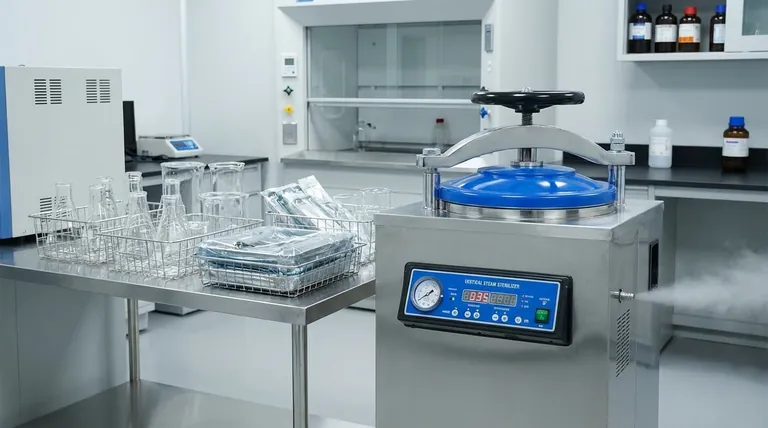
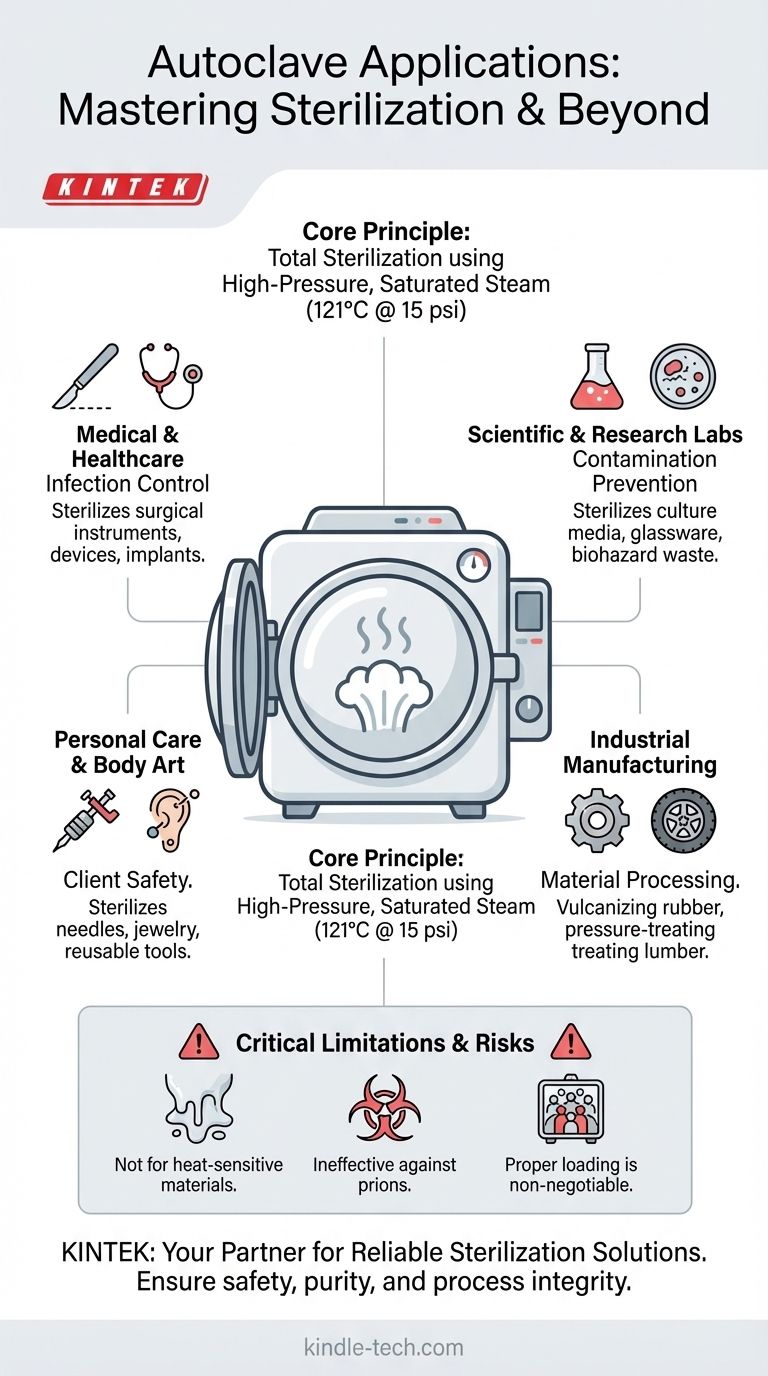
In essence, autoclaves are used for one primary purpose: sterilization. They are mission-critical devices in any field where the complete elimination of all microbial life—including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and highly resistant spores—is non-negotiable. Their applications span from safeguarding patient health in hospitals and dental clinics to ensuring the integrity of results in scientific laboratories and even processing materials in industrial manufacturing.
The core function of an autoclave is not just cleaning, but achieving absolute sterility through high-pressure, saturated steam. This makes it the definitive tool for applications where even microscopic contamination can have critical consequences for safety, health, or process integrity.

The Core Principle: Total Sterilization
An autoclave is more than just a high-temperature oven. It is a chamber that uses a combination of high pressure and saturated steam to sterilize its contents effectively.
How It Achieves Sterility
The key to an autoclave's effectiveness is its use of moist heat. Under pressure, water can be heated beyond its normal boiling point of 100°C (212°F). A typical cycle runs at 121°C (250°F) at 15 psi for at least 15-20 minutes.
This superheated, high-pressure steam is highly efficient at transferring thermal energy. It rapidly denatures essential proteins and enzymes within microorganisms, killing them far more effectively than dry heat alone. This process is lethal even to tough bacterial spores, which can survive boiling water and many chemical disinfectants.
Key Application Domains
The need for complete sterilization dictates where autoclaves are indispensable. They are found in any environment where microbial contamination poses a significant risk.
Medical and Healthcare Settings
This is the most recognized application. Autoclaves are the cornerstone of infection control in hospitals, surgical centers, dental offices, and veterinary clinics.
They are used to sterilize reusable surgical instruments, medical devices, implantable items, and hollow instruments that are difficult to clean. This prevents the transmission of infectious agents between patients.
Scientific and Research Laboratories
In microbiology and life sciences, preventing contamination is paramount to the validity of research.
Autoclaves sterilize culture media, glassware, pipette tips, and other lab equipment to ensure experiments are not compromised by unwanted microbes. They are also used for the critical step of decontaminating biohazardous waste (like used petri dishes) before disposal.
Personal Care and Body Art
To protect client health and meet public health regulations, autoclaves are standard equipment in tattoo parlors, piercing studios, and some high-end beauty salons.
They are used to sterilize needles, grips, jewelry, and any reusable equipment that comes into contact with skin or bodily fluids, minimizing the risk of infection.
Industrial and Manufacturing Processes
Beyond sterilization, industrial-scale autoclaves use the same principles of heat and pressure to alter material properties.
This includes pressure-treating lumber to infuse it with preservatives, making it resistant to rot and insects. In the automotive industry, autoclaves are used for vulcanizing rubber, a process that strengthens it for use in products like tires.
Understanding the Limitations and Risks
While incredibly effective, an autoclave is a precise instrument with clear limitations. Misunderstanding these can lead to failed sterilization and significant risk.
Not All Materials Are Autoclavable
The intense heat and pressure will destroy or damage many materials. Heat-sensitive plastics will melt, certain chemicals can become volatile, and sharp instruments may become dull over repeated cycles. Only items verified as "autoclavable" should be processed.
It Does Not Destroy Prions
Standard autoclave cycles are ineffective against prions, the infectious proteins responsible for diseases like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Destroying prions requires significantly higher temperatures and longer exposure times, often combined with chemical treatments.
Proper Loading is Non-Negotiable
The effectiveness of an autoclave cycle depends entirely on steam penetrating every surface. Overcrowding the chamber, using sealed containers, or incorrect placement can create air pockets that prevent items from reaching the required temperature, resulting in incomplete sterilization.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use an autoclave is driven by the absolute need for sterility or material transformation. Understanding your primary objective is key.
- If your primary focus is preventing infection: The autoclave is your definitive tool for sterilizing any reusable, heat-stable instrument that will contact a patient or client.
- If your primary focus is research integrity: Use the autoclave to prepare sterile media and equipment and to safely decontaminate all biological waste before disposal.
- If your primary focus is material processing: The autoclave serves as a controlled environment to apply heat and pressure, fundamentally changing the physical or chemical properties of materials like wood and rubber.
Ultimately, the autoclave is a powerful instrument that provides the highest level of assurance for safety, purity, and industrial processing.
Summary Table:
| Application Domain | Primary Use | Key Items Sterilized/Processed |
|---|---|---|
| Medical & Healthcare | Infection Control | Surgical instruments, medical devices, implants |
| Scientific & Research Labs | Contamination Prevention | Culture media, glassware, biohazardous waste |
| Personal Care & Body Art | Client Safety | Tattoo needles, piercing jewelry, reusable tools |
| Industrial Manufacturing | Material Processing | Vulcanizing rubber, pressure-treating lumber |
Need a reliable autoclave for your critical sterilization processes? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including autoclaves designed for the demanding needs of medical, dental, and research laboratories. Ensure absolute sterility and process integrity—contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- Why is the standard autoclave temperature set to 121? The Science of Effective Sterilization
- What are the advantages of using an autoclave equipped with a stirring device for molten salt testing? Dynamic Accuracy



















