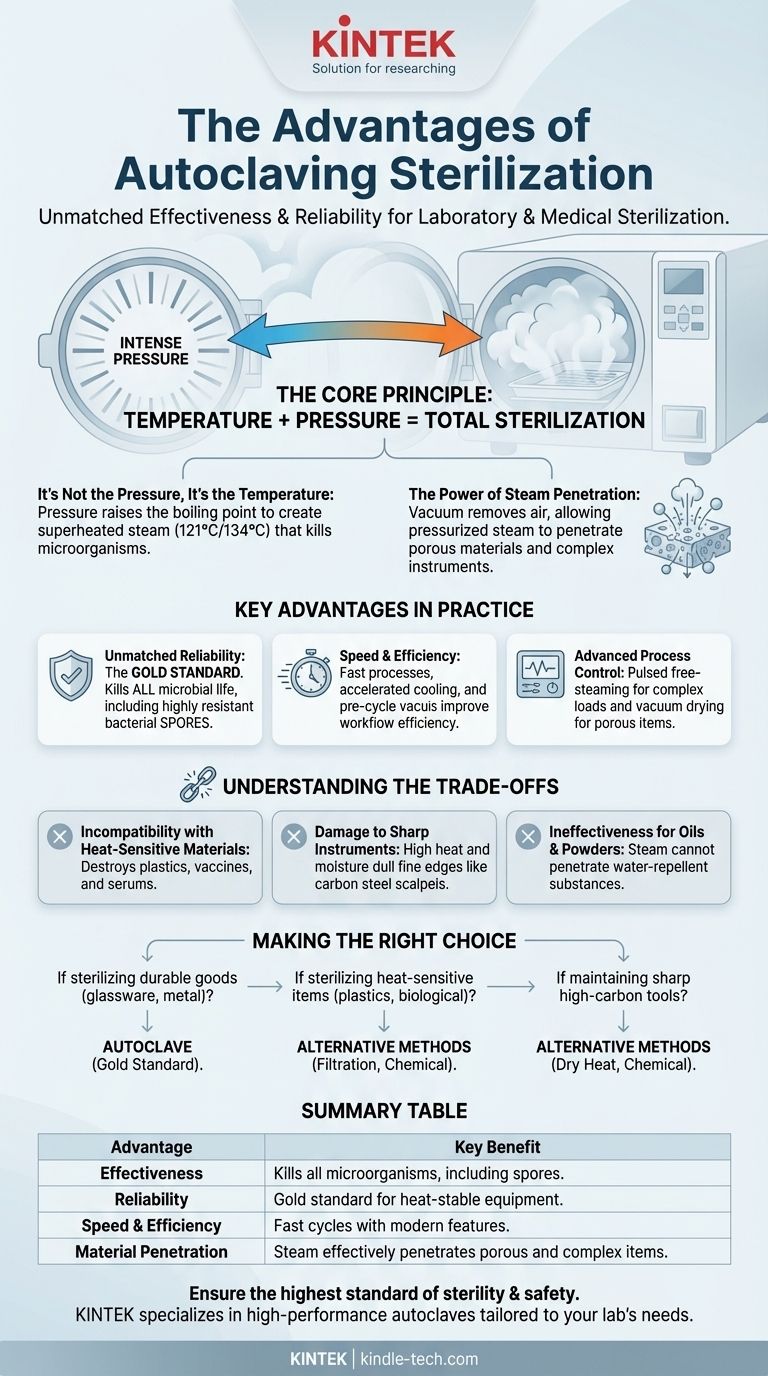
The primary advantage of autoclaving is its unmatched effectiveness and reliability. By using high-temperature steam under intense pressure, it provides a method of sterilization that is capable of killing a broad spectrum of microorganisms—including highly resistant bacterial spores—making it the gold standard for sterilizing most laboratory and medical equipment.
The core advantage of an autoclave is not simply the heat or the pressure, but the combination of both. The pressure allows steam to reach temperatures far exceeding the boiling point of water, ensuring rapid and deep heat penetration that effectively denatures the proteins of all microorganisms.

The Core Principle: How Autoclaving Achieves Total Sterilization
To appreciate its advantages, you must first understand its fundamental mechanism. An autoclave doesn't just clean an object; it renders it sterile by eliminating all forms of microbial life.
It's Not the Pressure, It's the Temperature
The pressure inside an autoclave chamber is a means to an end. Its purpose is to raise the boiling point of water, allowing the creation of superheated steam.
It is this high temperature (typically 121°C or 134°C) that actually kills microorganisms by irreversibly damaging essential proteins and enzymes.
The Power of Steam Penetration
Pressurized steam is the ideal medium for transferring lethal heat. Unlike dry heat, moist heat is more effective and works more rapidly.
Modern autoclaves first run a vacuum cycle to remove all air from the chamber. This allows steam to fill the space completely and penetrate porous materials or complex instruments, ensuring no part of the load is left untouched.
A Comprehensive Kill Spectrum
The combination of extreme heat and moisture is lethal to a vast range of microbes.
This includes bacteria, viruses, fungi, and most importantly, bacterial spores, which are notoriously resistant to other forms of sanitation and disinfection. This comprehensive effectiveness is what makes autoclaving a true sterilization process.
Key Advantages in Practice
The scientific principle translates into several practical benefits that have made the autoclave an indispensable tool in science and medicine.
Unmatched Reliability
When operated correctly, autoclaving is the most effective and dependable method for sterilizing items that can withstand the conditions. Its ability to destroy spores guarantees a level of sterility that is difficult to achieve with chemical or other methods.
Speed and Efficiency
While cycles can vary, autoclaving is generally a fast process. Advanced features in modern units, such as pre-cycle vacuums and accelerated cooling systems, significantly reduce the total time required, improving workflow efficiency.
Advanced Process Control
Modern autoclaves offer sophisticated control over the sterilization process. Features like pulsed free-steaming improve steam penetration for complex loads, while vacuum drying ensures that porous items like surgical gowns emerge ready for use.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When Not to Autoclave
Despite its power, an autoclave is not a universal solution. Its primary limitation is the very condition that makes it effective: intense heat and moisture. Understanding its trade-offs is crucial for safety and success.
Incompatibility with Heat-Sensitive Materials
The most significant disadvantage is that autoclaving will destroy or damage many common materials.
This includes most plastics, which can melt or warp, and heat-sensitive solutions like vaccines, serums, and certain proteins, which will be rendered useless.
Damage to Sharp Instruments
The high heat and moisture can dull the fine edges of certain instruments. High-grade carbon steel scalpels and scissors are often damaged by repeated autoclaving, making alternative sterilization methods necessary.
Ineffectiveness for Oils and Powders
Autoclaving relies on steam, which is water. Therefore, it is completely ineffective for sterilizing water-repellent substances like oils, greases, or dry powders that steam cannot penetrate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct sterilization method requires a clear understanding of your materials and your goal. Autoclaving is a powerful tool, but only when used appropriately.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing durable goods like glassware, metal instruments, or biohazardous waste: Autoclaving is the undisputed gold standard for its absolute reliability and ability to destroy spores.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive items like plastics or biological solutions: You must use an alternative such as filtration, chemical sterilization, or irradiation, as autoclaving will destroy them.
- If your primary focus is maintaining the sharpness of high-carbon steel tools: Consider dry heat or chemical sterilization methods specifically designed to protect delicate cutting edges from dulling.
Ultimately, choosing the right sterilization method begins with a simple question: can the material withstand the intense heat and moisture of pressurized steam?
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Effectiveness | Kills all microorganisms, including bacterial spores. |
| Reliability | The gold standard for sterilizing heat-stable equipment. |
| Speed & Efficiency | Fast cycles with modern features for improved workflow. |
| Material Penetration | Steam effectively penetrates porous and complex items. |
Ensure the highest standard of sterility and safety in your laboratory. KINTEK specializes in high-performance autoclaves and lab equipment designed for reliability and efficiency. Our solutions are tailored to meet the rigorous demands of modern laboratories. Contact our experts today to find the perfect autoclave for your specific needs and enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- What role does an autoclave play in the acid treatment for microalgae disruption? Unlock High-Yield Cell Pretreatment
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK
- What types of items and materials can be processed in a laboratory autoclave? Essential Guide for Lab Safety
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam



















