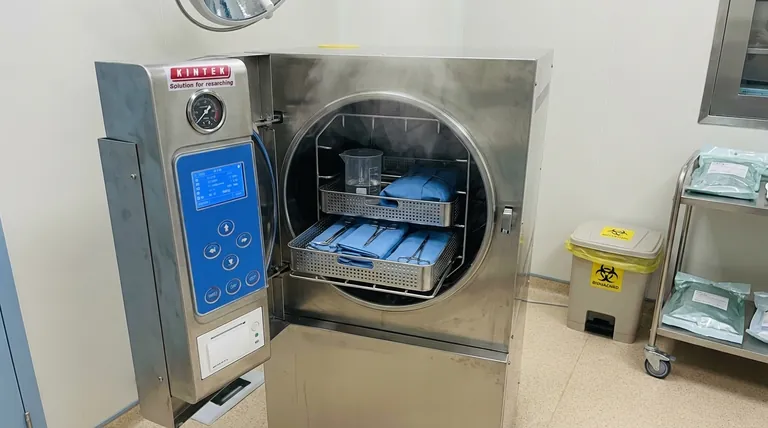
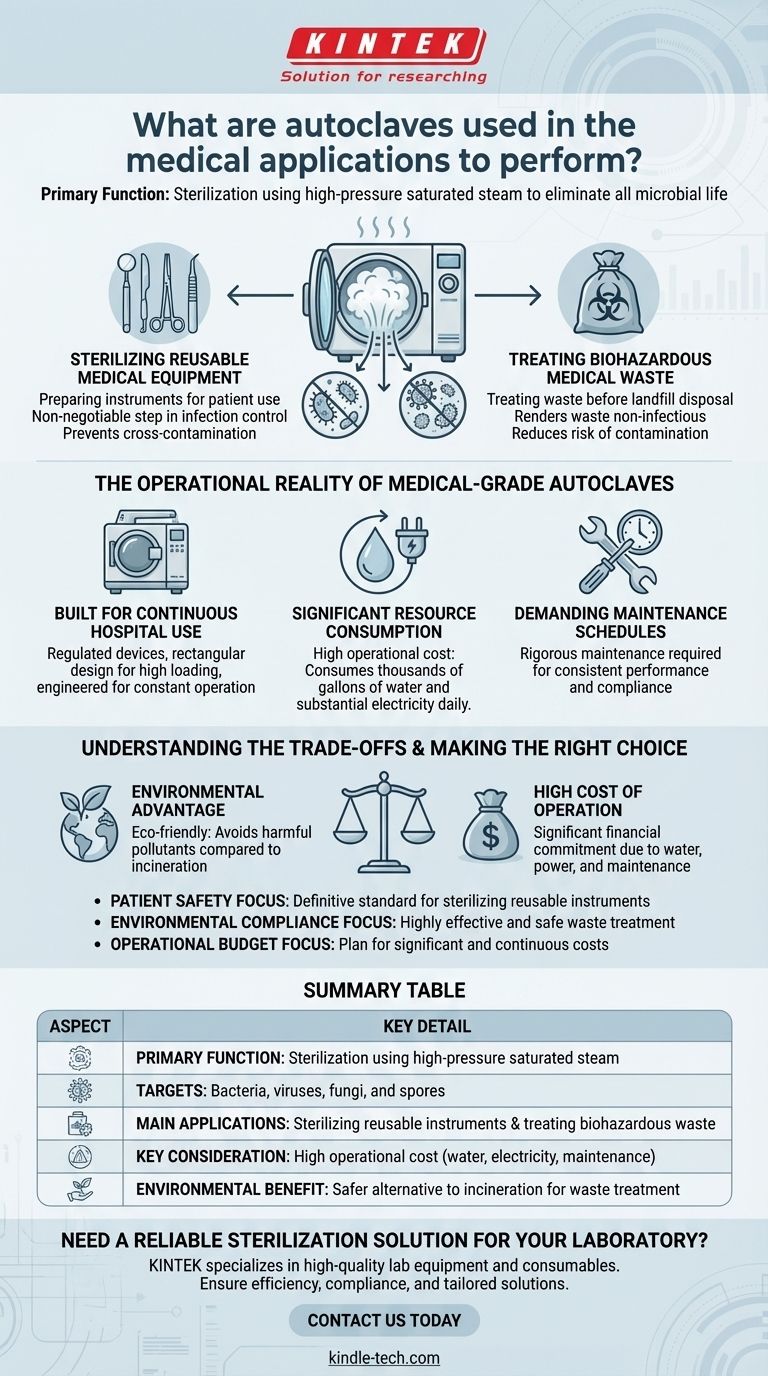
In medical applications, an autoclave's primary function is to perform sterilization. This process uses high-pressure saturated steam to eliminate all forms of microbial life—including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores—from medical instruments and waste materials, ensuring they are safe for reuse or disposal.
The core purpose of an autoclave in a medical setting is to guarantee sterility, which is fundamental to both patient safety and environmental compliance. While it is the benchmark for sterilizing equipment and treating hazardous waste, this reliability comes with significant operational demands in terms of cost, energy, and maintenance.

The Dual Roles of Sterilization in Healthcare
In a hospital or clinical environment, autoclaving serves two distinct but equally critical purposes: preparing instruments for patient use and treating waste before it leaves the facility.
Sterilizing Reusable Medical Equipment
The most recognized use of autoclaves is the sterilization of surgical instruments and other reusable medical devices. This is a non-negotiable step in infection control.
By destroying all microorganisms, autoclaving ensures that equipment used in procedures on one patient cannot transmit infections to the next. This process is vital for the safe and continuous operation of any healthcare facility.
Treating Biohazardous Medical Waste
Autoclaves also play a crucial role in medical waste management by sterilizing waste before it is sent to a landfill. This includes items contaminated with blood, bodily fluids, or other potentially infectious materials.
This sterilization process renders the waste non-infectious, significantly reducing the risk of contamination and disease transmission to waste handlers and the public.
The Operational Reality of Medical-Grade Autoclaves
Unlike smaller lab or industrial units, autoclaves designed for hospitals are specialized, high-demand machines with specific characteristics.
Built for Continuous Hospital Use
Medical-grade autoclaves are regulated devices, often featuring rectangular designs to maximize the loading of instrument trays and waste bags. They are engineered for constant, reliable operation in a demanding hospital environment.
Significant Resource Consumption
The effectiveness of these machines comes at a high operational cost. A hospital autoclave can consume thousands of gallons of water and a substantial amount of electricity every day to generate the necessary steam and pressure for sterilization.
Demanding Maintenance Schedules
To ensure consistent performance and compliance with health regulations, medical autoclaves require rigorous and demanding maintenance. This adds to the overall cost and complexity of their operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an autoclave for medical waste is a decision with clear benefits and significant drawbacks compared to other disposal methods like incineration.
The Environmental Advantage
Compared to burning medical waste, autoclaving is a more environmentally friendly process. It avoids the release of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere and effectively neutralizes biological hazards.
The High Cost of Operation
The primary trade-off is cost. The high daily consumption of water and electricity, combined with demanding maintenance needs, makes operating a medical-grade autoclave a significant financial commitment for any healthcare institution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When evaluating the role of autoclaves, your decision should be guided by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is patient safety: Autoclaving is the definitive standard for sterilizing reusable medical instruments to eliminate the risk of cross-contamination.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance: Autoclaving offers a highly effective and safe method for treating medical waste that is superior to incineration.
- If your primary focus is operational budget: You must carefully plan for the significant and continuous costs associated with the high water, power, and maintenance demands of a medical autoclave.
Understanding these factors allows you to fully appreciate the essential, high-stakes role that autoclaves play within the healthcare ecosystem.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Sterilization using high-pressure saturated steam |
| Targets | Bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores |
| Main Applications | Sterilizing reusable instruments & treating biohazardous waste |
| Key Consideration | High operational cost (water, electricity, maintenance) |
| Environmental Benefit | Safer alternative to incineration for waste treatment |
Need a Reliable Sterilization Solution for Your Laboratory?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to meet your sterilization and safety needs. Whether you are setting up a new clinical facility or upgrading your current autoclave system, our expertise ensures you get equipment that is efficient, compliant, and tailored to your operational demands.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's safety and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the guidelines when sterilizing items with a steam autoclave? Master the 3 Pillars for Guaranteed Sterility
- What are the conditions for autoclave in microbiology? Achieve Sterile Lab Materials with Confidence
- What are the three components of autoclaving? Master the Phases for Perfect Sterilization
- What is an example of autoclave in laboratory? Essential Sterilization for Reliable Science
- How do you sterilize glassware by autoclave? Master the 3-Step Process for Reliable Sterility



















