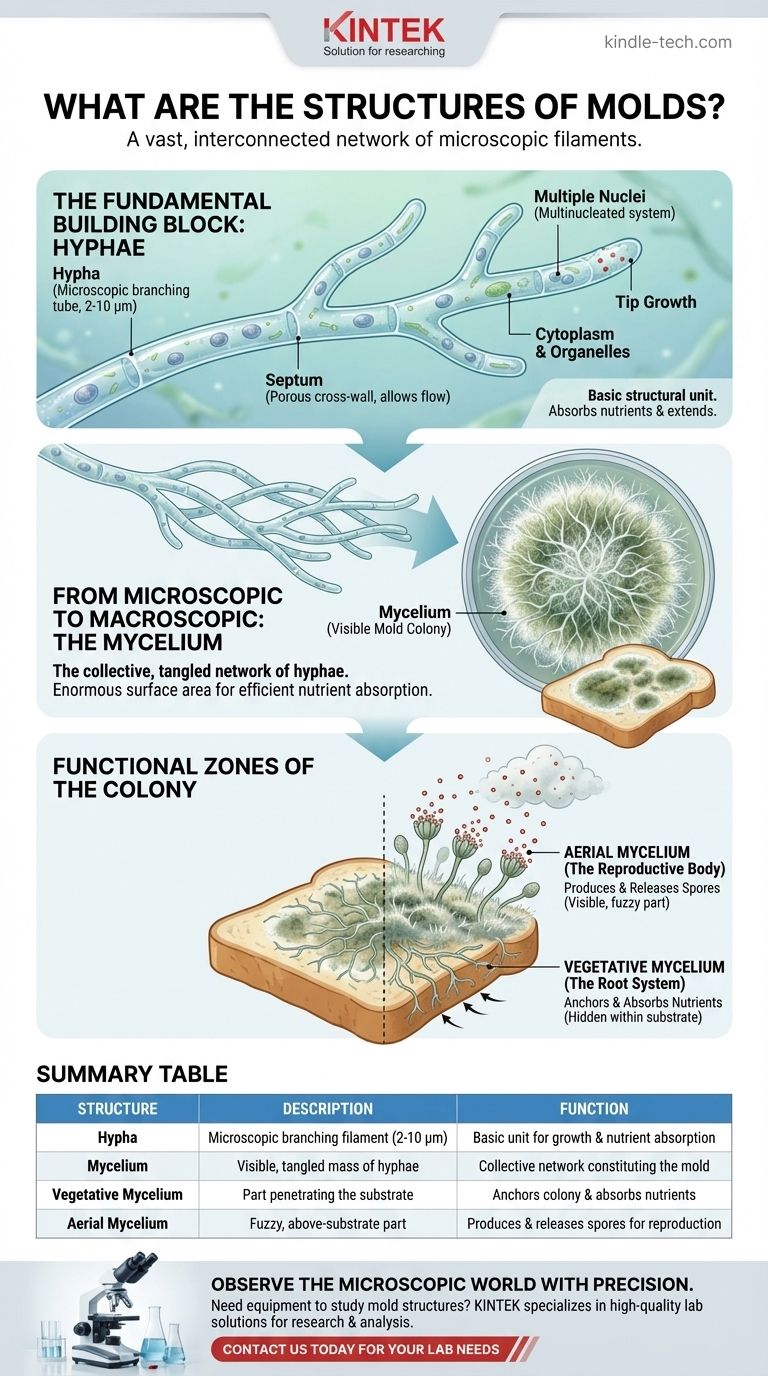
At its core, a mold is not a single entity but a vast, interconnected network of microscopic, thread-like filaments called hyphae. These individual hyphae branch and weave together to form the visible mass we recognize as a mold colony, which is technically known as a mycelium.
The fundamental structure of a mold is the hypha, a microscopic branching tube. The visible mold colony you see is the mycelium, which is simply a massive, tangled network of these individual hyphae.

The Fundamental Building Block: Hyphae
To understand a mold, you must first understand its individual components. The entire organism is built from repeating, simple units.
What is a Hypha?
A hypha (plural: hyphae) is the basic structural unit of a mold. It is a branching, tubular filament, similar to a single strand of thread.
These structures are microscopic, typically measuring only 2-10 micrometers in diameter. Their primary purpose is to grow, extend, and absorb nutrients from the environment.
Internal Divisions: Septa
Most hyphae are divided into cell-like compartments by internal cross-walls called septa.
These septa are not solid walls. They are perforated, allowing cytoplasm, organelles, and nutrients to flow freely between compartments, which facilitates rapid, coordinated growth across the entire network.
A Multinucleated System
Molds are multinucleated, meaning multiple nuclei can exist within a single compartment or share a common cytoplasm. This structure allows the organism to coordinate its functions and grow efficiently without having to form complete new cells for every extension.
From Microscopic to Macroscopic: The Mycelium
While a single hypha is invisible to the naked eye, their collective growth forms the structure we can easily see.
Defining the Mycelium
The mycelium is the term for the entire mass of intertwined hyphae that constitutes the mold colony.
When you see a fuzzy patch of mold on bread or a damp wall, you are looking at the mycelium—a vast, three-dimensional network of filaments.
Why This Structure is So Effective
The filamentous network of the mycelium is incredibly efficient at its job: absorbing nutrients.
This structure creates an enormous surface area, allowing the mold to make maximum contact with its food source and secrete digestive enzymes externally. This is why molds are such effective decomposers.
The Functional Parts of a Mold Colony
Not all parts of the mycelium perform the same function. The colony is typically organized into two distinct operational zones.
Vegetative Mycelium: The Root System
The portion of the mycelium that penetrates the food source (the substrate) is called the vegetative mycelium.
Its function is analogous to the roots of a plant. It anchors the colony and is primarily responsible for absorbing water and nutrients. This part is often hidden from view within the material the mold is growing on.
Aerial Mycelium: The Reproductive Body
The aerial mycelium grows upward, away from the substrate, and rises into the air. This is the fuzzy, often colorful part of the mold we are most familiar with.
Its primary function is reproduction. This part of the mycelium develops specialized structures that produce and release microscopic spores, which can then travel through the air to establish new colonies.
Key Structural Concepts at a Glance
Understanding these structural layers is key to understanding how molds function and grow.
- If your primary focus is the microscopic level: The key structure is the hypha, the individual, branching filament that absorbs nutrients.
- If your primary focus is the visible colony: You are observing the mycelium, which is the collective, tangled mass of countless hyphae.
- If your primary focus is the mold's lifecycle: Distinguish between the vegetative mycelium for feeding and the aerial mycelium for reproduction via spores.
This simple, repeating filamentous structure is what allows a microscopic spore to develop into a large, complex, and highly effective organism.
Summary Table:
| Structure | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Hypha | A microscopic, branching, tubular filament (2-10 μm in diameter) | The basic unit for growth and nutrient absorption |
| Mycelium | The visible, tangled mass of hyphae forming the colony | The collective network that constitutes the mold |
| Vegetative Mycelium | The part that penetrates the substrate (food source) | Anchors the colony and absorbs nutrients |
| Aerial Mycelium | The fuzzy, above-substrate part of the mycelium | Produces and releases spores for reproduction |
Need precise equipment to study microscopic structures like mold hyphae? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your laboratory needs. Whether you're in research, education, or quality control, our tools help you observe, analyze, and understand complex biological systems with accuracy and ease. Contact us today to find the perfect solution for your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- Customizable XRD Sample Holders for Diverse Research Applications
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of post-deposition heat treatment at 700°C for Al coatings? Enhance Oxidation Resistance
- Why do we use sputter coating? For Superior Thin Film Uniformity and Adhesion
- Is there a difference between a kiln and a furnace? Choose the Right Tool for Your Material
- What are the advantages of physical vapor deposition? Achieve High-Purity, Durable Thin Films
- What is the physical Vapour deposition method? A Guide to High-Performance Thin Films
- How to make carbon fiber conductive? Bridge the Insulating Gaps in Your Composite
- Why must PEO and lithium salt raw materials be pre-treated in a vacuum drying oven? Ensure Battery Stability
- How does biochar affect carbon sequestration? Turning Biomass into a Permanent Carbon Sink



















