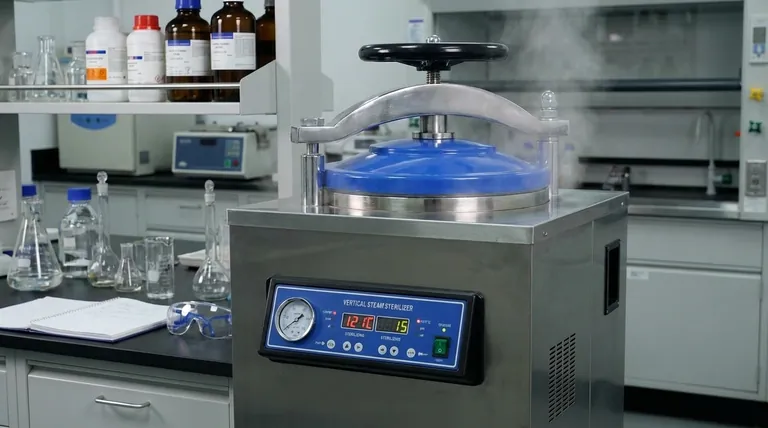
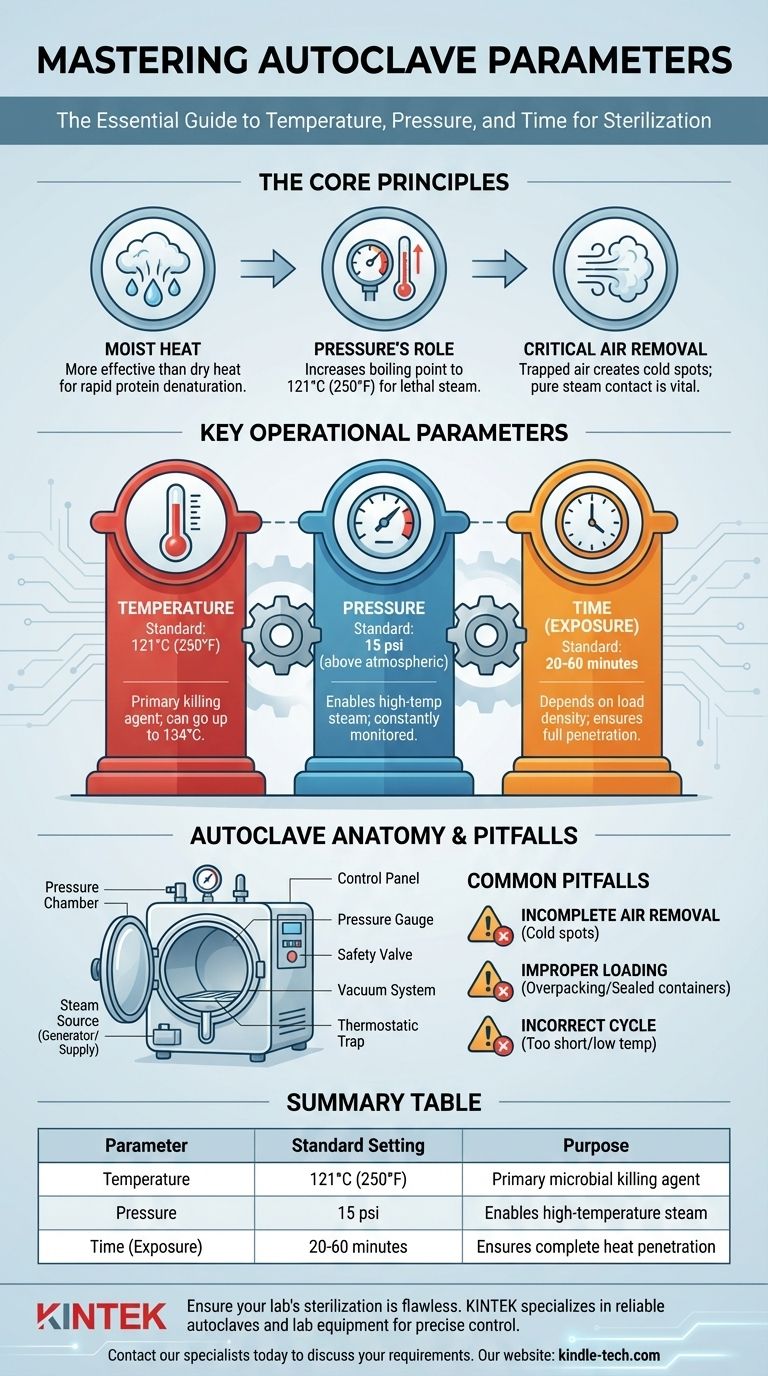
The essential parameters of an autoclave are temperature, pressure, and time. These three variables work in concert to achieve sterilization. For most general laboratory applications, the standard cycle is set to a temperature of 121°C (250°F) and a pressure of approximately 15 pounds per square inch (psi) above atmospheric pressure, maintained for a duration of 30 to 60 minutes.
Effective sterilization is not achieved by heat alone. The true power of an autoclave lies in its use of high-pressure saturated steam, which allows for rapid and deep heat penetration that is impossible to achieve with dry air. Understanding the relationship between the core parameters is the key to ensuring complete sterility.

The Core Principles of Autoclave Sterilization
To properly use an autoclave, you must first understand the scientific principles that make it so effective. It is a process of controlled violence against microorganisms.
Moist Heat vs. Dry Heat
Moist heat in the form of steam is significantly more effective at killing microbes than dry heat. Steam transfers thermal energy far more efficiently than hot air, rapidly denaturing the essential proteins and enzymes that microorganisms need to survive.
The Critical Role of Pressure
The pressure inside an autoclave does not kill microbes directly. Its primary function is to increase the boiling point of water. At normal atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C (212°F). By increasing the pressure to 15 psi, the autoclave raises water's boiling point to 121°C (250°F), allowing the steam to exist at a much higher, more lethal temperature.
Why Air Removal is Crucial
Sterilization will fail if air is trapped within the chamber. Air acts as an insulator, creating "cold spots" that steam cannot penetrate. This is why modern autoclaves incorporate vacuum systems or steam flush cycles to actively remove all air before the sterilization phase begins. Pure, saturated steam must make direct contact with every surface.
Understanding the Key Operational Parameters
The three main parameters are levers you control to define a sterilization cycle. Each is codependent on the others.
Temperature
Temperature is the primary killing agent. While 121°C is the most common standard, some applications, especially those involving the deactivation of prions or for very rapid cycles, may use temperatures up to 134°C.
Pressure
Pressure is the enabler of high-temperature steam. A pressure of approximately 15 psi (or 1 bar) above atmospheric pressure is required to achieve a steam temperature of 121°C. The autoclave's control system constantly monitors and maintains this pressure throughout the exposure time.
Time (Exposure or Dwell Time)
This is the duration for which the load is held at the target temperature and pressure. The required time depends heavily on the nature of the load. A simple load of glassware may need only 20-30 minutes, while dense biohazardous waste may require 60 minutes or more to ensure full heat penetration.
The Anatomy of an Autoclave
Several key components work together to control these parameters and ensure a safe, effective cycle.
The Pressure Chamber
This is the main vessel, typically a cylinder with double walls forming an inner chamber and an outer jacket. The jacket is often pre-filled with steam to help heat the chamber and reduce cycle times.
The Steam Source
Autoclaves are fed steam in one of two ways: either from a central steam supply within a facility or from an integrated electric steam generator that boils purified water on demand.
The Control and Safety System
This includes the control panel for selecting cycles, a pressure gauge to display internal pressure, and one or more safety valves. The safety valve is a critical feature that automatically releases pressure if it exceeds a safe threshold, preventing catastrophic failure.
The Air and Water Management System
A vacuum system is used to pump air out of the chamber before a cycle. A thermostatic trap or steam trap allows air and cooled water (condensate) to exit while keeping steam in. Finally, a wastewater cooler ensures that discharged water is at a safe temperature before it enters the building's drainage.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Even with a perfect machine, user error can lead to sterilization failure. Awareness of these pitfalls is essential.
Pitfall: Incomplete Air Removal
This is the most common cause of failed cycles. If a pre-cycle vacuum fails or if materials are wrapped in a way that traps air, cold spots will persist, and the items will not be sterile.
Pitfall: Improper Loading
Overpacking the chamber or using tightly sealed containers prevents steam from circulating and making contact with all surfaces. Loads must be packed loosely, and containers must be vented to allow for steam penetration.
Pitfall: Incorrect Cycle Selection
Choosing a cycle that is too short or at too low a temperature for the specific load is a frequent error. A large, dense bag of waste requires a much longer exposure time than a small flask of liquid media. Always match the cycle to the load.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your autoclave parameters based on the specific material you are sterilizing and your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is routine sterilization of lab media or glassware: The standard cycle of 121°C at 15 psi for 20-30 minutes is your reliable default.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing dense or large loads: You must increase the exposure time to ensure heat fully penetrates the entire volume.
- If your primary focus is treating biohazardous waste: Use a dedicated gravity or pre-vacuum waste cycle with extended time (45-60 minutes) to guarantee complete decontamination.
- If your primary focus is preventing sterilization failure: Always prioritize proper loading techniques and verify that your autoclave's air removal function is working correctly.
Mastering an autoclave means understanding that temperature, pressure, and time are inextricably linked in the pursuit of absolute sterility.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Standard Setting | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 121°C (250°F) | Primary microbial killing agent |
| Pressure | 15 psi above atmospheric | Enables high-temperature steam |
| Time (Exposure) | 20-60 minutes | Ensures complete heat penetration |
Ensure your lab's sterilization is flawless. KINTEK specializes in reliable autoclaves and lab equipment designed for precise control of temperature, pressure, and time. Our experts can help you select the right autoclave for your specific needs—whether for routine media preparation, handling biohazardous waste, or complex research applications.
Contact our lab equipment specialists today to discuss your sterilization requirements and ensure complete safety and compliance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What media cannot be autoclaved? Protect Heat-Sensitive Reagents from Sterilization Damage
- Is autoclave the same as sterilization? Unlocking the Key Differences for Lab Safety
- How long does an autoclave take to sterilize? Optimize Your Sterilization Cycle for Safety & Efficiency
- What core environmental conditions does a supercritical water autoclave provide? Simulating SCWR alloy performance.
- What temperature should incubator be for sterilization? The Critical Mistake You Must Avoid
- What is the difference between types of autoclave? Choose the Right Sterilization Method for Your Lab
- What factors may result in sterilization failure when using an autoclave? Prevent Failed Cycles with Expert Tips
- What are the methods of validation of autoclave? Ensure Sterility with a 3-Pillar Approach



















