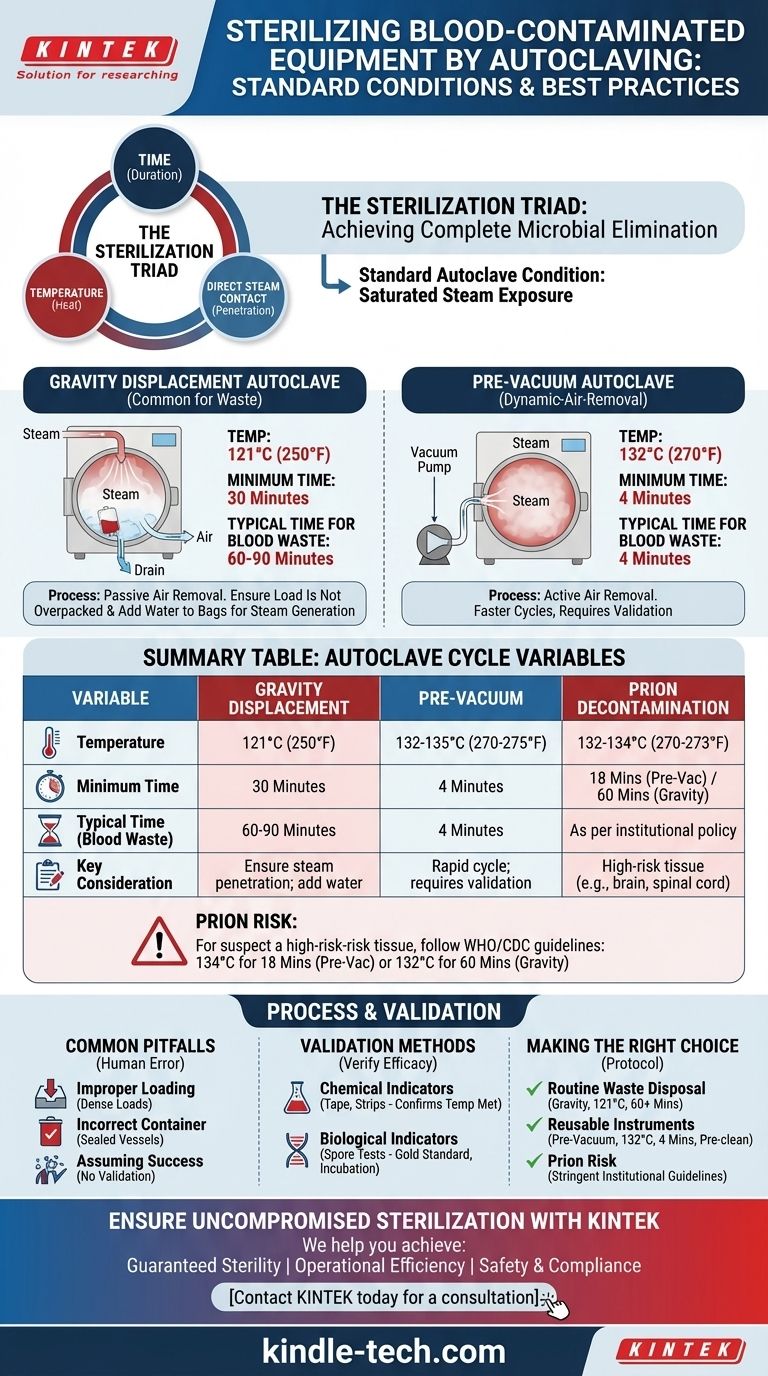
To effectively sterilize blood-contaminated equipment, the standard autoclave condition is exposure to saturated steam at 121°C (250°F) for a minimum of 30 minutes in a gravity displacement autoclave. This time is often extended to 60-90 minutes depending on the load's size and density to ensure complete steam penetration. For faster cycles, a pre-vacuum autoclave can achieve sterility at 132°C (270°F) in as little as 4 minutes, but proper equipment preparation remains critical for both methods.
The specific time and temperature settings are only one part of the equation. True sterilization depends on a triad of time, temperature, and direct steam contact. Failing to ensure steam can penetrate every surface of the contaminated load is the most common reason for sterilization failure.

The Science of Steam Sterilization
To ensure safety, you must understand why these conditions work. An autoclave is not simply a pressure cooker; it is a precision instrument designed to kill all forms of microbial life, including the most resilient bacterial spores.
How Autoclaves Destroy Microorganisms
The killing power of an autoclave does not come from pressure. Pressure is only used to raise the boiling point of water to a temperature where saturated steam can be created.
This high-temperature steam rapidly denatures and coagulates the essential proteins and enzymes within microorganisms, rendering them non-functional and leading to cell death. It is effective against viruses, bacteria, fungi, and spores.
The Critical Role of Saturated Steam
Saturated steam—steam at the highest possible temperature for a given pressure—is essential. It carries a tremendous amount of thermal energy.
When this steam contacts a cooler item, it condenses into water, instantly transferring its energy and heating the surface. Crucially, any trapped air acts as an insulator, preventing steam from making contact and creating cold spots where microorganisms can survive.
Standard Autoclave Cycles for Biohazards
The cycle you use depends on the type of autoclave available and the nature of the biohazardous material. Blood-contaminated waste requires robust treatment.
Gravity Displacement Cycles
This is the most common type of autoclave. It works by piping steam into the top of the chamber, which is heavier than air and displaces the cooler, heavier air downwards and out through a drain.
Because this air removal is passive, cycles are longer. A minimum of 121°C for 30 minutes is the baseline, but 60 minutes is the widely accepted standard for biohazard bags to ensure penetration.
Pre-Vacuum (Dynamic-Air-Removal) Cycles
These more advanced autoclaves use a vacuum pump to actively remove air from the chamber before steam is introduced. This allows for near-instantaneous steam penetration.
Because air removal is so efficient, cycles are much faster and can be run at higher temperatures. A typical cycle is 132-135°C for 3-4 minutes. This is common in hospital settings for rapid turnaround of surgical instruments.
The "Prion" Consideration
Prions are infectious proteins (not living organisms) that cause fatal neurodegenerative diseases like Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD). They are exceptionally resistant to standard sterilization methods.
If there is any suspicion of contamination with high-risk tissue (e.g., brain or spinal cord), or as a matter of institutional policy, prion-specific cycles are required. The World Health Organization recommends either 134°C for 18 minutes in a pre-vacuum sterilizer or 132°C for a full hour in a gravity displacement sterilizer.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Achieving sterility is a process, not a button press. Human error is the most frequent cause of cycle failure.
Pitfall: Improper Loading
Never overpack an autoclave. Tightly packed biohazard bags or instruments create dense loads where air cannot be removed and steam cannot penetrate.
Always leave space between items. If using biohazard bags, add a small amount of water (approx. 1/4 cup) to the bag before loosely closing it to help generate steam from within.
Pitfall: Incorrect Container Choice
Never autoclave items in a completely sealed container. The pressure differential will cause it to shatter or even explode.
Use only autoclavable plastics or glass (borosilicate). Containers must be covered loosely with foil or a cap that allows steam to enter. Trays should be placed on their edge, not stacked flat.
Pitfall: Assuming the Cycle Ran Correctly
Just because the machine finishes its cycle does not guarantee sterility. A mechanical failure or, more commonly, an error in loading can prevent the load from reaching the required conditions. Validation is essential.
How to Validate Sterilization Success
You must verify that every cycle is effective. This is done using a combination of indicators.
Chemical Indicators
Autoclave tape and indicator strips change color when a certain temperature is reached. They are a useful process indicator, confirming the item has been through a cycle.
However, they do not prove that the item was held at that temperature for the required amount of time. They confirm temperature was met, but not sterility.
Biological Indicators (Spore Tests)
This is the gold standard for sterility assurance. A biological indicator is a vial containing a known population of highly resistant bacterial spores, typically Geobacillus stearothermophilus.
The vial is placed in the most challenging part of the load. After the cycle, the vial is incubated. If the spores were killed, there is no growth. If they survive, it indicates a sterilization failure. Most protocols require weekly or even daily spore testing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Protocol
Your approach should be dictated by your material and your available equipment.
- If your primary focus is routine disposal of blood-contaminated waste (gauze, tubes, PPE): Use a gravity displacement autoclave at 121°C for at least 60 minutes, ensuring bags are not overpacked and contain a small amount of water.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing reusable instruments contaminated with blood: Pre-clean the instruments thoroughly to remove all visible bioburden, then use a pre-vacuum cycle at 132°C for 4 minutes if available.
- If your materials have any risk of prion contamination: You must follow stringent institutional and CDC/WHO guidelines, which typically involve extended cycle times like 134°C for 18 minutes or 132°C for one hour.
By mastering the principles of time, temperature, and steam contact, you transform autoclaving from a routine task into a guaranteed process of safety and sterility.
Summary Table:
| Variable | Gravity Displacement Autoclave | Pre-Vacuum Autoclave | Prion Decontamination |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 121°C (250°F) | 132-135°C (270-275°F) | 132-134°C (270-273°F) |
| Minimum Time | 30 minutes | 4 minutes | 18 minutes (pre-vacuum) or 60 minutes (gravity) |
| Typical Time for Blood Waste | 60-90 minutes | 4 minutes | As per institutional policy |
| Key Consideration | Ensure steam penetration; add water to bags | Rapid cycle; requires validation | For high-risk tissue (e.g., brain, spinal cord) |
Ensure Uncompromised Sterilization in Your Lab
Mastering autoclave protocols is critical for safety and compliance when handling blood-contaminated materials. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab autoclaves and consumables designed to meet the stringent demands of sterilization cycles.
We help you achieve:
- Guaranteed Sterility: Our equipment ensures precise temperature control and effective steam penetration for complete microbial elimination.
- Operational Efficiency: Choose from gravity displacement or pre-vacuum models to optimize your workflow and turnaround time.
- Safety & Compliance: Validate your cycles with confidence using our compatible indicators and spore tests, adhering to strict safety protocols.
Let's discuss your laboratory's specific needs. Whether you're processing waste or sterilizing reusable instruments, we have the solution.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and ensure your lab operates with the highest standards of safety and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is the protocol for autoclave machine? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe Sterilization
- What is cycle time as related to autoclaving? Master the Full Process for Effective Sterilization
- What is the pressure of autoclave at 121 C? The Key to Effective Steam Sterilization
- What are the uses of autoclave in laboratory equipment? Ensure Sterile Conditions for Your Research
- What is the function of autoclave in tissue culture laboratory? Ensure Absolute Sterility for Successful Cell Growth



















