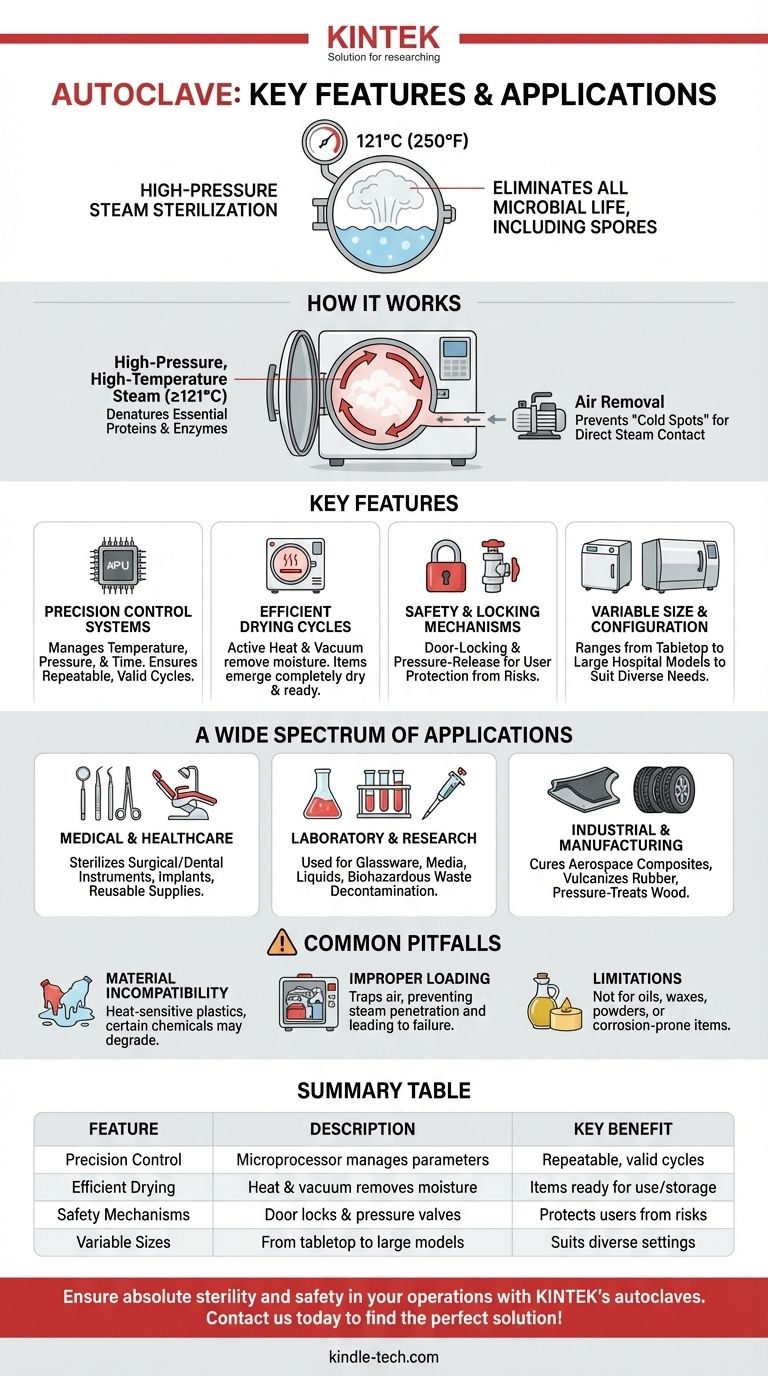
At its core, an autoclave is a device that uses high-pressure steam to sterilize equipment and materials. Its key features revolve around the precise control of temperature, pressure, and time to eliminate all forms of microbial life, including resilient bacteria and spores. This capability makes it indispensable in a wide range of applications, from sterilizing surgical instruments in hospitals to preparing culture media in research labs.
The true purpose of an autoclave is not just to heat items, but to leverage the physical properties of pressurized steam. This method achieves temperatures far exceeding boiling water, ensuring a level of sterilization that is absolute, repeatable, and essential for safety and scientific validity.

The Core Principle: How an Autoclave Works
The effectiveness of an autoclave is rooted in a simple principle of physics. By increasing the pressure within a sealed chamber, it is possible to raise the boiling point of water well above 100°C (212°F). This superheated steam is the active sterilizing agent.
High-Pressure, High-Temperature Steam
Standard sterilization cycles typically operate at 121°C (250°F) or higher. At this temperature, the high-energy steam rapidly denatures the essential proteins and enzymes that all microorganisms, including tough bacterial spores, need to survive.
The Critical Role of Air Removal
For sterilization to be successful, steam must make direct contact with every surface of the items being processed. Trapped air creates "cold spots" that steam cannot penetrate, leading to sterilization failure. Modern autoclaves use systems like vacuum pumps to remove air before the steam is introduced.
Key Features of Modern Autoclaves
While the core principle is consistent, specific features determine an autoclave's efficiency, reliability, and suitability for different tasks.
Precision Control Systems
The heart of any autoclave is its ability to precisely manage temperature, pressure, and cycle time. Modern units use microprocessor controls to ensure these parameters are met and held constant for the required duration, guaranteeing a repeatable and valid sterilization process.
Efficient Drying Cycles
After the sterilization phase, moisture can compromise the sterility of wrapped instruments or materials. Active drying systems, often using a combination of heat and vacuum, are a critical feature for removing residual moisture and ensuring items emerge completely dry and ready for storage or use.
Safety and Locking Mechanisms
Working with high pressure and temperature creates inherent risks. Essential safety features include door-locking mechanisms that prevent the chamber from being opened while pressurized and pressure-release valves to prevent over-pressurization.
Variable Size and Configuration
Autoclaves are not one-size-fits-all. They range from small, tabletop units common in dental offices and tattoo studios to large horizontal autoclaves used in hospital Central Sterile Services Departments (CSSD) to process hundreds of instruments at once.
A Wide Spectrum of Applications
The autoclave's ability to provide absolute sterility makes it a cornerstone technology in numerous fields.
Medical and Healthcare
This is the most recognized application. Autoclaves are used to sterilize surgical and dental instruments, implantable devices, and reusable medical supplies in hospitals, clinics, and veterinary offices.
Laboratory and Research
In microbiology and biotechnology, autoclaves are used daily to sterilize laboratory glassware, plastic tubes, pipette tips, and culture media. They are also essential for decontaminating and sterilizing biohazardous waste before disposal.
Industrial and Manufacturing
Beyond medicine, industrial autoclaves are used in manufacturing. They cure composite materials for the aerospace industry, vulcanize rubber for tires, and pressure-treat wood to increase its durability and resistance to decay.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
While highly effective, autoclaves are not a universal solution, and improper use can lead to failure.
Material Incompatibility
Not all materials can withstand the high heat and moisture of an autoclave. Heat-sensitive plastics can melt, sharp instruments can be dulled, and certain chemicals or powders can be degraded.
Improper Loading Techniques
Overloading the chamber or placing items in a way that traps air will prevent proper steam penetration. This is one of the most common causes of sterilization failure and underscores the need for proper user training.
Limitations for Certain Items
Autoclaves are not suitable for sterilizing oils, waxes, or powders that are impervious to steam. They are also generally not used for items that can be damaged by moisture or corrosion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right features and type of autoclave depends entirely on its intended application.
- If your primary focus is a clinical or dental setting: A reliable tabletop autoclave with pre-programmed cycles for wrapped and unwrapped instruments, and an effective drying cycle, is crucial.
- If your primary focus is a research laboratory: Versatility is key. Seek a model with dedicated cycles for liquids (with slow cooling), glassware, and biohazardous waste decontamination.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput sterile processing: A large-capacity horizontal autoclave with advanced pre-vacuum systems and rapid cycles is necessary to meet the demanding workflow of a central hospital department.
Ultimately, understanding an autoclave's features and principles transforms it from a simple machine into a powerful tool for ensuring safety, compliance, and procedural success.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Precision Control | Manages temperature, pressure, and time via microprocessor | Ensures repeatable, valid sterilization cycles |
| Efficient Drying | Uses heat and vacuum to remove residual moisture | Prevents contamination; items are ready for storage/use |
| Safety Mechanisms | Includes door locks and pressure-release valves | Protects users from high-pressure and high-temperature risks |
| Variable Sizes | Ranges from tabletop units to large horizontal models | Suits diverse settings (e.g., clinics, hospitals, labs) |
Ensure absolute sterility and safety in your operations with KINTEK's autoclaves. Whether you're in a medical clinic needing reliable instrument sterilization, a research lab requiring versatile cycles for media and waste, or an industrial facility curing composites, KINTEK provides lab equipment tailored to your needs. Contact us today to find the perfect autoclave solution for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the limitations of autoclave sterilization? Avoid Costly Damage to Your Lab Equipment
- What is the primary purpose and principle of autoclaving? The Definitive Guide to Sterilization
- What media cannot be autoclaved? Protect Heat-Sensitive Reagents from Sterilization Damage
- Why are the design pressure and temperature ranges of high-pressure autoclaves critical for biomass HTL processes?
- What are the safety concerns when autoclaving? A Guide to Preventing Burns, Explosions, and Biohazards
- What are the safety concerns of autoclave? Managing Heat, Pressure, and Steam Risks
- How do batch high-pressure autoclaves facilitate the catalytic hydrogenation of glucose? Boost Sorbitol Yield to 99%+
- What are the applications of autoclave? Essential Sterilization for Medical, Lab, and Industrial Needs



















