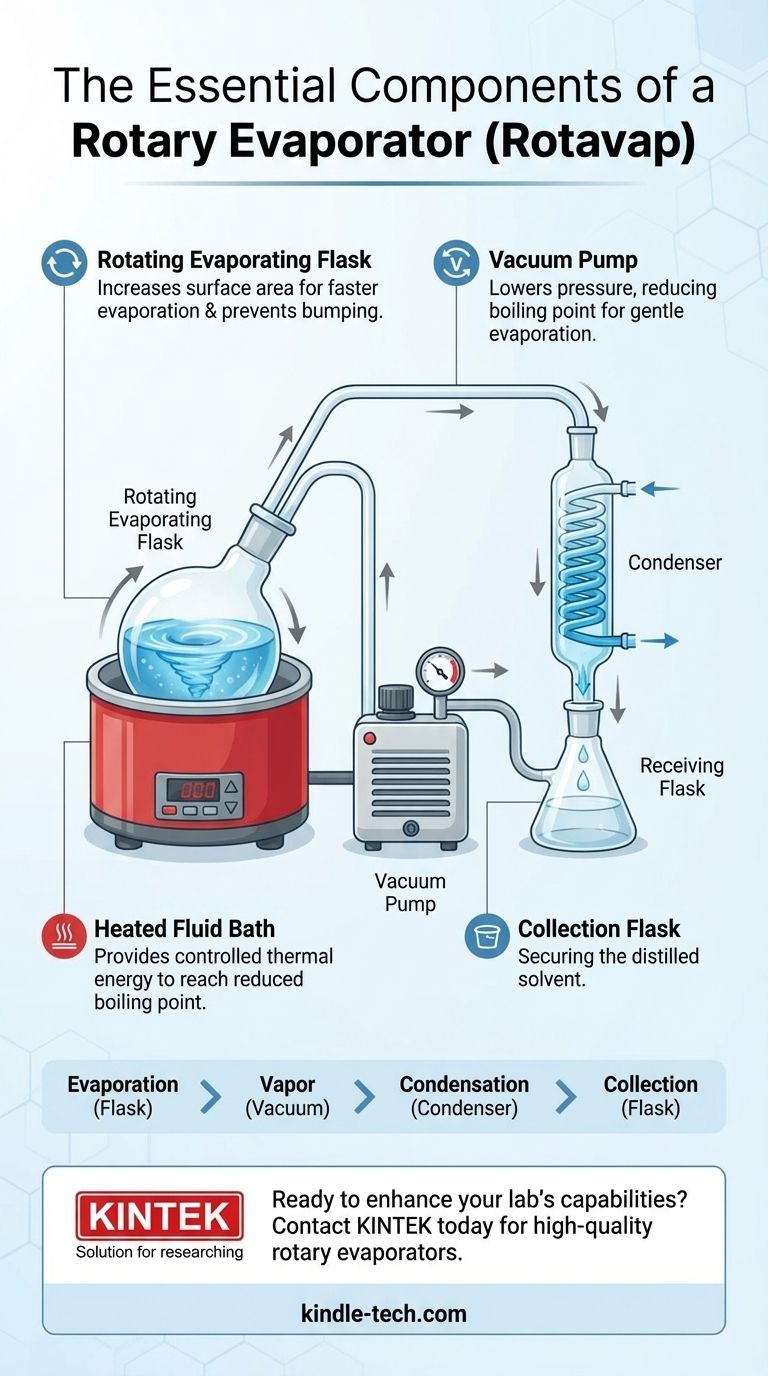
At its core, a rotary evaporator, or rotavap, is a system of five primary components. These are the rotating evaporating flask containing your sample, a heated fluid bath (water or oil), a condenser with a cooling coil, a collection flask to receive the distilled solvent, and a vacuum pump to lower the system's pressure. Together, these parts work in concert to gently and rapidly remove solvents from a sample.
The central principle of a rotavap is not to simply boil a solvent away. Instead, it combines a vacuum to lower the solvent's boiling point with rotation to dramatically increase the sample's surface area, achieving efficient evaporation at a low temperature that preserves the integrity of your compound.

How a Rotavap Achieves Gentle Evaporation
Understanding a rotavap isn't just about naming its parts; it's about understanding how those parts manipulate physical principles to achieve a specific goal. The primary goal is to remove a solvent without damaging the desired compound left behind.
The Principle: Reducing the Boiling Point
Every liquid has a boiling point, which is the temperature at which its vapor pressure equals the pressure of the surrounding environment. By lowering the pressure above the liquid, you lower the temperature required for it to boil.
The Vacuum System
The vacuum pump is the engine of this process. It actively removes air from the sealed glassware, creating a low-pressure environment. This is why a rotavap is so effective at removing even high-boiling point solvents at moderate temperatures.
The Heating Bath
The heated water or oil bath provides the thermal energy (heat) necessary to bring the solvent to its new, lower boiling point. The temperature is carefully controlled to be just enough to induce evaporation without "superheating" or degrading the sample.
The Power of Rotation
The rotating flask is the rotavap's key innovation. As the flask spins, it constantly spreads the sample into a thin film across the entire inner surface. This massively increases the surface area available for evaporation, making the process far faster than static boiling. This rotation also prevents bumping—the violent boiling that can occur under vacuum—by keeping the sample agitated.
Capturing and Recovering the Solvent
Once the solvent turns into a vapor, the system must be able to remove and collect it efficiently. This preserves the vacuum and allows for the solvent to be reused or disposed of properly.
The Condenser: Turning Vapor Back to Liquid
The condenser is a glass coil through which a cold fluid (usually tap water or a recirculating coolant) flows. When the warm solvent vapor from the flask comes into contact with the cold surface of the coil, it rapidly condenses back into a liquid.
The Collection Flask: Securing the Distillate
This condensed liquid solvent then drips down the coil and is collected in the receiving flask at the bottom of the condenser. This physically separates the removed solvent from the original sample, which remains concentrated in the rotating evaporating flask.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety Considerations
While powerful, a rotavap requires careful operation. Understanding its limitations is critical for safety and achieving good results.
Risk of Bumping and Foaming
Applying vacuum or heat too quickly can cause violent boiling (bumping) or excessive foaming, which can carry your sample over into the collection flask, ruining your separation. Always apply vacuum and heat gradually and ensure the rotation speed is adequate.
Implosion Hazard
The entire glass apparatus is under a significant vacuum, which creates an implosion risk. Always inspect glassware for stars or cracks before use. Many modern heating baths include a plastic safety shield that should always be used.
Maintaining the Vacuum Seal
The seal that allows the flask to rotate while connected to the stationary condenser is a critical component. It must be clean, properly lubricated (if required), and made of a material chemically resistant to your solvent to maintain the vacuum.
Balancing Temperature and Pressure
There is no single "correct" setting. You must balance the vacuum level and bath temperature based on the solvent being removed and the thermal sensitivity of your compound. Too much of either can lead to loss of sample.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific settings will depend on your objective. A rotavap is not a "set and forget" instrument; it is a tool that you control.
- If your primary focus is speed: Use a deep vacuum (low pressure) and the highest safe temperature for your compound, but be vigilant for bumping and foaming.
- If your primary focus is protecting a sensitive compound: Use a milder vacuum and a lower bath temperature, accepting that the process will take more time.
- If your primary focus is high solvent recovery: Ensure your condenser coolant is sufficiently cold and the flow rate is high enough to capture all the vapor before it reaches the vacuum pump.
- If you are working with very volatile or corrosive solvents: Consider using a secondary cold trap between the condenser and the vacuum pump to protect the pump from damage.
By understanding how each component contributes to the process, you move from simply operating the equipment to mastering the technique of gentle evaporation.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Rotating Evaporating Flask | Holds the sample; rotation increases surface area for faster evaporation. |
| Heated Fluid Bath | Provides controlled heat to reach the solvent's reduced boiling point. |
| Vacuum Pump | Lowers system pressure to significantly reduce the solvent's boiling point. |
| Condenser | Cools solvent vapor, turning it back into a liquid for collection. |
| Collection Flask | Receives and stores the distilled solvent, separating it from the sample. |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precision evaporation?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory equipment, including rotary evaporators designed for reliability, safety, and efficiency. Whether you are concentrating sensitive compounds, recovering solvents, or need robust equipment for demanding applications, our solutions are tailored to meet your specific laboratory needs.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how our lab equipment and consumables can help you achieve superior results. Let our experts guide you to the perfect solution for your research or production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
People Also Ask
- What determines the vacuum degree achievable by a water circulating vacuum pump? Unlock the Physics of Its Limits
- How does the impeller rotation affect the gas flow in a water circulating vacuum pump? A Guide to the Liquid Ring Principle
- What are the advantages of a water circulating vacuum pump? Superior Durability for Demanding Lab Environments
- How does a water circulating vacuum pump operate? Discover the Efficient Liquid Piston Principle
- What is the importance of a vacuum pump for Schottky hybrid interfaces? Achieve Atomic-Level Purity and Bonding



















