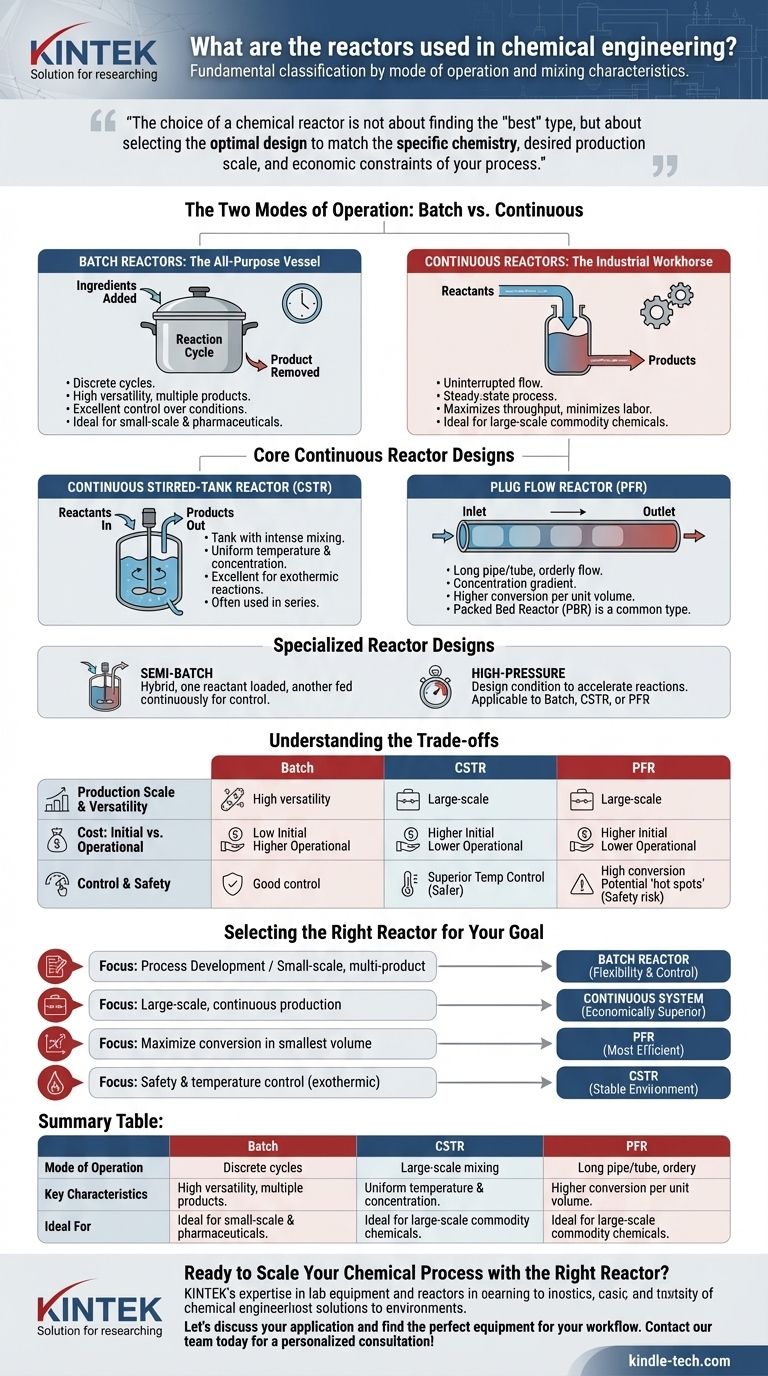
In chemical engineering, reactors are fundamentally classified by their mode of operation—batch, continuous, or semi-batch—and their mixing characteristics. The most common types are Batch Reactors, Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactors (CSTRs), and Plug Flow Reactors (PFRs), each designed to handle specific production scales, reaction kinetics, and heat transfer requirements.
The choice of a chemical reactor is not about finding the "best" type, but about selecting the optimal design to match the specific chemistry, desired production scale, and economic constraints of your process.

The Two Modes of Operation: Batch vs. Continuous
The first and most fundamental distinction in reactor design is whether the process runs in discrete cycles or as an uninterrupted flow.
Batch Reactors: The All-Purpose Vessel
A batch reactor is the simplest type of reactor. Think of it like a cooking pot: you add all your ingredients (reactants) at the start, let the reaction proceed under controlled conditions (heating, mixing), and then remove the entire final product.
This design is highly versatile, allowing a single vessel to be used for different reactions and products. It provides excellent control over reaction time and conditions.
Continuous Reactors: The Industrial Workhorse
Continuous reactors operate without interruption. Reactants are constantly fed into the vessel, and the product is continuously withdrawn, creating a steady-state process.
This mode of operation is ideal for large-scale production of a single commodity chemical, as it maximizes throughput and minimizes labor costs per unit of product. The two primary types of continuous reactors are the CSTR and the PFR.
Core Continuous Reactor Designs
Within the continuous category, the flow pattern and degree of mixing define the reactor's behavior and application.
Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactor (CSTR)
A CSTR is essentially a tank with an impeller that ensures the contents are perfectly mixed. Due to this intense mixing, the conditions throughout the reactor—temperature, concentration, and reaction rate—are uniform and identical to the conditions of the exit stream.
CSTRs are excellent at controlling temperature, especially for reactions that release a lot of heat. They are often used in series to increase overall conversion.
Plug Flow Reactor (PFR)
A PFR (also known as a Tubular Reactor) is typically a long pipe or tube. Fluid flows through it in an orderly fashion, like a "plug," with minimal mixing in the direction of flow.
As the fluid moves along the reactor's length, reactants are consumed, and the concentration changes continuously. This gradient allows PFRs to achieve higher conversion rates per unit volume than CSTRs for most reactions. A Packed Bed Reactor (PBR) is a common type of PFR filled with solid catalyst particles.
Specialized Reactor Designs
Other designs exist for specific needs. Semi-batch reactors are a hybrid where one reactant is loaded initially while another is fed continuously, useful for controlling concentration or managing heat. High-pressure reactors, as mentioned in industry literature, are not a fundamental type but rather a specific design condition applied to Batch, CSTR, or PFR systems to accelerate reactions and improve yields.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a reactor involves balancing competing factors. No single reactor is superior in all situations.
Production Scale and Versatility
Batch reactors excel in small-scale production, pilot plants, and manufacturing high-value products like pharmaceuticals, where flexibility to produce multiple products in the same equipment is critical.
Continuous reactors (CSTRs and PFRs) are the standard for large-scale, single-product commodity chemical manufacturing where efficiency and high throughput are the primary economic drivers.
Cost: Initial vs. Operational
Batch reactors generally have a lower initial capital cost and are simpler to construct. However, their operational costs per unit of product are higher due to downtime for cleaning, filling, and emptying, as well as higher labor involvement.
Continuous reactors have a higher upfront investment but offer significantly lower operating costs at large scales due to automation and uninterrupted production.
Control and Safety
CSTRs offer superior temperature control because the entire volume is at a single, uniform temperature, making them safer for highly exothermic reactions.
PFRs can develop "hot spots"—areas of high temperature—which can be a safety risk or lead to undesirable side reactions if not managed carefully.
Selecting the Right Reactor for Your Goal
Your choice must be driven by your primary objective for the chemical process.
- If your primary focus is process development or small-scale, multi-product manufacturing: A batch reactor offers the necessary flexibility and control.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, continuous production of a single chemical: A continuous system (CSTR or PFR) is the economically superior choice.
- If your primary focus is maximizing conversion in the smallest possible volume: A PFR is generally the most efficient design.
- If your primary focus is safety and temperature control for a highly exothermic reaction: A CSTR provides the most stable and uniform operating environment.
Ultimately, selecting the correct reactor is a foundational decision in chemical engineering that directly shapes the efficiency, safety, and economic viability of a process.
Summary Table:
| Reactor Type | Mode of Operation | Key Characteristics | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch Reactor | Discrete cycles | High versatility, simple design | Small-scale, multi-product (e.g., pharmaceuticals) |
| CSTR (Continuous Stirred-Tank) | Continuous, steady-state | Perfect mixing, uniform temperature | Large-scale production, exothermic reactions |
| PFR (Plug Flow) | Continuous, steady-state | High conversion per volume, orderly flow | Large-scale, single-product, high conversion needs |
Ready to Scale Your Chemical Process with the Right Reactor?
Choosing the optimal reactor is critical for your lab's efficiency, safety, and economic success. The experts at KINTEK specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including reactors and related systems, tailored to your specific chemical engineering needs. Whether you are scaling up from batch to continuous production or require precise temperature control for sensitive reactions, we have the solutions to support your goals.
Let's discuss your application and find the perfect equipment for your workflow. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What are the technical advantages of using AISI 304 stainless steel? Superior Thermal Stability for Pyrolysis Reactors
- What is the significance of a Catalytic Hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) reactor? Transform Bio-Oil into High-Quality Fuel
- What is the role of a pressure reactor with an internal stirrer for red oak pretreatment? Optimize Biomass Conversion
- Why is high-pressure nitriding equipment with a dual-pressure balance structure utilized? Boost Speed and Hardness
- How do stainless steel high-pressure autoclaves facilitate MXene synthesis? Achieve High-Performance Nanocomposites
- What conditions does a reactor provide for nitrobenzene reduction? Optimize H2 Solubility for Aniline Purity
- Why use high-pressure reactors for food waste pretreatment? Boost Hydrogen Production Efficiency Today!
- What is the function of a high-pressure reactor in the hydrothermal synthesis of boehmite? Expert Process Insights



















