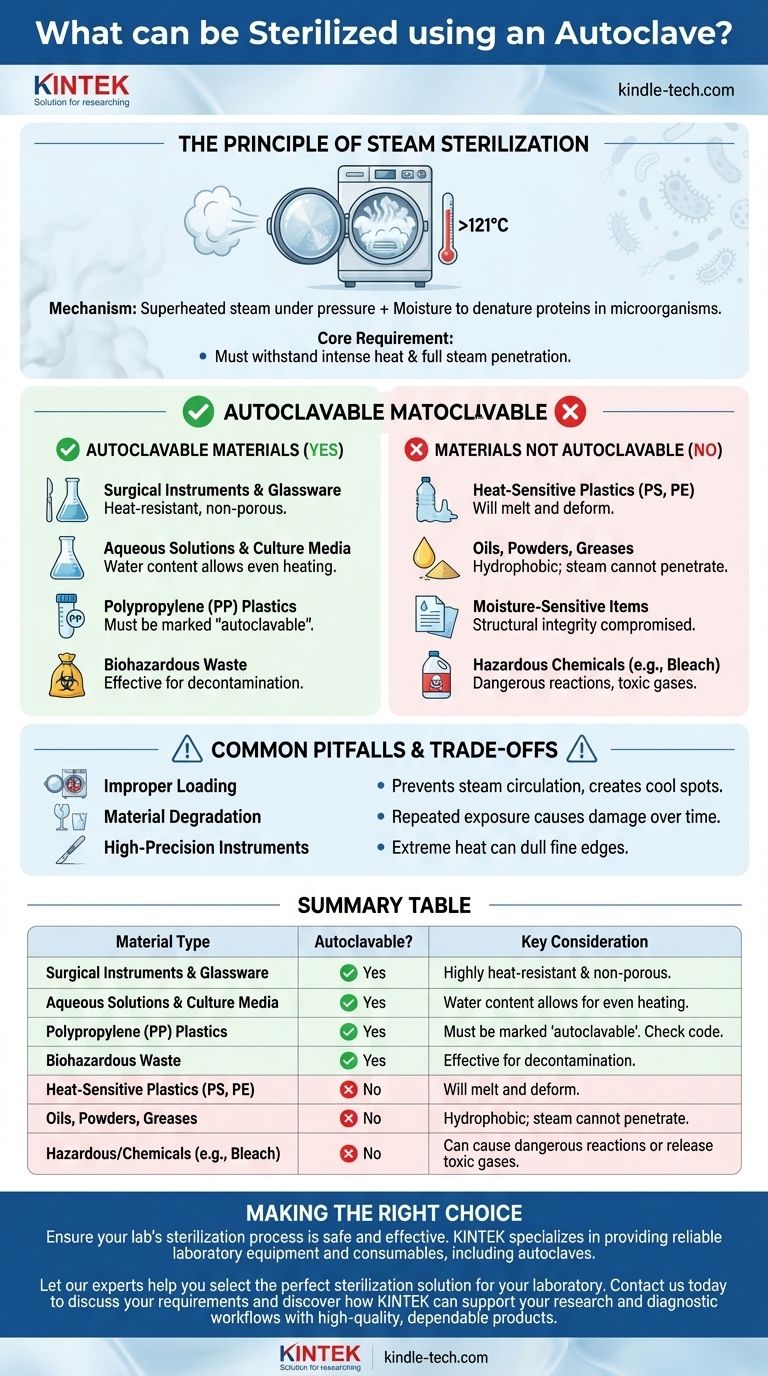
At its core, an autoclave is designed to sterilize materials that can withstand high temperatures and direct contact with pressurized steam. This makes it highly effective for sterilizing items like surgical instruments, heat-resistant glassware, culture media, aqueous solutions, and specific types of autoclavable plastics. The process uses superheated steam under pressure to kill microorganisms, making it a cornerstone of sterilization in laboratory and medical settings.
The fundamental rule for autoclaving is that the material must be able to tolerate both intense heat (typically 121°C or higher) and full steam penetration. If an item will melt, degrade from heat, or cannot be penetrated by moisture, it is not suitable for an autoclave.

The Principle of Steam Sterilization
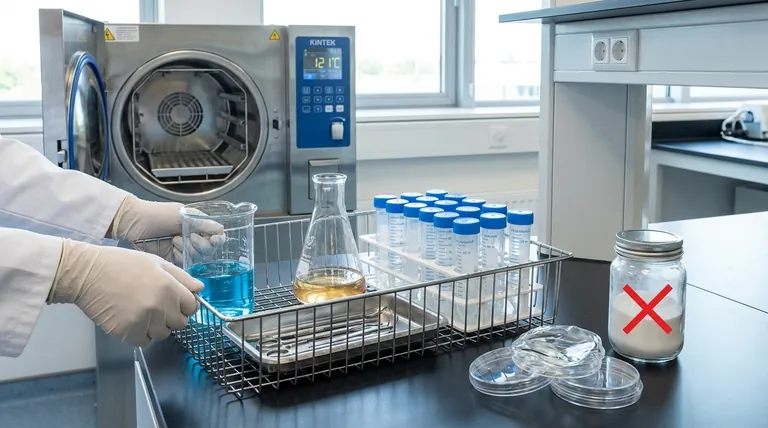
To understand what can and cannot be autoclaved, we must first understand the mechanism. Autoclaving is a form of steam sterilization, which is fundamentally different from dry heat.
How It Works: Heat and Moisture
An autoclave creates a high-pressure environment that allows water to boil at temperatures far above 100°C. This superheated steam is the active sterilizing agent.
The combination of intense heat and moisture efficiently denatures the proteins within microorganisms like bacteria and spores, rendering them inactive and non-viable.
Why Steam Penetration is Critical
For sterilization to be successful, the steam must make direct contact with every surface of the item. If steam cannot penetrate a material or reach a specific area, that area will not be sterilized.
This principle is the primary reason why certain materials are incompatible with autoclaving.
Autoclavable Materials: A Detailed Look
The following materials are generally considered safe for autoclave sterilization, provided proper protocols are followed.
Surgical Instruments and Glassware
Most metal surgical instruments and standard laboratory glassware (like Pyrex or Kimax) are designed to withstand repeated autoclave cycles without damage.
They are non-porous and highly heat-resistant, making them ideal candidates for steam sterilization.
Aqueous Solutions and Culture Media
Autoclaves are perfectly suited for sterilizing water, saline solutions, and most biological culture media. The water content of these materials allows them to heat evenly within the steam environment.
Specific Heat-Resistant Plastics
Many common lab plastics, like pipette tips and centrifuge tubes, are made from polypropylene (PP), which can withstand autoclaving temperatures.
Always check plastics for an "autoclavable" symbol or material code (like PP) before sterilizing, as materials like polystyrene (PS) or polyethylene (PE) will melt.
Biohazardous Waste
Autoclaving is a primary method for decontaminating and sterilizing biohazardous waste, such as used culture plates or contaminated tubes, before disposal.
Materials That Cannot Be Autoclaved
Putting the wrong material in an autoclave can result in a failed sterilization cycle, damage to the item, or even hazardous conditions.
Heat-Sensitive (Heat-Labile) Materials
This is the largest category of restricted items. This includes most plastics that lack high heat resistance, as they will melt and deform.
Furthermore, high-protein solutions like vaccines, serums, or urea will degrade and lose their efficacy when exposed to the autoclave's intense heat.
Waterproof or Non-Aqueous Substances
Oils, powders, and greasy substances cannot be sterilized effectively by autoclaving. Steam cannot penetrate these materials because they are hydrophobic (repel water).
Without direct steam contact, the items will not reach the necessary temperature for sterilization.
Items Damaged by Moisture
Porous materials that are sensitive to moisture, such as paper and linens, are not ideal for steam sterilization. The steam can compromise their structural integrity.
High-Precision Sharp Instruments
While most metal instruments are safe, the extreme heat of an autoclave can dull the fine cutting edge on high-grade carbon steel scalpels and scissors over time.
Hazardous and Reactive Chemicals
Under no circumstances should you autoclave flammable, corrosive, toxic, or radioactive materials. This also includes common household bleach (sodium hypochlorite), which can release toxic chlorine gas when heated under pressure.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Successful autoclaving requires more than just knowing what to put inside; it demands adherence to a strict protocol.
The Risk of Improper Loading
Overloading the autoclave chamber or sealing containers tightly can prevent steam from circulating and penetrating the load. This creates cool spots where microorganisms can survive, resulting in an incomplete sterilization cycle.
The Danger of Material Degradation
Even "autoclavable" materials have a lifespan. Repeated exposure to high heat and pressure can cause plastics to become brittle and glassware to develop micro-fractures over time, increasing the risk of failure.
Forgetting Post-Cycle Cool Down
Sterilized materials are extremely hot and under pressure when the cycle finishes. They must be allowed to cool properly before being handled to prevent burns and to avoid thermal shock that can crack glassware.
Making the Right Choice for Your Material
Your decision should always be based on the material's composition and the goal of the sterilization process.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing liquids or culture media: The autoclave is the ideal and most reliable method.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing lab plastics: You must verify they are made of a heat-resistant material like polypropylene (PP) or are explicitly marked as autoclavable.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing reusable instruments: The autoclave is excellent for most tools, but consider alternative methods for delicate, sharp-edged instruments to preserve their lifespan.
- If your primary focus is decontaminating waste: An autoclave is a highly effective method, but ensure no prohibited chemicals like bleach are present in the waste stream.
Ultimately, matching the material's properties to the sterilization method's mechanism is the key to achieving safe and effective results.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Autoclavable? | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Surgical Instruments & Glassware | Yes | Highly heat-resistant and non-porous. Ideal for steam sterilization. |
| Aqueous Solutions & Culture Media | Yes | Water content allows for even heating. Perfect for liquids. |
| Polypropylene (PP) Plastics | Yes | Must be marked 'autoclavable'. Check material code before use. |
| Biohazardous Waste | Yes | Effective for decontamination before disposal. |
| Heat-Sensitive Plastics (PS, PE) | No | Will melt and deform. Not suitable. |
| Oils, Powders, Greases | No | Hydrophobic; steam cannot penetrate for effective sterilization. |
| Hazardous/Chemicals (e.g., Bleach) | No | Can cause dangerous reactions or release toxic gases. |
Ensure your lab's sterilization process is safe and effective. Choosing the right equipment is crucial for maintaining sterility and protecting your valuable samples and instruments. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable laboratory equipment and consumables, including autoclaves and autoclavable labware, to meet your specific needs.
Let our experts help you select the perfect sterilization solution for your laboratory. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your research and diagnostic workflows with high-quality, dependable products.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What experimental conditions do stainless steel autoclaves provide for PCT-A leaching? Optimize Phosphate Glass Testing
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What is the function of laboratory autoclaves in SCWR research? Predict Material Compatibility and Corrosion Kinetics
- What extreme conditions does a laboratory autoclave simulate? Testing Wear Resistance of Nuclear Fuel Cladding
- What role does an autoclave play in remediation experiments? Ensure Precision by Eliminating Biological Noise



















