In healthcare, the two primary applications of radioactive materials are diagnostics and therapy. These two functions leverage the unique properties of radioisotopes to either see inside the body to understand how it is functioning or to deliver targeted energy to destroy diseased cells, such as cancer.
The core principle is simple: radioactive materials can be used as either a camera or a weapon. For diagnosis, they act as trackable beacons that illuminate biological processes; for therapy, they become precision tools to eradicate specific cellular targets.
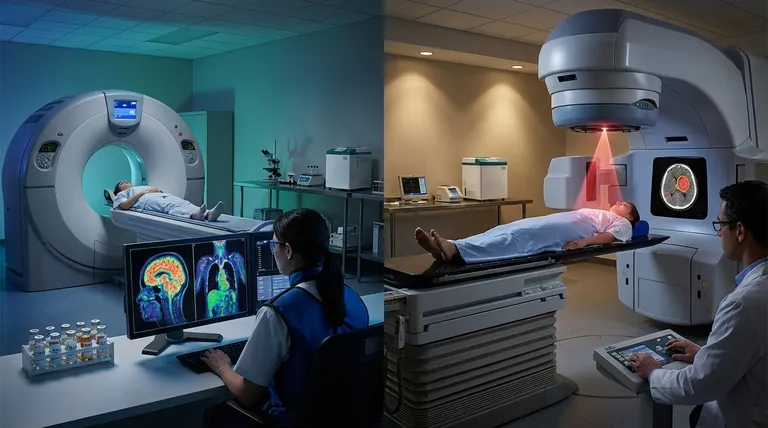
Application 1: Diagnostic Imaging (Seeing the Unseen)
The primary diagnostic use of radioactive materials is in a field known as nuclear medicine. It provides information about the function of organs and tissues, not just their anatomical structure like an X-ray or CT scan.
The Principle of Radiotracers
To achieve this, a radioactive isotope is chemically attached to a biologically active molecule, creating a compound called a radiopharmaceutical or radiotracer.
This radiotracer is then introduced into the body, typically by injection. Because it mimics a natural biological compound, the body transports it to a specific organ or tissue.
How Radiotracers Work
As the radioactive isotope decays, it emits energy, most often in the form of gamma rays. These rays can pass out of the body and be detected by a special device, such as a gamma camera or a PET scanner.
A computer then reconstructs these signals into a detailed image that shows where the radiotracer has accumulated, revealing the metabolic activity of the target area.
Common Diagnostic Techniques
The most common examples include PET (Positron Emission Tomography) and SPECT (Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography) scans. These are used to diagnose a wide range of conditions, from cancer and heart disease to neurological disorders.
For instance, Technetium-99m is a workhorse isotope for SPECT scans due to its short half-life and the low-energy gamma rays it emits, making it ideal for safe imaging.
Application 2: Therapeutic Treatment (Targeting Disease)
The goal of radiotherapy is fundamentally different from diagnosis. Here, the radiation is not used to create an image but to deliver a lethal dose of energy to destroy targeted cells, primarily cancer cells.
The Goal of Radiotherapy
Radiation damages the DNA of cells. While it affects both healthy and cancerous cells, cancer cells are often more susceptible because of their rapid division and reduced ability to repair DNA damage.
The objective is to maximize the dose to the tumor while minimizing exposure to the surrounding healthy tissue.
External Beam Radiotherapy
This is the most common form of radiation therapy. A machine, such as a linear accelerator, directs high-energy beams of radiation from outside the body to the tumor's location.
The treatment is carefully planned to have beams converge on the tumor from multiple angles, concentrating the dose there.
Internal Radiotherapy
Radioactive materials can also be placed inside the body. This can be done via brachytherapy, where a sealed radioactive source is surgically placed inside or next to a tumor.
Another method is systemic radiotherapy, where a radiopharmaceutical (like those used in diagnostics but with a more powerful isotope) is injected or ingested. It then travels through the body and accumulates in the cancerous tissue to deliver a targeted dose, such as using Iodine-131 to treat thyroid cancer.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
The use of radioactive materials always involves a careful balance between benefit and risk. The choice of isotope and delivery method is dictated by the specific medical goal.
The Importance of Half-Life
Half-life is the time it takes for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay.
For diagnostics, a short half-life is ideal. The material should remain active just long enough to complete the scan and then decay quickly to minimize the patient's radiation exposure.
For therapy (especially brachytherapy), a longer half-life may be chosen to deliver a steady, continuous dose of radiation to the tumor over several days or weeks.
Balancing Efficacy and Safety
The fundamental trade-off is destroying the target versus harming the patient. In diagnostics, the radiation dose is kept extremely low—just enough to be detectable. In therapy, the dose is intentionally high and destructive, requiring immense precision to protect healthy organs.
Making the Right Choice for the Medical Goal
The application of a radioactive material is determined entirely by the intended outcome.
- If your primary focus is diagnosis: You use a low-energy, short-lived isotope attached to a tracer molecule to safely visualize a biological function without altering it.
- If your primary focus is therapy: You use a higher-energy isotope delivered with maximum precision to destroy specific cells while sparing surrounding tissue.
Ultimately, radioactive materials provide an unparalleled ability to observe and influence the body at a molecular level.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Goal | Common Examples | Key Isotopes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnostics | Visualize biological function & detect disease | PET Scan, SPECT Scan | Technetium-99m |
| Therapy | Destroy diseased cells (e.g., cancer) | External Beam Radiotherapy, Brachytherapy | Iodine-131 |
Need precise equipment for handling radioactive materials in your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for nuclear medicine and research. Our products ensure safety and accuracy in diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Contact us today to find the right solutions for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
People Also Ask
- What is a lab autoclave? Your Guide to Sterilization with Pressurized Steam
- What temperature must be reached for sterilization in 10-12 minutes? Achieve Rapid, Reliable Sterility with Flash Autoclaving
- What are the advantages of autoclaving in hospitals? Achieve Unmatched Sterilization for Patient Safety
- Can autoclave sterilize liquid? Master Safe and Effective Liquid Sterilization
- Do you need to autoclave glassware? A Guide to Sterilization vs. Cleaning

















