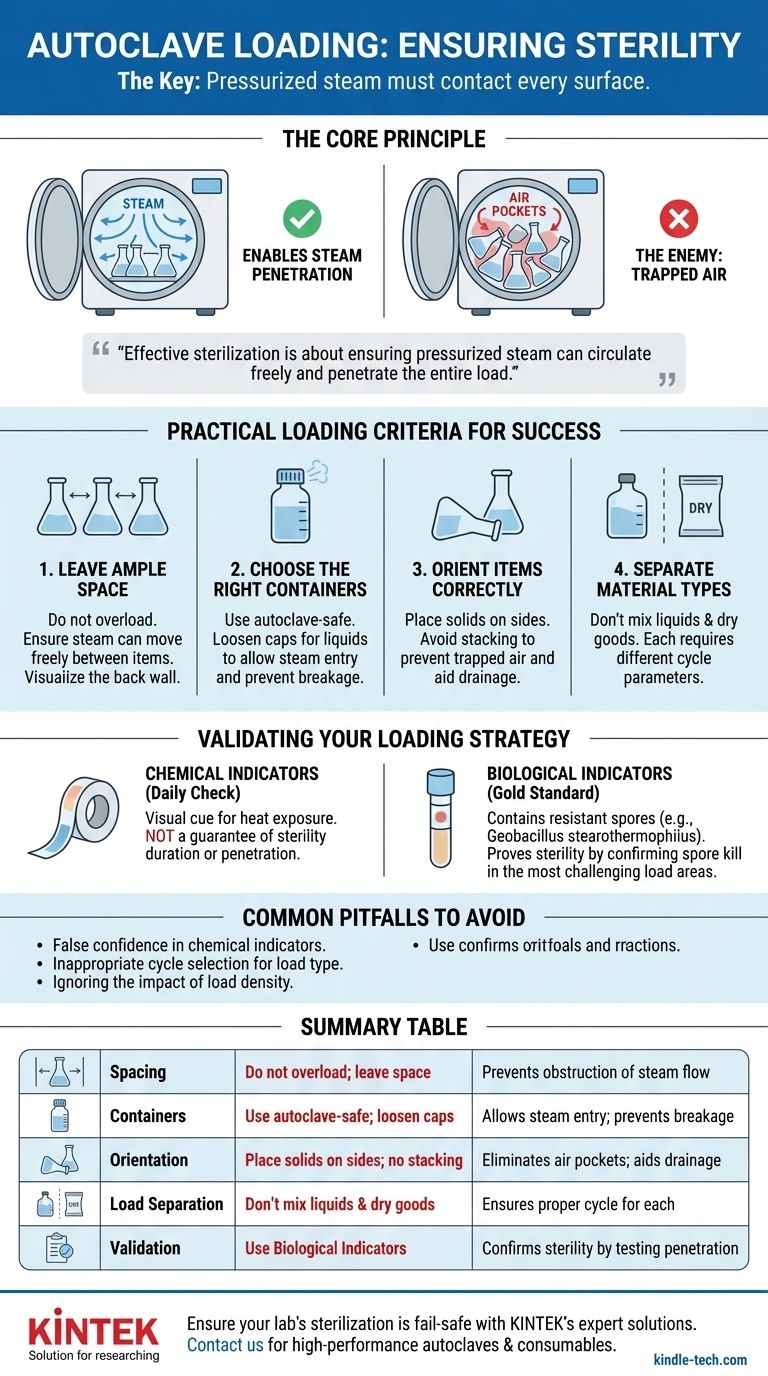
To ensure sterility, you must load an autoclave so that pressurized steam can contact every surface of every item. This is achieved by preventing overcrowding, choosing appropriate containers, and orienting items to avoid trapping air. These physical loading techniques are the foundation, while chemical and biological indicators are used to verify that these techniques were successful.
Effective sterilization isn't about heat alone; it's about ensuring pressurized steam can circulate freely and penetrate the entire load. Your loading technique is the primary factor that either enables or obstructs this critical process.
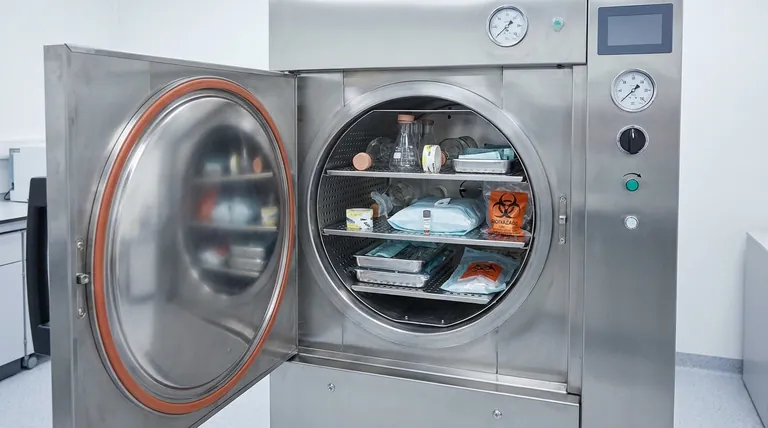

The Core Principle: Enabling Steam Penetration
To load an autoclave correctly, you must first understand how it works. The sterilizing agent is not dry heat, but saturated steam under pressure.
Why Steam is the Sterilizing Agent
Pressurized steam transfers heat far more efficiently than dry air. It condenses on cooler surfaces, releasing thermal energy that denatures the proteins and enzymes essential for microbial life.
The Enemy: Trapped Air
Air pockets are the primary obstacle to successful sterilization. Air is an insulator that prevents steam from making direct contact with surfaces. If steam cannot reach a surface, that surface will not be sterilized, regardless of the autoclave's temperature reading.
Practical Loading Criteria for Success
Every loading rule is designed to facilitate steam circulation and eliminate air pockets.
Leave Ample Space
Do not overload the autoclave chamber. A densely packed load prevents steam from moving freely between items. A good rule of thumb is to ensure you can still see the back wall of the chamber after loading.
Choose the Right Containers
Use containers designed for autoclaving. For liquids, caps must be loosened or vented to allow steam to enter and prevent the container from shattering under pressure. For instrument packs or biohazard bags, ensure they are not sealed airtight.
Orient Items Correctly
Place solid containers, trays, and glassware on their sides. This orientation prevents air from being trapped inside and allows water to drain out during the drying phase. Stacking items should be avoided unless they are in a perforated rack that allows for vertical steam flow.
Separate Different Material Types
Avoid mixing loads of liquids and dry goods. Liquids require slower heating and cooling cycles to prevent boiling over, whereas dry goods can be processed much faster. Processing them together compromises the efficacy for one or both.
Validating Your Loading Strategy
Proper loading creates the conditions for sterility. Indicators prove that those conditions were met throughout the chamber.
Chemical Indicators (The Daily Check)
Autoclave tape and other chemical indicators change color when exposed to a specific temperature. They provide an immediate visual cue that the load has been through a heat cycle.
However, as noted, autoclave tape alone is not an adequate monitor of efficacy. It confirms heat was present, but it does not confirm the duration of exposure or that steam penetrated the entire load.
Biological Indicators (The Gold Standard)
The most reliable method for validation is a biological indicator containing spores of a highly heat-resistant bacterium, such as Geobacillus stearothermophilus.
These spores are placed in the most challenging part of the load, such as the center of a dense pack. If the autoclave achieves the correct temperature, pressure, and steam penetration for the required time, the spores are killed. If not, they will germinate and grow when incubated, indicating a sterilization failure.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Even with good intentions, simple mistakes can lead to a failed cycle.
False Confidence from Chemical Indicators
The most common pitfall is assuming a color change on autoclave tape means the load is sterile. This is a dangerous assumption. Only a negative result from a biological indicator can truly validate the sterilization process.
Inappropriate Cycle Selection
Using a "dry goods" cycle for a large volume of liquid is a classic error. The cycle will finish before the liquid has reached the sterilization temperature, resulting in non-sterile media. Always match the cycle type to the load's contents.
The Impact of Load Density
A validated cycle for a light load may not be effective for a very dense load. The denser the load, the longer it will take for steam to penetrate. You must validate your process using a biological indicator placed within the most challenging load you typically run.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your approach to loading and validation should match the criticality of the materials being sterilized.
- If your primary focus is decontaminating routine biohazardous waste: Prioritize preventing overpacking and ensuring bags are properly vented to allow steam entry. A chemical indicator on each bag is a good daily practice.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing critical media, surgical tools, or equipment: Employ meticulous loading techniques, separate liquids from dry goods, and implement a routine validation schedule using biological indicators placed in the most challenging locations of your typical loads.
A properly loaded autoclave, verified with the right indicators, transforms sterilization from an assumption into a reliable, repeatable process.
Summary Table:
| Loading Criteria | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Spacing | Do not overload; leave space for steam circulation | Prevents obstruction of steam flow between items |
| Containers | Use autoclave-safe containers; loosen caps for liquids | Allows steam entry and prevents breakage |
| Orientation | Place solid items on their sides; avoid stacking | Eliminates air pockets and aids drainage |
| Load Separation | Do not mix liquids and dry goods in the same cycle | Prevents cycle compromise and ensures proper sterilization for each material type |
| Validation | Use biological indicators (e.g., Geobacillus stearothermophilus spores) | Confirms sterility by testing steam penetration in the most challenging load areas |
Ensure your lab's sterilization process is fail-safe with KINTEK's expert solutions.
Proper autoclave loading is critical, but having the right equipment and support makes all the difference. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab autoclaves and consumables designed for reliable, repeatable sterilization. Whether you're processing biohazardous waste, surgical instruments, or sensitive media, our products and expertise help you achieve and validate sterility with confidence.
Contact us today to discuss your autoclave needs and let us help you build a safer, more efficient laboratory. Reach out now via our contact form!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
People Also Ask
- Why is a Teflon-lined autoclave necessary for the hydrothermal treatment of porous TiO2 nanomaterials? Expert Insights
- What is an autoclave sterilizer? Achieve Absolute Sterility with Steam and Pressure
- How long does it take to autoclave instruments? Get the Full Breakdown for Effective Sterilization
- What is the principle of autoclave quizlet? Master the Science of Steam Sterilization
- Why is autoclave temperature 121°C? The Science Behind Sterilization's Critical Point
- What is the difference between an autoclave and a sterilizer? Understanding Sterilization Methods
- What is the normal temperature of an autoclave? Achieve Sterile Confidence with Precise Control
- What is a biological indicator (BI) and its purpose in autoclave monitoring? Ensure Sterilization Success



















