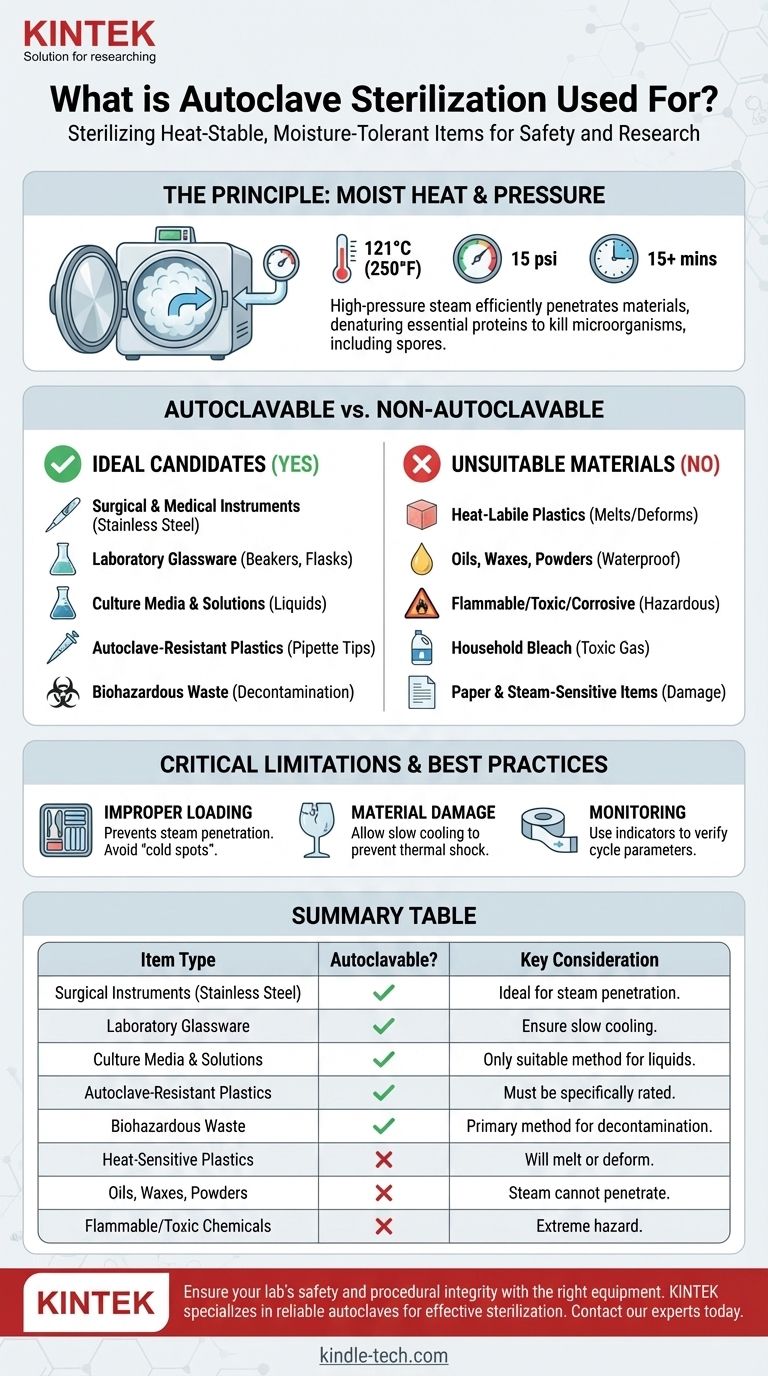
In simple terms, an autoclave is used for sterilizing items that are stable at high temperatures and can tolerate moisture. This includes common laboratory and medical equipment such as surgical instruments, glassware, culture media, solutions, water, autoclavable plastics like pipette tips, and biohazardous waste. The process relies on high-pressure steam to effectively kill microorganisms.
The critical factor for autoclaving isn't the item itself, but its material composition. An autoclave is the correct sterilization method for any object that is both heat-stable and permeable to steam, ensuring complete destruction of all microbial life.

The Principle of Steam Sterilization
An autoclave operates like a sophisticated pressure cooker. It uses high-pressure steam to achieve temperatures that are impossible for boiling water to reach at normal atmospheric pressure, ensuring a much more effective and rapid sterilization process.
Why Pressurized Steam is Effective
The power of an autoclave comes from its use of moist heat delivered by pressurized steam. This high-temperature moisture can efficiently penetrate materials and transfer heat, which denatures essential proteins in bacteria, viruses, and spores, rendering them inactive.
This method is particularly useful for sterilizing liquids and media-containing water, which cannot be effectively sterilized using dry heat methods like a hot air oven.
The Standard Sterilization Cycle
While cycles can be adjusted, the most common setting for sterilization is maintaining a temperature of 121°C (250°F) at a pressure of 15 pounds per square inch (psi) for at least 15 minutes. This combination is proven to be lethal to even the most heat-resistant bacterial spores.
Autoclavable vs. Non-Autoclavable Materials
Understanding what can and cannot go into an autoclave is essential for both safety and effectiveness. The decision is based entirely on the material's ability to withstand high temperatures and steam.
Ideal Candidates for Autoclaving
These items are routinely and safely sterilized using an autoclave:
- Surgical and Medical Instruments: Stainless steel tools are perfectly suited for steam sterilization.
- Laboratory Glassware: Beakers, flasks, and test tubes are easily sterilized.
- Culture Media and Solutions: The liquid nature of these items makes them ideal for moist heat sterilization.
- Autoclave-Resistant Plastics: Many modern lab plastics, including some containers, tubes, and pipette tips, are designed to withstand autoclave temperatures.
- Biohazardous Waste: An autoclave is a primary method for decontaminating pathogenic hospital and lab waste before disposal.
Materials Unsuitable for Autoclaving
Placing the wrong item in an autoclave can result in a melted mess, a failed sterilization cycle, or a hazardous situation.
- Heat-Labile Products: Any plastic that is not specifically rated for autoclaving will likely melt or deform.
- Waterproof or Water-Resistant Materials: Items like oils, waxes (paraffin), and powders cannot be autoclaved because the steam cannot penetrate them to ensure sterilization.
- Flammable, Corrosive, or Toxic Materials: Introducing these items into a high-pressure, high-heat environment is extremely dangerous.
- Household Bleach: Heating bleach produces toxic chlorine gas and should never be done.
- Paper and Other Steam-Sensitive Items: High-moisture environments will damage or destroy these materials.
Understanding the Critical Limitations
Effective sterilization requires more than just knowing what to put inside. Following the correct protocol is crucial to ensure the process actually works and doesn't create new hazards.
The Risk of Incomplete Penetration
The most common failure point is improper loading. If items are packed too tightly, the steam cannot circulate and penetrate the entire load. This creates "cold spots" where microorganisms can survive, rendering the entire cycle invalid.
The Danger of Material Damage
Even with an approved material, improper procedure can cause problems. For example, not allowing glassware to cool down slowly after a cycle can cause it to crack from thermal shock.
The Importance of Monitoring
Secure sterilization requires strict adherence to protocol. This includes using the correct time and temperature settings for the specific load, performing regular calibrations, and using sterilization indicators (like autoclave tape) to verify that conditions were met.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct sterilization method depends entirely on the material you are working with and your objective.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing reusable lab or medical equipment: The autoclave is the gold standard for robust items like glassware and stainless steel instruments.
- If your primary focus is preparing sterile liquids or culture media: The autoclave is the only appropriate choice, as its moist heat is essential for sterilizing aqueous solutions.
- If your primary focus is handling heat-sensitive plastics or electronics: You must use an alternative method, such as chemical sterilization (ethylene oxide) or radiation.
- If your primary focus is decontaminating biohazardous waste: The autoclave is the most effective and widely used method for rendering pathogenic waste safe for disposal.
Ultimately, using an autoclave correctly is a cornerstone of safety and procedural integrity in any clinical or research setting.
Summary Table:
| Item Type | Autoclavable? | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Surgical Instruments (Stainless Steel) | Yes | Ideal for steam penetration and heat resistance. |
| Laboratory Glassware | Yes | Ensure slow cooling to prevent thermal shock. |
| Culture Media & Solutions | Yes | The only suitable method for sterilizing liquids. |
| Autoclave-Resistant Plastics | Yes | Must be specifically rated for high temperatures. |
| Biohazardous Waste | Yes | Primary method for decontamination before disposal. |
| Heat-Sensitive Plastics | No | Will melt or deform; use alternative methods. |
| Oils, Waxes, Powders | No | Steam cannot penetrate; sterilization will fail. |
| Flammable/Toxic Chemicals | No | Extreme hazard; can cause dangerous reactions. |
Ensure your lab's safety and procedural integrity with the right equipment.
KINTEK specializes in providing reliable autoclaves and lab equipment designed for effective sterilization. Whether you are decontaminating biohazardous waste, preparing sterile culture media, or maintaining surgical instruments, our solutions deliver the precise temperature control and steam penetration you need for complete microbial destruction.
Don't compromise on safety—contact our experts today to find the perfect autoclave for your laboratory's specific requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory high-pressure autoclave sterilizer necessary? Ensure Accuracy in Antibacterial Research
- What is the function of laboratory autoclaves in SCWR research? Predict Material Compatibility and Corrosion Kinetics
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- What role does an autoclave play in the acid treatment for microalgae disruption? Unlock High-Yield Cell Pretreatment
- Are there any specific types of contamination that an autoclave cannot remove? Understanding the Limits of Steam



















