At its core, a lab reactor is a specialized, closed vessel designed to give chemists and engineers precise control over a chemical or physical process. Unlike simple glassware, it integrates functions like stirring, heating, and cooling into a single system, allowing for the safe and repeatable execution of reactions under specific, managed conditions.
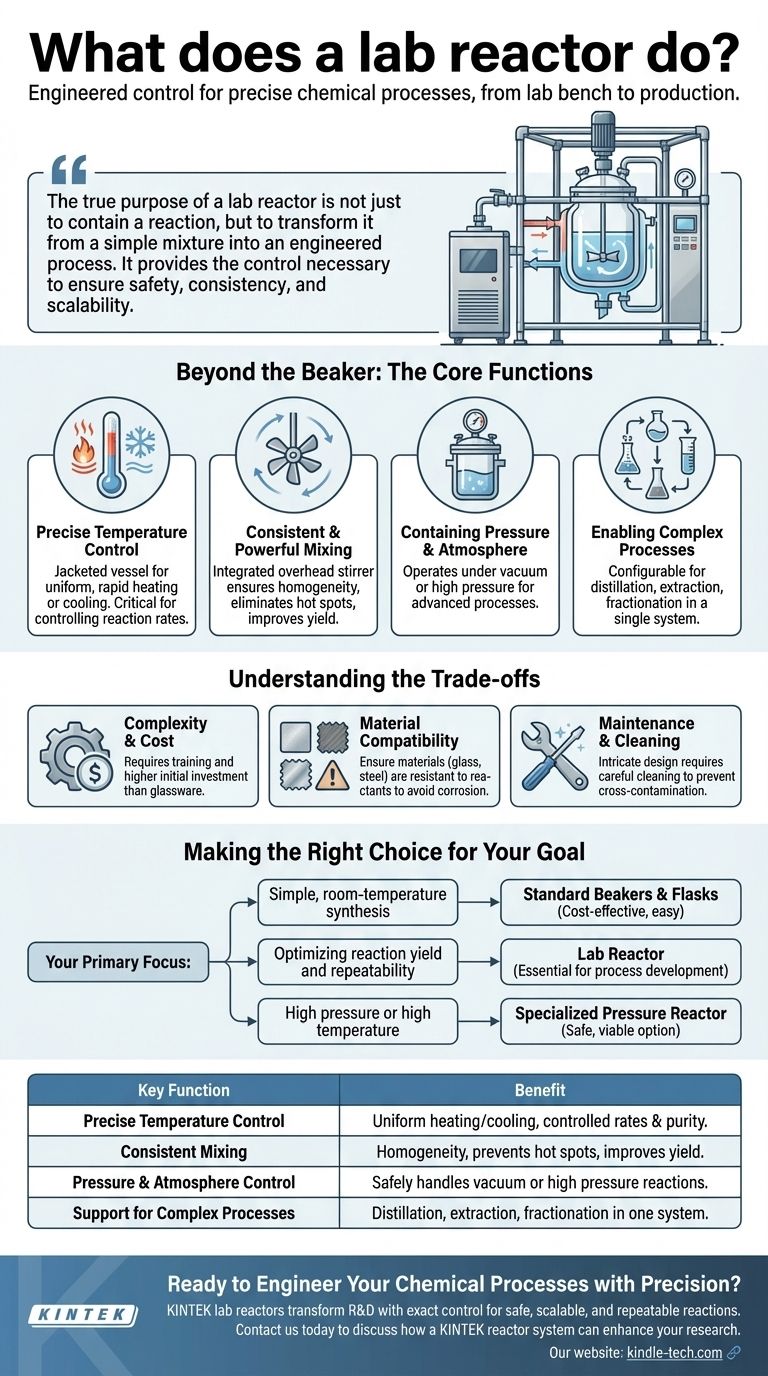
The true purpose of a lab reactor is not just to contain a reaction, but to transform it from a simple mixture into an engineered process. It provides the control necessary to ensure safety, consistency, and scalability from the lab bench to production.

Beyond the Beaker: The Core Functions of a Reactor
While a simple beaker can hold chemicals, a reactor is an active system designed to precisely manage the environment in which a reaction takes place. This control is what enables complex and sensitive chemistry.
Precise Temperature Control
A reactor is typically jacketed, meaning it has an outer shell through which a thermal fluid can be circulated. This allows for uniform, rapid, and highly accurate heating or cooling of the vessel's contents, which is critical for controlling reaction rates and preventing unwanted side reactions.
Consistent and Powerful Mixing
The integrated stirring mechanism, often an overhead stirrer with a precisely shaped impeller, ensures the entire reaction mass is homogenous. This eliminates hot spots, improves heat transfer, and guarantees that reactants are consistently interacting, leading to more predictable and higher-yielding results.
Containing Pressure and Atmosphere
Many chemical reactions need to occur under conditions other than normal atmospheric pressure. A reactor's sealed design allows it to operate under a vacuum for processes like evaporation or under high pressure to increase reaction rates or keep volatile substances in a liquid state.
Enabling Complex Processes
The structure of a reactor and its supporting equipment can be configured for advanced operations beyond a simple reaction. This includes functions like distillation to remove byproducts, extraction to isolate a desired compound, or fractionation to separate a mixture into its components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a lab reactor is a specialized piece of equipment. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Complexity and Cost
A complete reactor system, including the vessel, stirrer, and temperature control unit, is significantly more complex and expensive than standard laboratory glassware. It requires training to operate safely and correctly.
Material Compatibility
Reactors are made from materials like borosilicate glass or stainless steel. You must ensure that all components of the reactor, including seals and gaskets, are chemically resistant to the specific reactants, solvents, and products being used to avoid corrosion or contamination.
Maintenance and Cleaning
The intricate design of a reactor, with its various ports, valves, and stirring assembly, can make it more challenging to clean thoroughly between experiments compared to simple glassware. This is a critical consideration for preventing cross-contamination.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right equipment depends entirely on the specific requirements of your chemical process.
- If your primary focus is a simple, room-temperature synthesis: Standard beakers and flasks are often sufficient, cost-effective, and easy to use.
- If your primary focus is optimizing reaction yield and repeatability: A lab reactor is essential for the precise control of temperature and mixing needed for process development.
- If your primary focus is working under high pressure or high temperature: A specialized pressure reactor is the only safe and viable option.
Ultimately, adopting a lab reactor is about moving from simply observing a chemical reaction to actively engineering its outcome.
Summary Table:
| Key Function | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Precise Temperature Control | Enables uniform heating/cooling for controlled reaction rates and purity. |
| Consistent Mixing | Ensures homogeneity, prevents hot spots, and improves yield. |
| Pressure & Atmosphere Control | Safely handles reactions under vacuum or high pressure. |
| Support for Complex Processes | Allows for distillation, extraction, and fractionation within a single system. |
Ready to Engineer Your Chemical Processes with Precision?
A lab reactor from KINTEK transforms your R&D by providing the exact control needed for safe, scalable, and repeatable reactions. Whether you're developing new compounds or optimizing synthesis, our specialized lab equipment and consumables are designed to meet your laboratory's unique challenges.
Contact us today to discuss how a KINTEK reactor system can enhance your research and process development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable Laboratory High Temperature High Pressure Reactors for Diverse Scientific Applications
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
People Also Ask
- Why are high-precision pressure sensors and temperature control systems critical for hydrothermal reaction equilibrium?
- Why are high-strength alloy tube reactors critical for HHIP? Ensuring Safety and Purity in High-Pressure Environments
- Why is a high-pressure hydrothermal synthesis autoclave necessary for MnO2 nanowires? Precision Catalyst Growth
- What are the technical characteristics of PTFE (Teflon) lined hydrothermal reactors? Comparing α-ZrP Synthesis Methods
- What role does a high-pressure reactor play in the hydrodeoxygenation (HDO) of bio-oil? Drive Deep Fuel Upgrading



















