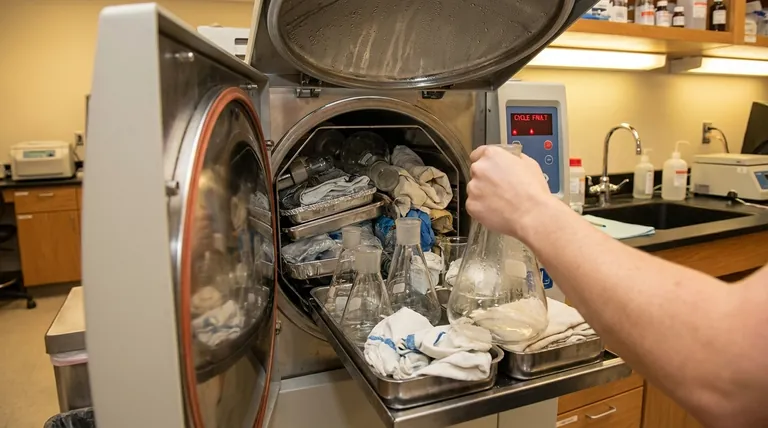
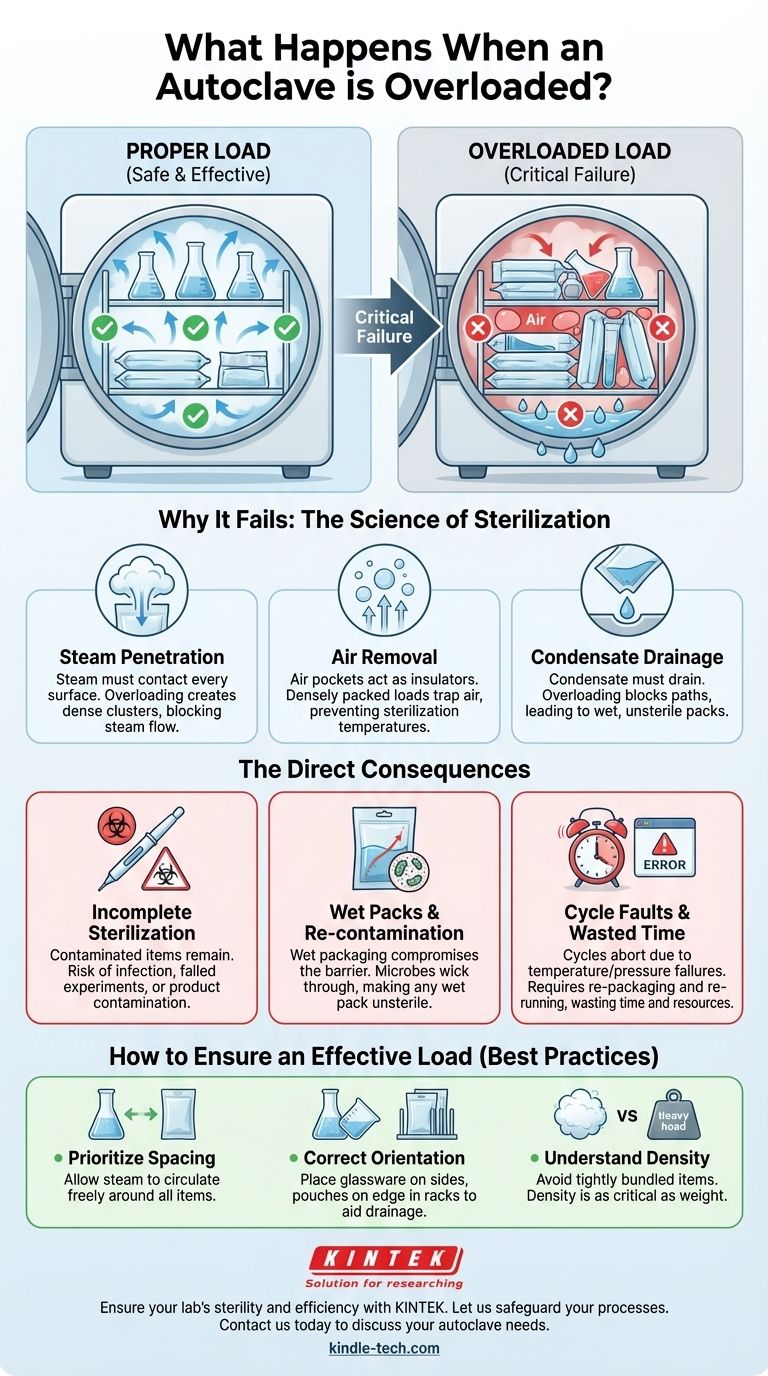
Overloading an autoclave is a critical failure that fundamentally compromises the sterilization process. When a chamber is packed too tightly, the pressurized steam cannot penetrate the load to reach every surface, resulting in items that are not sterile and often emerge excessively wet, which poses a re-contamination risk.
Overloading an autoclave is not an efficiency gain; it is a guarantee of sterilization failure. The core issue is that densely packed items physically obstruct the pressurized steam—the actual sterilizing agent—from reaching every surface, rendering the entire cycle ineffective.

The Science of Sterilization: Why Space Is Critical
To understand the consequences of overloading, you must first understand how an autoclave works. It does not simply bake items with dry heat; it uses steam under pressure to kill microorganisms.
Steam Must Penetrate Everything
The sterilizing agent is saturated steam, which carries a massive amount of thermal energy. For an item to be sterilized, this steam must make direct contact with every single one of its surfaces.
Overloading creates dense clusters where steam cannot flow, leaving the items in the center of the pack or bundle completely untouched by the sterilizing agent.
Air Must Be Fully Removed
At the start of a cycle, the chamber is full of air. This air must be removed and replaced with steam. Air pockets act as an insulating barrier, preventing steam from reaching the required temperature for sterilization.
A densely packed load traps significant amounts of air, creating "cold spots" where microorganisms will survive the cycle.
Condensate Must Be Able to Drain
As steam transfers its heat to the items in the load, it cools and turns back into water (condensate). This condensate must be able to drain away from the packs and out of the chamber.
Overloading blocks drainage paths, leading to super-saturated, "wet packs" at the end of the cycle.
The Direct Consequences of an Overloaded Chamber
When the core principles of sterilization are violated, the results are predictable and severe. These failures compromise safety, waste resources, and can even damage the equipment.
Incomplete Sterilization
This is the most dangerous outcome. Instruments and materials that are presumed sterile are, in fact, still contaminated. Using these items can lead to infection, failed experiments, or product contamination.
"Wet Packs" and Re-contamination
Packaging for sterile items is designed to be permeable to steam but impermeable to microbes when dry. If a pack emerges from the autoclave wet, its barrier is compromised.
Microorganisms from the air or handling can travel through the damp material—a process called "wicking"—and contaminate the contents. For this reason, any wet pack is considered unsterile.
Cycle Faults and Wasted Time
Modern autoclaves have sensors that monitor temperature and pressure. An overloaded chamber may prevent the autoclave from reaching or holding its target temperature.
This will often trigger an alarm or a cycle fault, forcing you to abort the process. The entire load must then be re-packaged and re-run, completely negating any time you thought you were saving.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
The pressure for efficiency often leads to poor loading practices. Understanding these pitfalls is key to avoiding them.
The False Economy of "One More Item"
The temptation to squeeze in one last item to avoid a second run is the primary cause of overloading. This is a false economy. A failed cycle wastes far more time, energy, and materials than simply running a second, properly-sized load.
Misunderstanding Density vs. Weight
Autoclave capacity is not just about the total weight of the items. It is primarily about arrangement and density. A light load of tightly bundled linens can fail more easily than a heavier, well-spaced load of glassware because it traps more air.
Incorrectly Orienting Items
The way items are placed is as important as the space between them.
- Glassware and containers should be placed on their sides to prevent air from being trapped and to allow condensate to drain out.
- Pouches should be arranged in racks, standing on their edge like files in a cabinet, never stacked flat on top of each other.
- Hard goods should be placed on lower shelves, with porous items (like fabrics or wrapped packs) on top shelves.
How to Ensure an Effective Load
Proper loading is a non-negotiable step for safe and effective sterilization. Your approach should depend on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is guaranteed sterility: Prioritize space between items above all else, ensuring steam can contact every surface from all directions.
- If your primary focus is efficiency and throughput: Commit to running multiple, smaller loads instead of one overloaded one to eliminate the risk of failed cycles and costly rework.
- If your primary focus is safety and compliance: Treat wet packs as an immediate sign of a loading or machine problem and ensure all items are arranged to allow for complete air removal and condensate drainage.
Proper loading is not a suggestion; it is a fundamental requirement for the science of sterilization to work.
Summary Table:
| Consequence | Cause | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Incomplete Sterilization | Steam cannot penetrate dense loads, leaving air pockets and cold spots. | Contaminated items pose infection and experiment/product failure risks. |
| Wet Packs | Condensate cannot drain, saturating packaging. | Wet packaging allows microbial wicking, leading to re-contamination. |
| Cycle Faults & Wasted Time | Autoclave fails to reach target temperature/pressure. | Cycle aborts, requiring complete re-packaging and re-running of the load. |
Ensure your lab's sterility and efficiency with KINTEK.
Overloading an autoclave is a critical error that compromises safety and wastes valuable time and resources. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and expert guidance to help you avoid these pitfalls. Our autoclaves are designed for optimal performance, and our team can help you establish best practices for loading and operation.
Let KINTEK safeguard your processes. We provide the equipment and support your laboratory needs to maintain compliance and achieve flawless sterilization every time.
Contact us today to discuss your autoclave needs and ensure your lab operates at peak safety and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- How often should a dental autoclave be cleaned? A Daily, Weekly, and Monthly Guide
- Are there any specific types of contamination that an autoclave cannot remove? Understanding the Limits of Steam
- What is the size of a laboratory autoclave? A Guide to Choosing the Right Capacity
- What are the common categories of autoclave loads for waste decontamination? Optimize MBL Safety and Sterilization
- Why is the standard autoclave temperature set to 121? The Science of Effective Sterilization
- What should be autoclaved in a lab? A Guide to Safe and Effective Sterilization
- What is the pressure of autoclave at 121 C? The Key to Effective Steam Sterilization
- What role does a high-pressure autoclave play in Pennisetum alopecuroides pretreatment? Optimize Biomass Breakdown



















