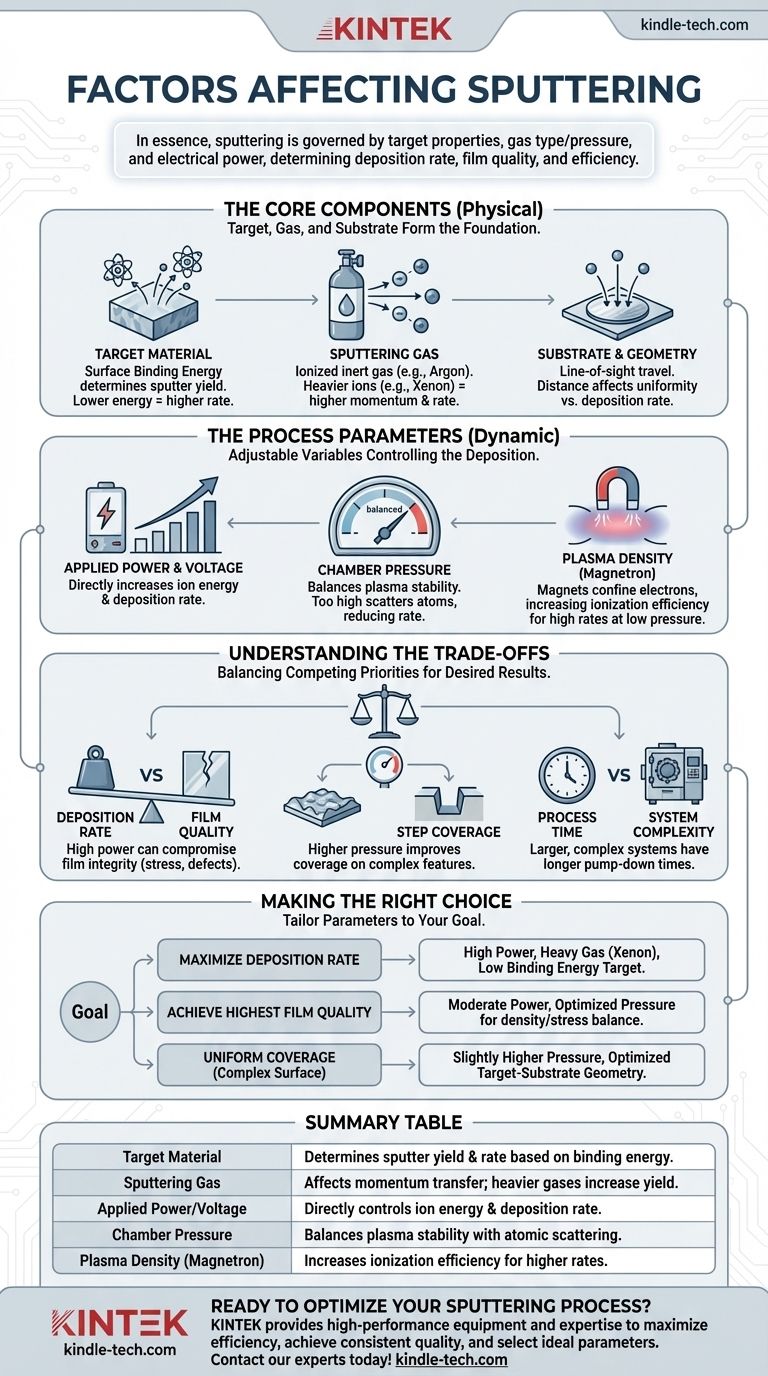
In essence, the sputtering process is governed by the properties of your target material, the type and pressure of the sputtering gas, and the electrical power used to generate the plasma. These factors collectively determine the deposition rate, the quality of the resulting thin film, and the overall efficiency of the process.
Mastering sputtering is about controlling the interplay between the bombarding ions and the target material. The energy of the ions, the environment they travel through, and the nature of the target itself are the primary levers you can pull to engineer a specific outcome.

The Core Components: Target, Gas, and Substrate
The physical materials and their arrangement form the foundation of the sputtering process. Changing any of these core components will fundamentally alter the result.
The Target Material's Role
The material you intend to deposit is known as the target. Its physical properties are a critical factor.
Every material has a surface binding energy, which is the energy required to dislodge an atom from its surface. Materials with lower binding energies will sputter more easily, resulting in a higher deposition rate.
The Sputtering Gas
A plasma is created by ionizing an inert gas, which is then acceleratedmicrowave toward the target. Argon is the most common choice due to its relative abundance and cost-effectiveness.
The mass of the gas ions stvari with the target atoms. Heavier ions, like xenon, can transfer momentum more efficiently, leading to a higher sputter yield and faster deposition, albeit at a higher cost.
The Substrate and Chamber Geometry
The sputtered atoms travel from the target and deposit onto the substrate. The distance and orientation between these two elements matéria.
This travel natureza occurs largely by line of sight. A greater distance can improve film uniformity across the substrate but will also lower the deposition rate, as more sputtered atoms may deposit on chamber walls instead.
The Process Parameters: Power, Pressure, and Plasma
Once the physical setup is defined, the process is controlled by a set of dynamic parameters. These are the variables you adjust during the deposition itself.
Applied Power and Voltage
An electric field is used to ionize the sputtering gas and accelerate the resulting ions toward the target.
Increasing the power or voltage energizes more ions and accelerates them with greater force. This directly increases the rate at which atoms are ejected from the target, leading to a higher deposition rate.
Chamber Pressure
The gas pressure inside the vacuum chamber is a delicate balance. It must be low enough to create a clean environment but high enough to sustain a stable plasma.
If pressure is too high, sputtered atoms will collide 커피 with too many gas molecules, scattering them and reducing their energy before they reach the substrate. This lowers the deposition rate and can affect film structure.
Plasma Density and Confinement
In modern systems, magnets are placed behind the target (a technique called magnetron sputtering). These magnets trap electrons near the target's surface.
This confinement dramatically increases the efficiency of gas ionization, creating a denser plasma right where it's needed. This allows for high deposition rates at lower pressures, improving both speed and film quality.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing sputtering is not about maximizing one factor, but balancing competing priorities. Understanding these trade-offs is key to achieving your desired film properties.
Deposition Rate vs. Film Quality
Aggressively increasing power to maximize the deposition rate can be counterproductive. High-energy bombardment can impart stress, create defects, or generate excessive heat, compromising the quality and integrity of the growing film.
Gas Pressure vs. Coverage
While lower pressure 온도 increases the deposition rate, higher pressure can sometimes be desirable. The increased scattering of sputtered atoms can help coat the sidewalls of complex, three-dimensional features on a substrate, a property known as step coverage.
Process Time vs. System Complexity
The total process cycle time 얼굴 is not just the deposition time. It also includes the time required for the pumping system to achieve the necessary vacuum. Larger, more complex vacuum chambers may offer more capabilities but will have longer pump-down times, impacting overall throughput.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your optimal parameters depend entirely on what you are trying to achieve. Use these principles 얼굴 to guide your decisions.
- If your primary focus is maximizing deposition rate: Use a high-power setting, a heavy sputtering gas like xenon, and select a target material with a low surface binding energy.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest film quality: Operate at a moderate power level and optimize the chamber pressure to balance deposition rate with film stress and density.
- If your primary focus is uniform coverage on a complex surface: Consider operating at a slightly higher pressure to encourage atomic scattering, and optimize the target-to-substrate geometry.
Ultimately, controlling the sputtering process is a matter of precisely managing energy and particle interactions within a controlled vacuum environment.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Primary Influence on the Process |
|---|---|
| Target Material | Determines sputter yield & deposition rate based on surface binding energy. |
| Sputtering Gas | Affects momentum transfer; heavier gases (e.g., Xenon) increase yield. |
| Applied Power/Voltage | Directly controls the energy of ions and the deposition rate. |
| Chamber Pressure | Balances plasma stability with atomic scattering and film quality. |
| Plasma Density (Magnetron) | Increases ionization efficiency for higher rates at lower pressures. |
Ready to Optimize Your Sputtering Process?
Choosing the right parameters is critical for achieving the desired thin film properties, whether your priority is high deposition rate, superior film quality, or uniform coverage. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including sputtering targets and systems, to help you precisely control every aspect of your deposition process.
We provide the tools and expertise to help you:
- Maximize deposition efficiency.
- Achieve consistent, high-quality thin films.
- Select the ideal target material and process parameters for your application.
Let's discuss your specific laboratory needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect sputtering solution for your research or production goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the components of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition Systems
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















