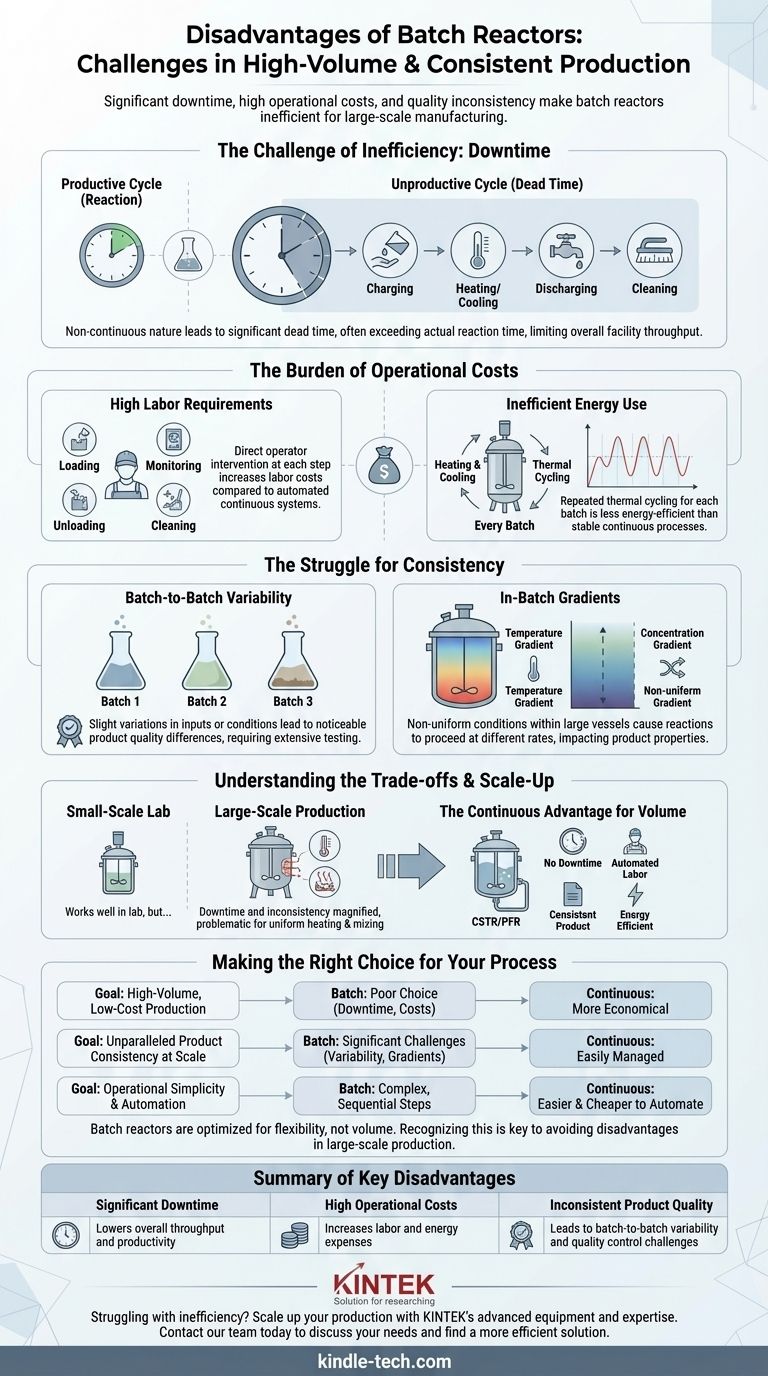
The primary disadvantages of batch reactors are significant unproductive downtime between production runs, high operational labor costs, and inherent challenges in maintaining consistent product quality. These factors make them poorly suited for high-volume manufacturing where efficiency and uniformity are paramount.
While valued for their versatility in small-scale or multi-product manufacturing, batch reactors become economically and operationally inefficient as production volume increases. Their fundamental stop-and-start nature introduces downtime and variability that are difficult to overcome at scale.

The Challenge of Inefficiency: Downtime
The most significant operational drawback of a batch reactor is its non-continuous nature. A large portion of its operational life is spent in unproductive states.
Unproductive Cycle Time
For every productive reaction phase, there is a sequence of non-productive steps: charging the reactor with reactants, heating or cooling to reaction temperature, discharging the product, and cleaning the vessel for the next run. This "dead time" can often exceed the actual reaction time.
Impact on Overall Throughput
This inherent downtime directly limits the total output of a facility. A continuous reactor runs 24/7 with minimal interruption, whereas a batch reactor's total production is a sum of discrete, separated runs.
The Burden of Operational Costs
Batch processing is often more expensive to operate on a per-unit basis compared to continuous alternatives, especially as production scales up.
High Labor Requirements
Each step of the batch cycle—loading, monitoring, unloading, and cleaning—typically requires direct operator intervention. This leads to higher labor costs compared to automated, steady-state continuous systems.
Inefficient Energy Use
The vessel and its contents must be heated and cooled for every single batch. This repeated thermal cycling is less energy-efficient than maintaining a continuous process at a stable operating temperature.
The Struggle for Consistency
Achieving identical product quality from one batch to the next is a persistent challenge in batch operations.
Batch-to-Batch Variability
Slight variations in the amount of raw materials charged, minor differences in heating or cooling rates, or subtle changes in mixing can lead to noticeable differences in product quality between batches. This requires extensive quality control testing for each batch.
In-Batch Gradients
Even within a single batch, conditions may not be perfectly uniform. Temperature and concentration gradients can form, especially in large vessels, meaning the reaction proceeds at different rates in different parts of the reactor. This can lead to a wider distribution of product properties within the same batch.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When Batch Fails
The disadvantages of a batch reactor are most apparent when it is misapplied. Its drawbacks highlight the strengths of continuous reactors for specific applications.
The Problem with Scale-Up
The issues of downtime and inconsistency are magnified during scale-up. A process that works well in a 10-liter lab reactor may face significant quality and efficiency problems in a 10,000-liter production vessel due to the challenges of uniform heating and mixing at scale.
The Continuous Advantage for Volume
For high-volume production of a single commodity, a continuous reactor (like a CSTR or PFR) is almost always superior. It eliminates downtime, reduces labor costs through automation, provides a highly consistent product, and is more energy-efficient.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Choosing a reactor is about matching the technology to the production goal. The disadvantages of a batch reactor make it the wrong tool for certain jobs.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost production: A batch reactor is a poor choice due to its inherent downtime and high operational costs; a continuous reactor is far more economical.
- If your primary focus is unparalleled product consistency at scale: The batch-to-batch variability and internal gradients of a batch reactor present significant challenges that are more easily managed in a continuous system.
- If your primary focus is operational simplicity and automation: A mature, steady-state continuous process is typically easier and cheaper to automate than the complex, sequential steps of batch manufacturing.
Ultimately, recognizing that batch reactors are optimized for flexibility, not volume, is the key to avoiding their significant disadvantages in large-scale production.
Summary Table:
| Key Disadvantage | Primary Impact |
|---|---|
| Significant Downtime | Lowers overall throughput and productivity |
| High Operational Costs | Increases labor and energy expenses |
| Inconsistent Product Quality | Leads to batch-to-batch variability and quality control challenges |
Struggling with inefficiency or inconsistency in your process? The limitations of batch reactors can be a major hurdle for scaling up your production. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables to help you optimize your workflow, whether you're exploring continuous processing alternatives or need precise control for specialized batch applications. Our experts can help you select the right technology to improve your throughput, reduce costs, and ensure product uniformity. Contact our team today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and find a more efficient solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Super Sealed Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of high-pressure reactors in semiconductor catalyst preparation? Optimize Your Heterojunctions
- Why are stainless steel autoclaves key to PCL-TPE preparation? Mastering High-Vacuum Polycondensation
- What is the role of a PTFE-lined stainless steel high-pressure autoclave in ZrW2O8 synthesis? Achieve High Purity
- Which critical experimental conditions does a high-pressure autoclave provide? Optimize Mixed Sulfide Leaching
- How does a high-pressure hydrothermal autoclave facilitate the synthesis of BiVO4@PANI nanocomposites? Unlock Precision.



















