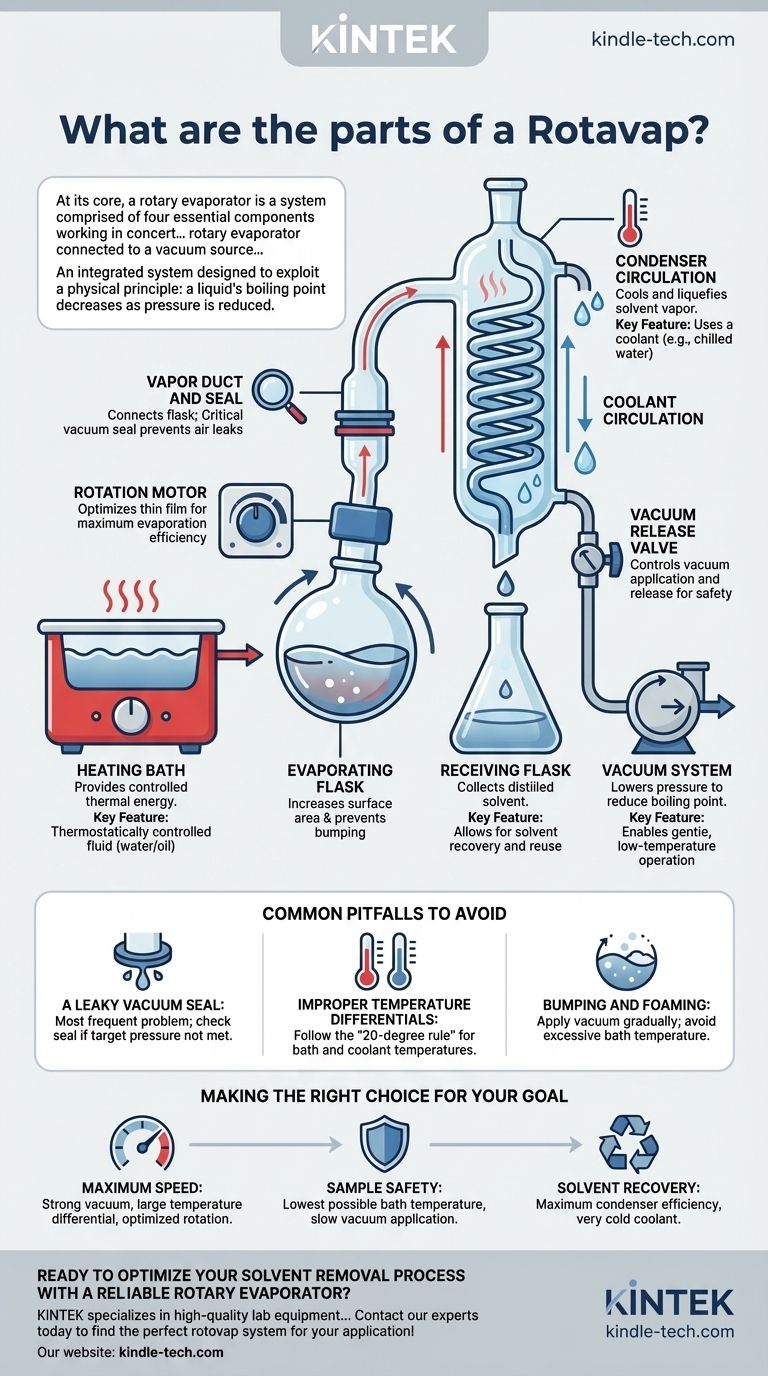
At its core, a rotary evaporator is a system comprised of four essential components working in concert: a heating fluid bath, a rotating evaporating flask, a condenser to cool solvent vapors, and a receiving flask to collect the distilled solvent. These parts are connected to a vacuum source, which is the key to the entire process.
The critical insight is not to see the rotovap as a collection of individual parts, but as an integrated system designed to exploit a physical principle: a liquid's boiling point decreases as pressure is reduced. Each component plays a specific role in controlling heat, pressure, and surface area to achieve gentle and rapid solvent removal.

The Core Functional Components
Each primary part of the rotovap has a distinct and vital role. Understanding their function is the first step to operating the instrument effectively.
The Heating Bath
The heating bath provides the controlled thermal energy needed for evaporation. It is typically filled with water or oil and is thermostatically controlled to maintain a precise temperature.
The goal is to gently heat the sample, providing just enough energy to overcome the solvent's enthalpy of vaporization at the reduced pressure.
The Evaporating Flask
This flask contains the sample solution. It is attached to the vapor duct and rotated by a motor, which is a defining feature of the instrument.
This rotation serves two critical purposes. First, it dramatically increases the surface area of the liquid, creating a thin film on the inner wall of theflask, which significantly speeds up the rate of evaporation. Second, the constant agitation prevents bumping—the violent boiling that can occur when a liquid is heated without nucleation sites.
The Vacuum System
While often a separate piece of equipment (like a diaphragm pump), the vacuum system is functionally the heart of the rotovap. It connects to the glassware assembly via a port, typically on the condenser.
Its sole purpose is to reduce the ambient pressure inside the system. By lowering the pressure, it lowers the boiling point of the solvent, allowing for rapid evaporation at a much lower temperature than would be required at atmospheric pressure. This protects heat-sensitive compounds from degradation.
The Condenser
The condenser is a glass coil through which a coolant (usually chilled water or a glycol mixture) is circulated. As the hot solvent vapor rises from the evaporating flask, it comes into contact with the cold surface of the coil.
This contact causes the vapor to rapidly cool and condense back into a liquid. The efficiency of your evaporation is directly tied to the efficiency of your condenser.
The Receiving Flask
This is the simplest component. As the solvent condenses on the coils, it drips down and is collected in the receiving flask.
This allows for the recovery and potential reuse of the solvent, which is both economical and environmentally responsible.
Understanding the Operational and Safety Parts
Beyond the core components, several other parts are essential for control, safety, and maintaining the integrity of the system.
The Vapor Duct and Seal
The vapor duct is the glass tube that connects the evaporating flask to the rest of the system. It is also the axis around which the flask rotates.
A critical component here is the vacuum seal, a polymer ring that sits around the vapor duct. This seal prevents air from leaking into the system while still allowing the duct and flask to spin freely. A worn or dirty seal is the most common cause of a poor vacuum.
The Rotation Motor
This is the electrical unit that drives the rotation of the evaporating flask. Modern rotovaps have variable speed controls.
Adjusting the rotation speed allows the user to optimize the thin film of liquid inside the flask for maximum evaporation efficiency without creating excessive splashing.
The Vacuum Release Valve
This is a stopcock or valve that allows the user to control the connection to the vacuum pump.
It is used to gently apply the vacuum at the start of the process and, just as importantly, to safely and slowly release the vacuum by re-introducing air into the system before attempting to remove any flasks.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding the parts is only half the battle. Knowing how they can fail or be misused is key to successful operation.
A Leaky Vacuum Seal
The most frequent problem is a vacuum leak, almost always originating from a compromised seal. If you cannot achieve the target pressure, check the seal first. It may be dirty, dry, or cracked.
Improper Temperature Differentials
For efficient condensation, a significant temperature difference is required between the heating bath and the condenser coolant. A common guideline is the "20-degree rule": the bath temperature should be about 20°C higher than the solvent's boiling point at your target pressure, and the coolant should be at least 20°C colder than that boiling point.
Bumping and Foaming
Applying a vacuum too quickly or having the bath temperature too high can cause violent bumping, leading to sample loss into the condenser. Always apply vacuum gradually and ensure smooth rotation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
How you operate the system depends entirely on your priority.
- If your primary focus is maximum speed: Ensure you have a strong vacuum, a large temperature differential between the bath and condenser, and a rotation speed that creates a thin, even film.
- If your primary focus is sample safety: Use the lowest possible bath temperature that still allows for evaporation and apply the vacuum slowly and carefully to prevent bumping heat-sensitive compounds.
- If your primary focus is solvent recovery: Ensure your condenser is operating at maximum efficiency with a very cold coolant temperature to capture as much vapor as possible.
By viewing the rotovap as an interconnected system rather than just a list of parts, you gain precise control over the entire evaporation process.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Bath | Provides controlled thermal energy | Thermostatically controlled fluid (water/oil) |
| Evaporating Flask | Holds and rotates the sample solution | Creates a thin film for rapid evaporation |
| Vacuum System | Lowers pressure to reduce boiling point | Enables gentle, low-temperature operation |
| Condenser | Cools and liquefies solvent vapor | Uses a coolant (e.g., chilled water) |
| Receiving Flask | Collects the distilled solvent | Allows for solvent recovery and reuse |
Ready to optimize your solvent removal process with a reliable rotary evaporator? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including rotary evaporators designed for precision, safety, and efficiency. Whether your priority is maximum speed, sample safety, or solvent recovery, our solutions are tailored to meet your laboratory's specific needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect rotovap system for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- Why is a water circulating vacuum pump suitable for handling flammable or explosive gases? Inherent Safety Through Isothermal Compression
- What can I use a vacuum pump for? Powering Industrial Processes from Packaging to Automation
- What is the importance of a vacuum pump for Schottky hybrid interfaces? Achieve Atomic-Level Purity and Bonding
- What is the purpose of the compression chamber in a vacuum pump? The Heart of Vacuum Generation
- How does a water circulating vacuum pump operate? Discover the Efficient Liquid Piston Principle


















