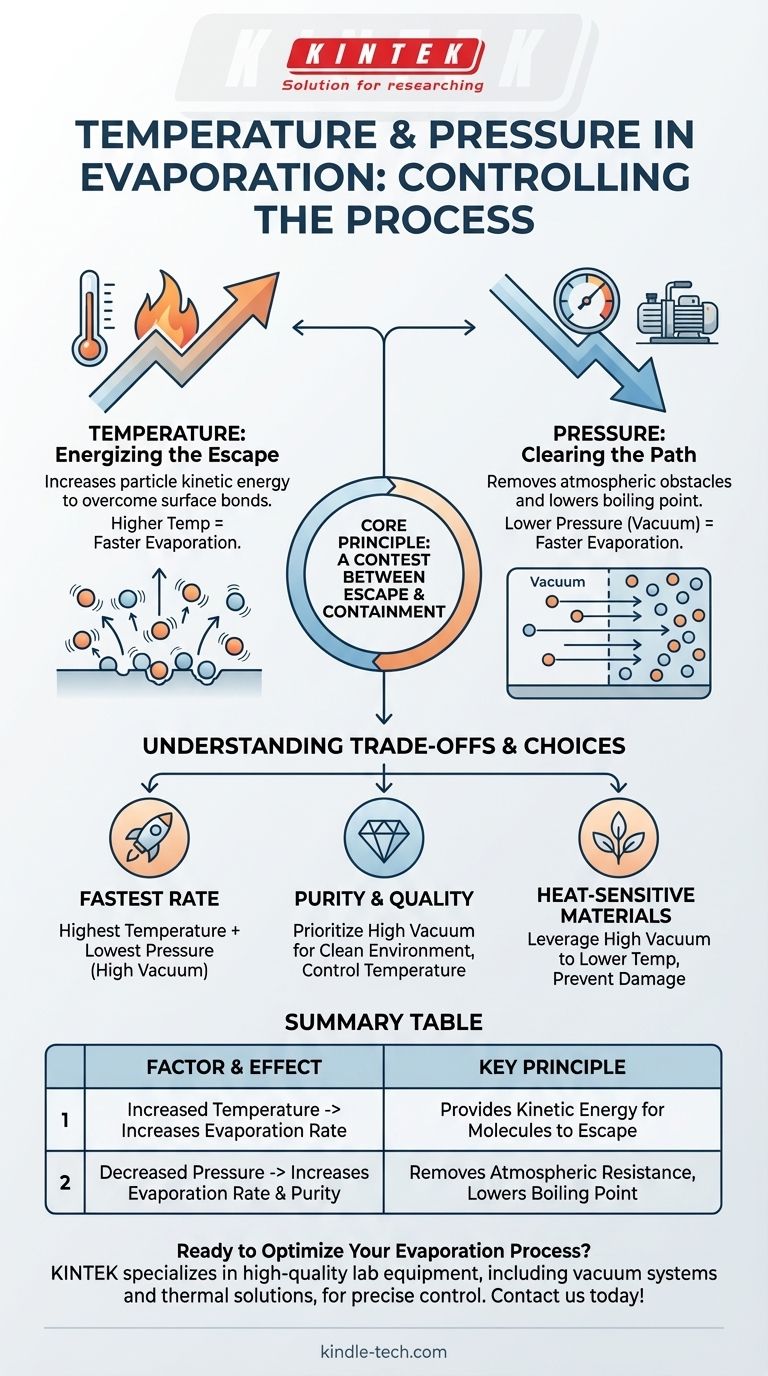
In any evaporation process, temperature and pressure are the two primary levers of control. Increasing the temperature provides molecules with the energy to escape a surface, thus increasing the evaporation rate. Conversely, decreasing the ambient pressure removes atmospheric obstacles, which also significantly increases the rate of evaporation.
The core principle is a contest between escape and containment. Temperature gives molecules the energy to escape, while lower pressure removes the external forces that contain them, making the entire process faster and more efficient.

The Role of Temperature: Energizing the Escape
Temperature is the most direct way to influence how quickly a material evaporates. The relationship is based on the energy of individual atoms or molecules.
Kinetic Energy is Key
Temperature is fundamentally a measure of the average kinetic energy (the energy of motion) of particles in a substance.
When you heat a material, you are increasing the speed and vibration of its constituent particles.
Overcoming Surface Bonds
For a particle to evaporate, it must have enough energy to break the bonds holding it to the surface of the material.
Higher temperatures mean a larger percentage of particles possess this necessary "escape velocity," leading to a higher overall rate of evaporation.
Application in Material Deposition
In processes like thin film deposition, heating the target substrate is critical. As mentioned, heating above 150 °C ensures good adhesion.
This is because the deposited atoms arrive with enough thermal energy to move around slightly on the surface, settling into a stable, uniform, and well-bonded crystalline structure.
The Role of Pressure: Clearing the Path
While temperature provides the "push" for evaporation, ambient pressure provides the "push back." Managing this external pressure is often just as important.
Atmospheric Resistance
The air or gas above a surface exerts pressure, creating a blanket of particles that an evaporating atom must push through.
At standard atmospheric pressure, an evaporating particle will collide with billions of air molecules, slowing its progress and even knocking it back to the surface.
The Power of a Vacuum
Lowering the pressure, or creating a vacuum, removes these atmospheric particles. This clears the path for the evaporating atoms.
In a high vacuum, an atom can travel in a straight line from its source to its destination (like a substrate) with a much lower chance of collision, dramatically increasing the net evaporation rate.
Lowering the Boiling Point
A critical effect of lowering pressure is that it reduces the material's boiling point. Boiling is simply rapid evaporation that occurs when a material's internal vapor pressure equals the external ambient pressure.
By creating a vacuum, you can make materials evaporate or boil at much lower temperatures than would be possible in open air. This is essential for processing heat-sensitive materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Controlling temperature and pressure allows for precise outcomes, but it requires balancing competing factors.
Purity vs. Rate
In a vacuum chamber, the goal is often not just a high rate but high purity. A lower pressure ensures that fewer contaminant gas molecules (like oxygen or nitrogen) are present to interfere with or get embedded in the final deposited film.
Energy Costs vs. Equipment Costs
Achieving high temperatures requires significant energy input. Achieving a high vacuum requires expensive and complex pumping systems.
The choice often depends on the material's properties. It may be more efficient to use a moderate vacuum and a higher temperature for a robust material, or a high vacuum and a lower temperature for a delicate one.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal settings for temperature and pressure depend entirely on what you are trying to achieve with the evaporation process.
- If your primary focus is the fastest possible evaporation rate: Use the highest temperature the material can tolerate combined with the lowest possible pressure (highest vacuum).
- If your primary focus is material purity and film quality: Prioritize achieving a high vacuum to create a clean environment, then carefully apply temperature to control the deposition rate.
- If your primary focus is processing a heat-sensitive material: Leverage a high vacuum to lower the evaporation temperature significantly, thereby preventing thermal damage to the substance.
Ultimately, mastering evaporation is about understanding how to use temperature and pressure in concert to achieve your specific material goals.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on Evaporation | Key Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Temperature | Increases evaporation rate | Provides kinetic energy for molecules to escape the surface |
| Decreased Pressure | Increases evaporation rate & purity | Removes atmospheric resistance, lowers boiling point |
Ready to Optimize Your Evaporation Process?
Understanding the interplay of temperature and pressure is crucial for achieving precise results in your lab. Whether you need to maximize purity, protect heat-sensitive materials, or increase deposition rates, having the right equipment is key.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including vacuum systems and thermal solutions, designed to give you precise control over your processes. Our experts can help you select the ideal setup for your specific application, ensuring efficiency, reliability, and superior outcomes.
Contact us today to discuss your needs and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
People Also Ask
- How can porosity be reduced? Achieve Maximum Material Strength and Density
- What are hot presses used for? Transforming Materials with Heat and Pressure
- How does temperature affect vacuum pressure? Master the Key to System Control
- Why is a heated laboratory hydraulic press necessary for composite laminates? Achieve Void-Free Structural Integrity
- What is a vacuum heat press machine? The Ultimate Tool for 3D Product Decoration



















