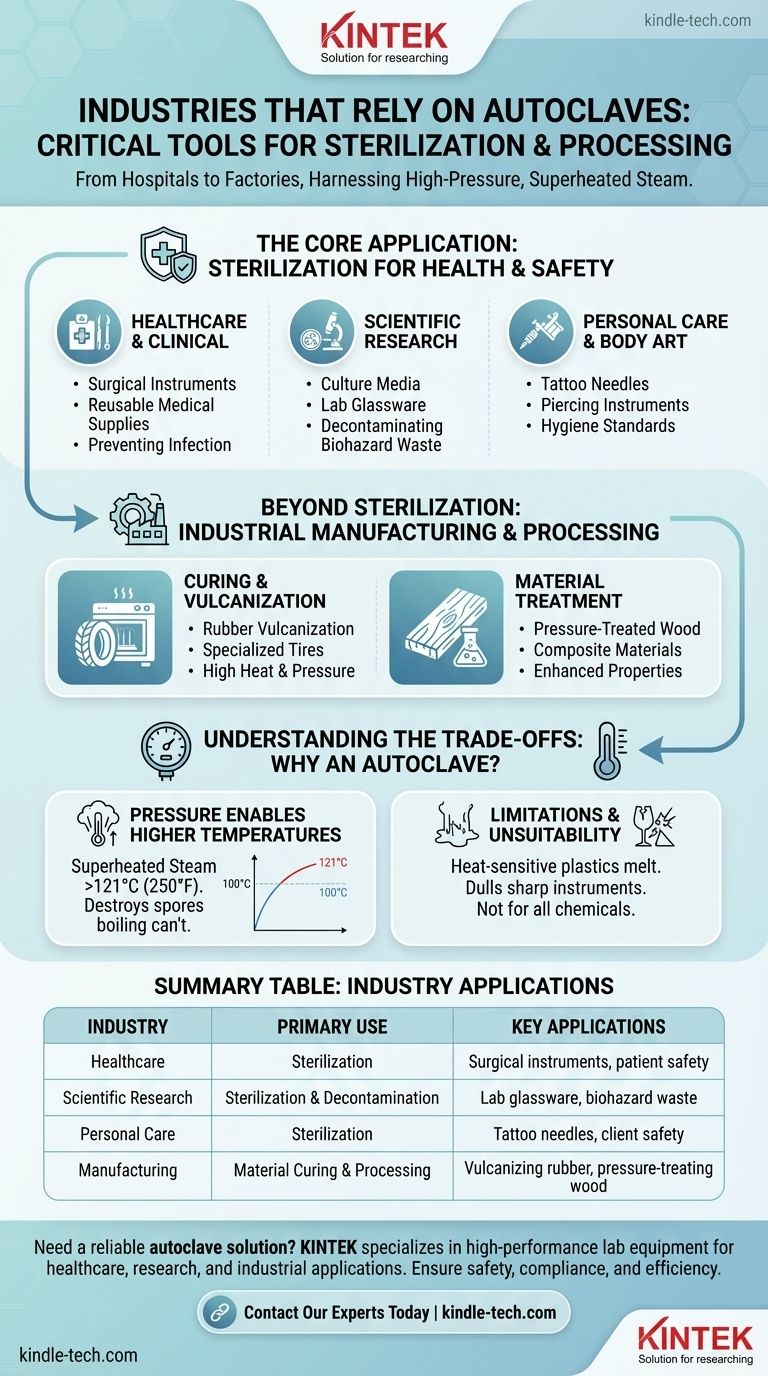
From hospitals to tire factories, autoclaves are critical tools used across a diverse set of industries. Their primary applications are in healthcare, scientific research, manufacturing, and even personal care services for their unmatched ability to sterilize equipment or process materials using high-pressure, superheated steam.
The autoclave's value comes from its ability to use pressurized steam to achieve temperatures far above the boiling point of water. This makes it indispensable for any industry where either complete microbial sterility is a non-negotiable safety requirement or where materials must be cured under intense heat and pressure.

The Core Application: Sterilization for Health and Safety
The most common use for an autoclave is to achieve total sterilization—the elimination of all forms of microbial life, including resilient bacteria, viruses, and spores.
Healthcare and Clinical Settings
This is the most recognized application. Hospitals, dental offices, and outpatient clinics rely on autoclaves to prevent cross-contamination and healthcare-associated infections.
They are used daily in a Central Sterile Services Department (CSSD) to process surgical instruments, glassware, and other reusable medical supplies. Smaller tabletop units are common in dental practices for sterilizing tools between patients.
Scientific and Research Laboratories
In a laboratory environment, preventing contamination is essential for the validity of experimental results and the safety of personnel.
Autoclaves sterilize culture media, laboratory instruments, pipette tips, and glassware. They are also used for the crucial final step of decontaminating biohazardous waste before it can be safely discarded.
Personal Care and Body Art
Any industry that involves breaking the skin barrier must adhere to strict hygiene standards to protect client health.
Tattoo parlors and beauty salons use small, tabletop autoclaves to sterilize needles, piercing instruments, and other reusable tools. This practice is often mandated by local health regulations to prevent the transmission of bloodborne pathogens.
Beyond Sterilization: Industrial Manufacturing and Processing
While sterilization is its most famous role, the industrial autoclave uses the same principles of heat and pressure to physically alter and cure materials.
Curing and Vulcanization
In heavy manufacturing, autoclaves function as industrial ovens that can apply immense pressure.
The rubber industry uses large autoclaves to vulcanize rubber for products like specialized tires. The process uses heat and pressure to create strong, durable cross-links within the material.
Material Treatment
Industrial autoclaves are also used to fundamentally change the properties of certain materials, making them stronger or more resistant.
A prime example is the production of pressure-treated wood. An autoclave forces chemical preservatives deep into the wood's structure, protecting it from rot and insects far more effectively than surface treatments.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why An Autoclave?
The unique function of an autoclave distinguishes it from simpler methods like boiling or using a dry-heat oven. The key is combining temperature with pressure.
Pressure Enables Higher Temperatures
By increasing the pressure inside its chamber, an autoclave allows water to exist as steam at temperatures well above its normal boiling point of 100°C (212°F).
This superheated steam can reach 121°C or higher, which is hot enough to destroy even the most heat-resistant bacterial spores—something boiling water cannot reliably do.
Limitations and Unsuitability
Autoclaves are not a universal solution. The high heat and moisture can damage or destroy certain materials.
Heat-sensitive plastics can melt, sharp instruments may become dulled over repeated cycles, and certain chemicals or liquids cannot be safely autoclaved. Every industry must validate that its specific materials are compatible with the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The type of autoclave an industry uses is directly tied to the problem it needs to solve, whether that is eliminating microbes or creating new materials.
- If your primary focus is preventing contamination: You need a medical or laboratory-grade autoclave designed for verifiable sterilization cycles that guarantee microbial death.
- If your primary focus is material production: You need a large-scale industrial autoclave engineered for specific pressure and temperature profiles to cure or treat materials like composites or rubber.
Ultimately, the autoclave's power lies in its precise control over a high-energy steam environment, making it a tailored solution for either absolute sterility or fundamental material transformation.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Use | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Sterilization | Surgical instruments, medical tools, patient safety |
| Scientific Research | Sterilization & Decontamination | Lab glassware, culture media, biohazard waste |
| Personal Care | Sterilization | Tattoo needles, piercing tools, client safety |
| Manufacturing | Material Curing & Processing | Vulcanizing rubber, pressure-treating wood, composites |
Need a reliable autoclave solution for your industry? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including autoclaves tailored for healthcare, research, and industrial applications. Whether you require precise sterilization for medical instruments or robust material processing for manufacturing, our solutions ensure safety, compliance, and efficiency. Contact our experts today to find the perfect autoclave for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What role does an autoclave play in the acid treatment for microalgae disruption? Unlock High-Yield Cell Pretreatment
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- What is the function of laboratory autoclaves in SCWR research? Predict Material Compatibility and Corrosion Kinetics
- What extreme conditions does a laboratory autoclave simulate? Testing Wear Resistance of Nuclear Fuel Cladding
- What experimental conditions do stainless steel autoclaves provide for PCT-A leaching? Optimize Phosphate Glass Testing



















