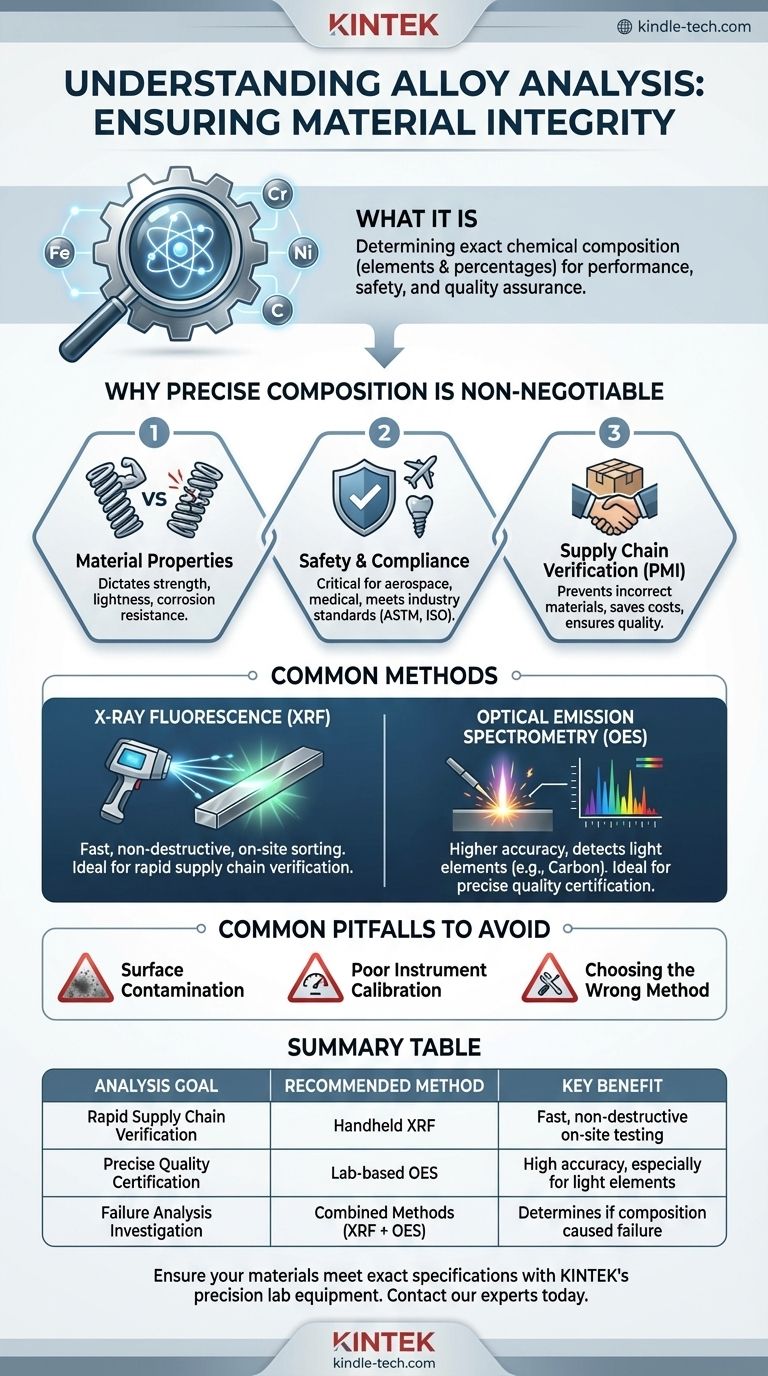
At its core, alloy analysis is a procedure used to determine the exact chemical composition of a metallic material. It identifies not only which elements are present—such as iron, chromium, or nickel—but also their precise percentages. This is done because an alloy is a mixture of elements, and its properties like strength, lightness, and corrosion resistance are dictated entirely by this specific chemical recipe.
The true purpose of alloy analysis extends beyond simple identification. It is a critical quality assurance process that verifies a material will perform as expected, meet safety regulations, and conform to design specifications.
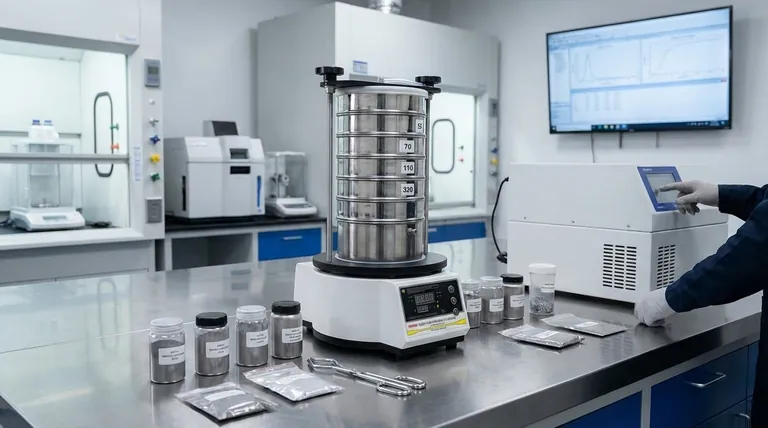

Why Precise Composition is Non-Negotiable
Understanding the exact elemental makeup of an alloy is fundamental in engineering, manufacturing, and safety. A tiny deviation in composition can lead to significant and often undesirable changes in the material's behavior.
Defining Material Properties
The performance characteristics of an alloy are a direct result of its elemental blend. For example, a small change in the carbon content of steel can be the difference between a soft, formable metal and a hard, brittle one.
Likewise, the percentage of chromium in stainless steel directly determines its resistance to rust and corrosion. Analysis confirms these critical percentages are correct.
Ensuring Safety and Compliance
In critical industries like aerospace, medical implants, and power generation, using the wrong alloy is not an option. A component made from a slightly off-specification material could lead to catastrophic failure.
Alloy analysis provides the certified proof that materials meet stringent industry standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO, SAE) and regulatory requirements.
Verifying the Supply Chain
This process is essential for what is known as Positive Material Identification (PMI). Companies use PMI to verify that the materials they receive from suppliers are exactly what they ordered.
This simple check prevents incorrect materials from entering the manufacturing process, saving enormous costs and preventing potential product recalls or failures down the line.
Common Methods for Alloy Analysis
While the goal is always the same—to determine composition—different techniques are used depending on the need for speed, precision, and portability.
X-ray Fluorescence (XRF)
XRF is a common non-destructive technique. A handheld analyzer shoots X-rays at the material, causing the elements within it to fluoresce, or emit secondary X-rays.
Each element emits a unique energy signature, which the device reads to identify the composition. This method is extremely fast and ideal for on-site sorting and verification.
Optical Emission Spectrometry (OES)
OES provides a higher degree of accuracy, especially for light elements like carbon, which XRF can struggle to detect.
This method uses an electrical spark to vaporize a tiny amount of the material, creating a plasma. The instrument then analyzes the specific spectrum of light emitted from this plasma to determine the elemental composition with high precision.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Accurate analysis requires more than just pointing a device at a metal. Missteps in preparation or interpretation can lead to incorrect and costly conclusions.
Surface Contamination
The analysis only measures what the instrument sees. Any paint, coating, oil, or even dirt on the surface will interfere with the reading and produce inaccurate results.
Proper sample preparation, such as grinding or cleaning the surface, is a mandatory first step for reliable analysis.
Poor Instrument Calibration
An alloy analyzer is only as good as its last calibration. These instruments must be regularly checked against Certified Reference Materials (CRMs)—samples with a known and verified composition.
Without proper calibration, results can drift over time, leading to a false pass or fail.
Choosing the Wrong Method
Relying on a method that isn't suited for the task is a frequent error. Using a handheld XRF to certify the carbon content in steel, for example, would be a mistake because of the technology's limitations. Understanding the right tool for the specific job is critical.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The appropriate analysis strategy depends entirely on your operational need.
- If your primary focus is rapid supply chain verification: Utilize a handheld XRF analyzer for on-the-spot Positive Material Identification of incoming or outgoing goods.
- If your primary focus is precise quality certification: Rely on lab-based OES to generate the high-accuracy reports needed to certify materials against strict client or regulatory standards.
- If your primary focus is failure analysis: Employ a combination of methods to investigate if a material's incorrect composition was the root cause of a component failure.
Ultimately, effective alloy analysis provides the certainty you need to trust the integrity of your materials.
Summary Table:
| Analysis Goal | Recommended Method | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Rapid Supply Chain Verification | Handheld XRF Analyzer | Fast, non-destructive on-site testing |
| Precise Quality Certification | Lab-based OES | High accuracy, especially for light elements like carbon |
| Failure Analysis Investigation | Combined Methods (XRF + OES) | Determines if incorrect composition caused failure |
Ensure your materials meet exact specifications with KINTEK's precision lab equipment.
Whether you're in aerospace, medical implants, or manufacturing, our analyzers and consumables provide the accuracy you need for quality assurance and compliance. Don't risk material failure—contact our experts today to find the right alloy analysis solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Customizable XRD Sample Holders for Diverse Research Applications
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Why is powder classification using standard sieves essential for SHS reactions? Unlock Superior Nitriding Results
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research
- Why is a laboratory electromagnetic vibratory sieve shaker used? Optimize Walnut Shell Chemical Pretreatment
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance



















