While highly effective, autoclaves are not a universal solution for sterilization. Their primary disadvantages stem from their reliance on high-pressure, high-temperature steam, which can damage sensitive materials, and their potential inability to sterilize complex, hollow, or porous items if the wrong type of autoclave is used.
The most significant limitation of an autoclave is not a flaw in the technology itself, but a mismatch between the autoclave class and the items being sterilized. Choosing the wrong type can lead to incomplete air removal, creating "cold spots" where sterilization fails entirely.
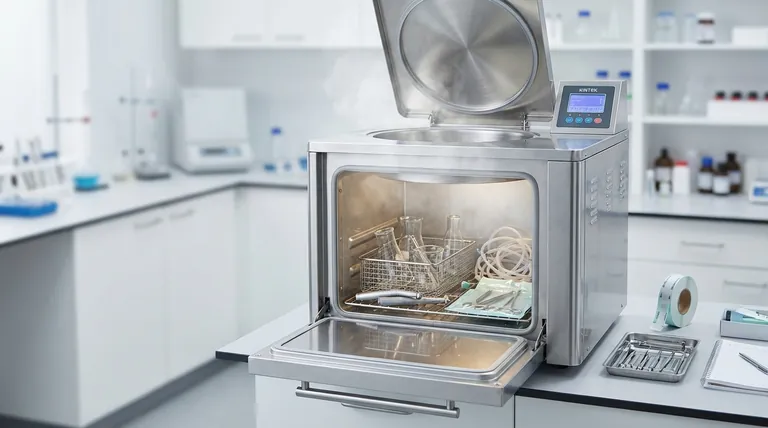

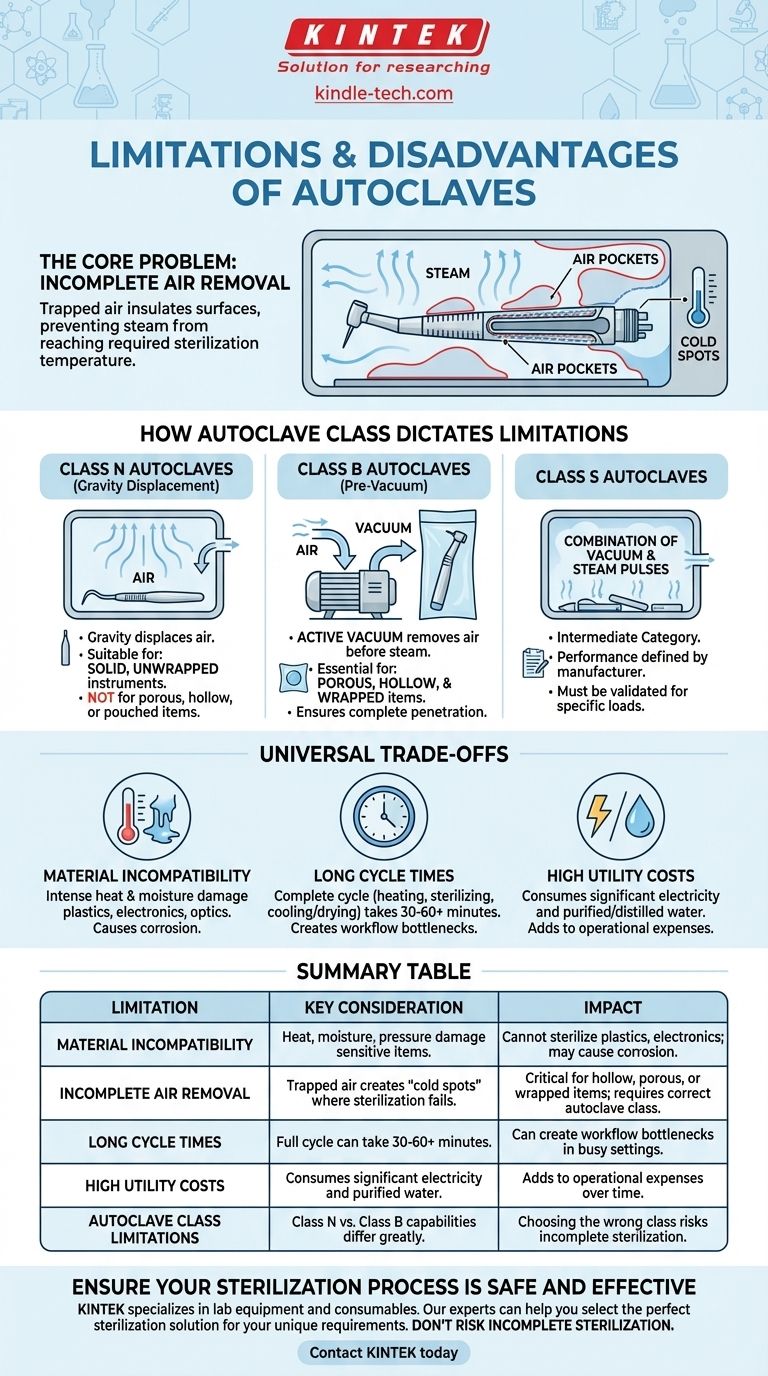
The Core Problem: Incomplete Air Removal
The effectiveness of an autoclave hinges on one critical factor: saturated steam must make direct contact with every surface of the item being sterilized. Any air that remains trapped in the chamber acts as an insulator, preventing the steam from reaching the required temperature to kill microorganisms.
How Trapped Air Prevents Sterilization
Air pockets prevent the surrounding steam from condensing on the item's surface. This condensation is what transfers the immense thermal energy needed for sterilization.
Without direct contact, the surface in the air pocket will not reach the necessary temperature for the required duration, leaving it non-sterile.
The Impact of Object Shape and Material
This is why the design of the object being sterilized is critical.
Porous materials (like textiles), hollow instruments (like cannulas or dental handpieces), and items inside sealed pouches are highly susceptible to trapping air. Gravity alone is often insufficient to force this trapped air out.
How Autoclave Class Dictates Limitations
The industry classifies autoclaves based on how they deal with the air removal problem. The limitations of your machine are defined by its class.
Class N Autoclaves (Gravity Displacement)
These are the simplest autoclaves. They operate by pumping steam into the chamber, which displaces the heavier, cooler air downwards and out through a vent.
This method is only reliable for solid, simple, unwrapped instruments. As noted in technical standards, Class N autoclaves cannot be trusted to sterilize textiles, porous loads, hollow items, or items in pouches, as they cannot guarantee complete air removal.
Class B Autoclaves (Pre-Vacuum)
These are more advanced systems designed for a much broader range of instruments. A Class B autoclave uses a vacuum pump to actively remove air from the chamber before the steam is introduced.
This pre-vacuum cycle ensures there are no air pockets, allowing steam to penetrate even complex, hollow, and wrapped loads effectively. This makes them suitable for use in dental, medical, and veterinary clinics.
Class S Autoclaves
Class S autoclaves are an intermediate category. Their performance and capabilities are defined by the manufacturer and must be validated for the specific types of loads they are intended to sterilize. They often use a combination of vacuum and steam pulses but may not meet the rigorous standards of a Class B unit for all load types.
Understanding the Universal Trade-offs
Beyond the issue of air removal, all autoclaves share some inherent disadvantages that you must consider.
Material Incompatibility
The combination of intense heat (typically 121°C or 134°C), high pressure, and moisture will destroy or degrade many materials.
This includes most plastics, heat-sensitive electronics, certain optics, and liquids or powders that cannot be exposed to moisture. It can also cause corrosion and dulling of sharp carbon steel instruments over time.
Long Cycle Times
A complete autoclave cycle, including heating, sterilization hold time, and cooling/drying, can take a significant amount of time, often ranging from 30 to 60 minutes or more. This can create bottlenecks in a busy clinical or laboratory workflow.
High Utility Costs
Autoclaves are resource-intensive machines. They consume a considerable amount of electricity to generate heat and pressure, and they use purified or distilled water to create steam, which adds to operational costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct sterilization method requires a clear understanding of your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing simple, solid, unwrapped glass or metal tools: A Class N autoclave is a cost-effective and suitable choice.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing dental handpieces, surgical kits, textiles, or wrapped instruments: A Class B pre-vacuum autoclave is the only safe and appropriate option.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing heat-sensitive plastics, electronics, or delicate instruments: An autoclave is the wrong tool; you must use a low-temperature method like Ethylene Oxide (EtO) or Vaporized Hydrogen Peroxide (VHP) sterilization.
By understanding these limitations, you can ensure that your sterilization process is not only efficient but, most importantly, effective and safe.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Key Consideration | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Material Incompatibility | Heat, moisture, and pressure can damage plastics, electronics, and certain metals. | Cannot sterilize heat-sensitive items; may cause corrosion. |
| Incomplete Air Removal | Trapped air creates 'cold spots' where sterilization fails. | Critical for hollow, porous, or wrapped items; requires correct autoclave class. |
| Long Cycle Times | Full cycle can take 30-60+ minutes. | Can create workflow bottlenecks in busy settings. |
| High Utility Costs | Consumes significant electricity and purified water. | Adds to operational expenses over time. |
| Autoclave Class Limitations | Class N (Gravity) vs. Class B (Pre-Vacuum) capabilities differ greatly. | Choosing the wrong class risks incomplete sterilization. |
Ensure Your Sterilization Process is Safe and Effective
Understanding autoclave limitations is the first step to protecting your patients, samples, and equipment. The right autoclave is not a one-size-fits-all solution—it must match your specific instruments and workflow.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect sterilization solution for your unique requirements, whether you need a cost-effective Class N autoclave for simple tools or a advanced Class B system for complex, hollow instruments.
Don't risk incomplete sterilization. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and ensure your lab's safety and compliance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
People Also Ask
- What role does an autoclave play in the acid treatment for microalgae disruption? Unlock High-Yield Cell Pretreatment
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- What is the normal temperature of an autoclave? Achieve Sterile Confidence with Precise Control
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK
- What is the life expectancy of an autoclave machine? Maximize Your Investment with Proper Care



















