At its core, a high pressure reactor is a specialized, fortified vessel designed to conduct chemical reactions under pressures significantly higher than the normal atmosphere. Often called an autoclave, this equipment uses pressure and high temperatures to drive chemical transformations that would otherwise be slow, inefficient, or impossible. They are constructed from robust materials to safely contain these extreme conditions, enabling a wide range of industrial and research applications.
A high pressure reactor is more than just a strong container; it is a fundamental tool that treats pressure as a controllable variable, alongside temperature and concentration, to manipulate chemical reactions, increase yields, and synthesize novel materials.

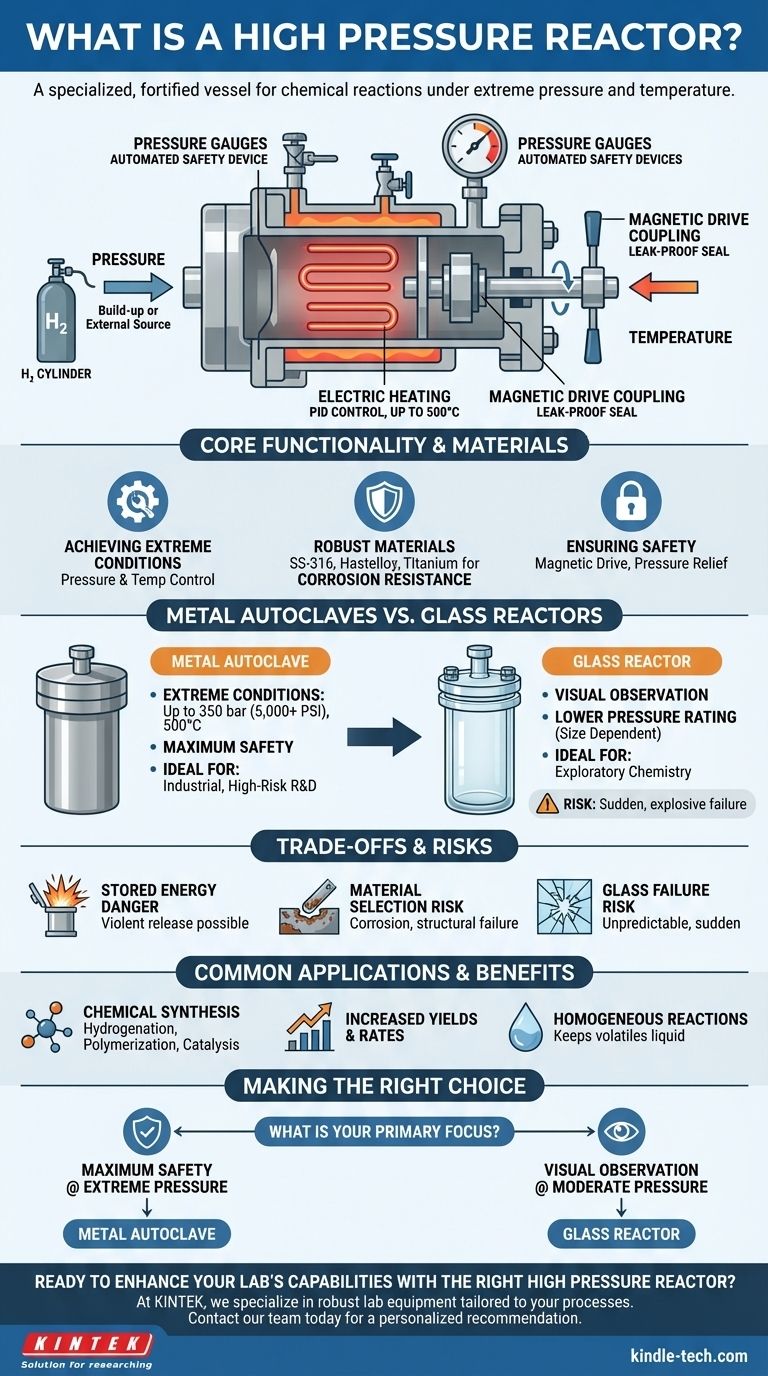
How a High Pressure Reactor Functions
A high pressure reactor is a system of components working together to create and safely manage a high-energy environment. Understanding these components is key to appreciating its capabilities.
Achieving High Pressure and Temperature
The pressure inside the vessel can be generated in two primary ways. It can build up naturally as a byproduct of the chemical reaction itself (e.g., gas evolution), or it can be introduced from an external source, such as a cylinder of compressed hydrogen for a hydrogenation reaction.
Precise temperature is achieved via PID-controlled electric heating systems, which allow for exacting regulation up to 500 °C, ensuring the reaction has the necessary energy to proceed.
The Critical Role of Construction Materials
The reactor vessel must withstand not only immense pressure but also potentially corrosive chemicals at high temperatures. Because of this, they are not made from ordinary materials.
They are typically constructed from high-strength, corrosion-resistant metal alloys. Common choices include Stainless Steel (SS-316), Hastelloy, Monel, Inconel, and Titanium, selected based on the specific chemistry of the intended reaction.
Ensuring Safety and Control
Safety is the paramount design consideration. A magnetic drive coupling is a key feature, providing a stir mechanism with a leak-proof seal that eliminates the risk of hazardous materials escaping.
The system is managed by an array of valves, pressure gauges, and automated safety devices. These components work in concert to regulate, monitor, and, if necessary, safely vent the pressure inside the reactor, preventing catastrophic failure.
Metal Autoclaves vs. Glass Pressure Reactors
The term "pressure reactor" can apply to different designs with vastly different capabilities. The most significant distinction is between high-pressure metal autoclaves and lower-pressure glass reactors.
The Case for Metal Autoclaves
When a process requires extreme conditions, a metal autoclave is the standard. These systems can reach pressures up to 350 bar (over 5,000 PSI) and temperatures of 500 °C.
Their opaque, robust metal construction makes them the definitive choice for high-risk, high-pressure industrial processes and research where safety and containment are non-negotiable.
The Niche for Glass Reactors
Glass pressure reactors are used when direct visual observation of the reaction is essential. Their transparency allows chemists and engineers to monitor changes in color, phase, or crystallization in real-time.
However, their pressure rating is significantly lower than that of metal reactors and is inversely related to the vessel's diameter—a larger vessel can withstand less pressure. They are suited for exploratory chemistry at more moderate pressures.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Choosing and operating a pressure reactor involves acknowledging and mitigating significant risks. The decision is a trade-off between experimental needs and safety imperatives.
The Inherent Danger of Stored Energy
Operating any vessel under high pressure involves storing a tremendous amount of potential energy. A failure in the vessel or its seals can result in a violent, dangerous release of that energy. This is why robust engineering and safety mechanisms are critical.
The Risk of Improper Material Selection
Choosing the wrong construction material can lead to corrosion, weakening the reactor's structural integrity over time. This can cause a failure at pressures well below the equipment's original design limits. Material compatibility must be verified for every new chemical process.
Glass Reactors and Catastrophic Failure
While useful for observation, glass reactors carry a distinct risk. Unlike metal, glass can fail suddenly and explosively if its pressure limit is exceeded. The references note that this can be hard to predict, and these systems may lack the advanced relief mechanisms of high-pressure metal autoclaves.
Common Applications and Reactions
High pressure reactors are workhorses in the chemical industry, used for a vast array of processes that are fundamental to modern manufacturing and science.
Driving Chemical Synthesis
These reactors are essential for many classes of organic and inorganic reactions, including:
- Hydrogenation
- Polymerization
- Oxidation & Alkylation
- Esterification & Amination
- Catalytic reactions
Why Pressure Is Necessary
Applying high pressure can dramatically influence a reaction. It can increase reaction rates, shift the chemical equilibrium to favor the desired product, or keep volatile reactants and solvents in the liquid phase at high temperatures, ensuring the reaction mixture remains homogenous.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your selection must be guided by the specific demands of your chemical reaction and your tolerance for risk.
- If your primary focus is maximum safety at extreme pressures (up to 350 bar): A metal autoclave built from a chemically compatible alloy is the only appropriate choice.
- If your primary focus is visual observation of a moderate-pressure reaction: A glass pressure reactor is suitable, provided you operate well within its specified and tested pressure limits.
- If your primary focus is versatile chemical synthesis (e.g., catalysis, polymerization): Evaluate the pressure and temperature requirements of your specific reaction to determine whether a robust metal reactor or a lower-pressure glass unit is sufficient.
Ultimately, understanding the principles of a high pressure reactor allows you to transform it from a simple container into a powerful instrument for controlling chemical reality.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Metal Autoclave | Glass Reactor |
|---|---|---|
| Max Pressure | Up to 350 bar (5,000+ PSI) | Lower, vessel size dependent |
| Max Temperature | Up to 500 °C | Lower than metal |
| Primary Advantage | Maximum safety for extreme conditions | Direct visual observation of reactions |
| Key Risk | Corrosion from material incompatibility | Sudden, explosive failure |
| Ideal For | Industrial processes, high-risk R&D | Exploratory chemistry, moderate pressure |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with the right high pressure reactor?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust lab equipment, including high-pressure reactors and autoclaves, tailored to your specific chemical processes. Whether you need the extreme safety of a metal autoclave for hydrogenation or the visual clarity of a glass reactor for synthesis, our experts will help you select the perfect solution to increase yields and ensure operational safety.
Contact our team today to discuss your application and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable Laboratory High Temperature High Pressure Reactors for Diverse Scientific Applications
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- What specific reaction environment does a high-pressure reactor provide for HTL? Master Biomass to Biocrude Conversion
- What is the function of a laboratory reactor in polycondensation? Ensure Precision in Cardanol-Modified Resin Synthesis
- Why are high-temperature and high-pressure reactors required to have specific material properties? Ensure Process Safety
- What are the advantages of using a 316L stainless steel reactor in ELA hydrolysis? Optimize Cost & Performance
- What is the function of a laboratory reactor in fire-retardant coating synthesis? Ensuring Chemical Uniformity
- Why must CoCeBa catalysts use a high-pressure tube fluidized bed reactor? Unlock Superior Activation Performance
- What is a stainless steel reactor? A Guide to Material Selection and Process Control
- What role does a high-pressure laboratory reactor play in the hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites? Essential Guide



















