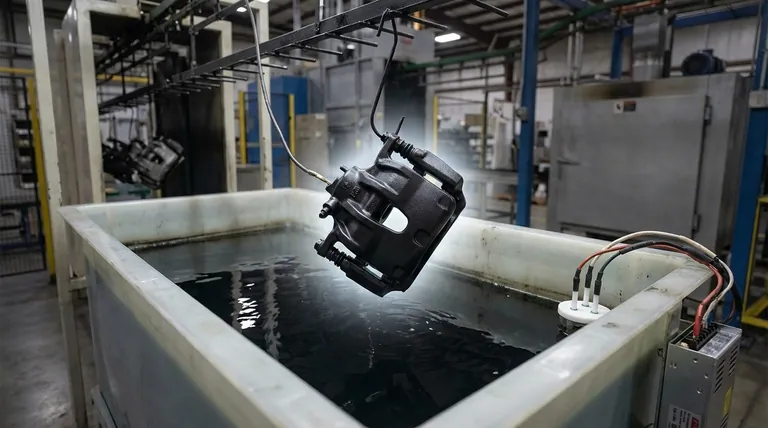
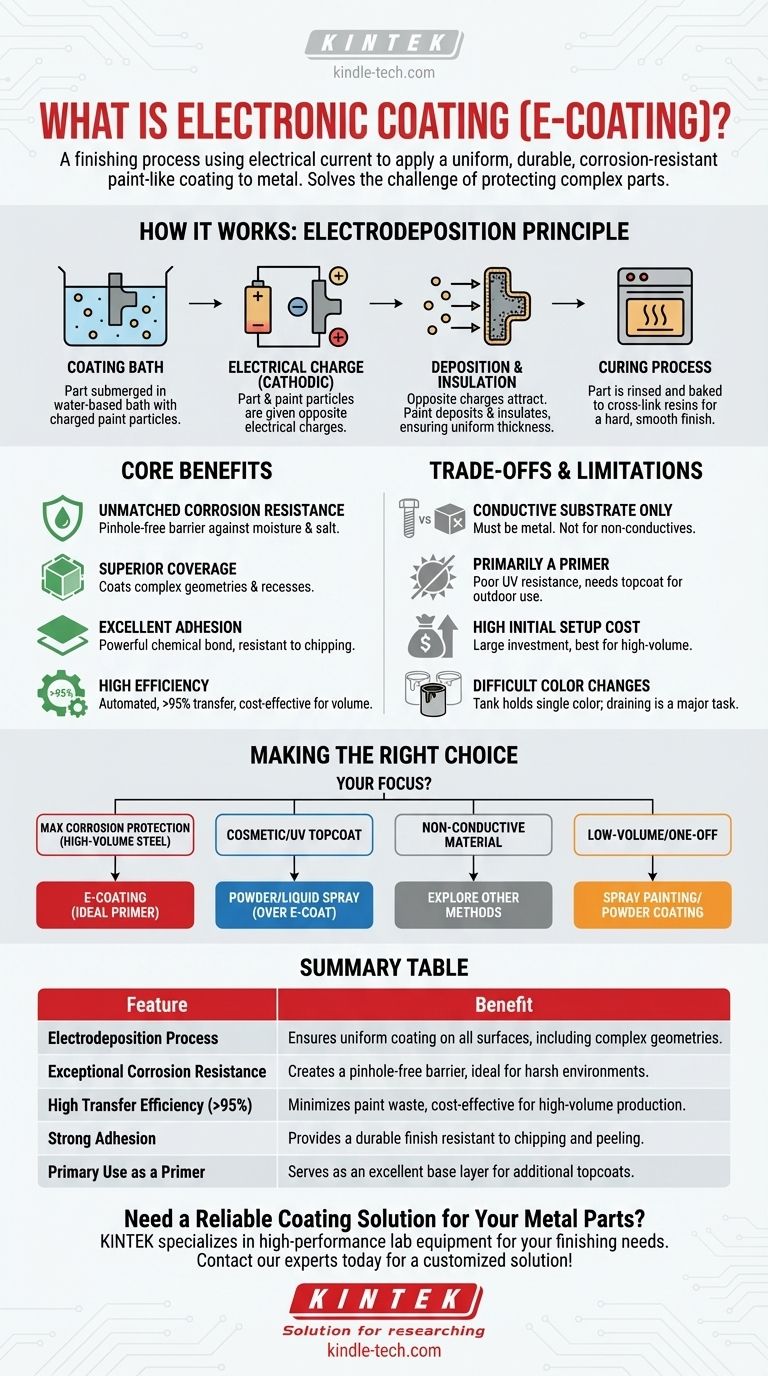
In simple terms, electronic coating, or E-coating, is a finishing process that uses an electrical current to apply a paint-like coating to a metal surface. Originally developed for the automotive industry, it is prized for its ability to provide a highly uniform, durable, and corrosion-resistant finish on any metal part that can conduct electricity, such as steel, aluminum, and zinc.
E-coating solves a fundamental manufacturing challenge: how to completely protect a metal part, including its complex edges and internal cavities. It achieves this by using electricity to attract paint particles to the metal surface, resulting in an exceptionally even and resilient protective layer.

How Electronic Coating Works: The Principle of Electrodeposition
The E-coating process is fundamentally different from traditional spraying. It's more akin to electroplating, but with paint particles suspended in a water-based solution.
The Coating Bath
The process begins with a large tank containing an E-coat bath. This bath consists of deionized water, paint solids (typically epoxy or acrylic), and small amounts of solvent. The paint particles are given an electrical charge.
The Electrical Charge
The metal part to be coated is submerged in the bath and connected to an electrode, giving it the opposite electrical charge. In modern systems, the part is typically the cathode (negative charge), and the paint particles are positive—a method called cathodic electrodeposition.
Deposition and Insulation
Because opposite charges attract, the paint particles migrate through the water and deposit themselves onto every conductive surface of the part. As the coating builds up, it insulates the surface, which automatically forces the current to find the remaining uncoated areas. This "self-limiting" effect is what guarantees a perfectly uniform thickness, even inside hollow sections and on sharp edges.
The Curing Process
After a set time, the part is removed from the bath. It is then rinsed to remove any loose paint particles and baked in an industrial oven. This curing process cross-links the polymer resins, transforming the deposited film into a hard, durable, and smooth finish.
Core Benefits of the E-Coating Process
Manufacturers choose E-coating for a specific set of high-performance advantages that other methods struggle to match.
Unmatched Corrosion Resistance
The primary benefit of E-coating is its exceptional ability to protect against corrosion. The continuous, pinhole-free film it creates provides a robust barrier against moisture and salt, which is why it's the standard for automotive bodies and chassis components.
Superior Coverage and Uniformity
Because the process is driven by electrical current, the coating is "pulled" into every recess and corner of the part. This eliminates the "line-of-sight" limitations of spray painting, ensuring complex geometries are fully protected.
Excellent Adhesion
E-coating creates a powerful chemical bond with the metal substrate. This results in outstanding adhesion, making the finish highly resistant to chipping, flaking, or peeling compared to many other coating types.
High Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
The process is highly automated and has a transfer efficiency of over 95%, meaning very little paint is wasted. For high-volume production runs, this makes E-coating an extremely economical finishing choice.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, E-coating is not a universal solution. Its specific nature comes with important limitations.
Requires a Conductive Substrate
The most fundamental requirement is that the part must be made of a conductive metal. E-coating cannot be used directly on plastics, wood, composites, or other non-conductive materials.
Primarily Used as a Primer
Most E-coat formulas, especially the common epoxy-based ones, have poor UV resistance. They will chalk and degrade with prolonged sun exposure. For this reason, E-coat is most often used as a world-class primer, which is then top-coated with a more UV-stable paint or powder coat.
High Initial Setup Cost
The infrastructure for E-coating—including the large immersion tanks, rectifiers, and curing ovens—represents a significant capital investment. This makes the process best suited for dedicated, high-volume manufacturing lines.
Difficulty in Changing Colors
An E-coat tank holds thousands of gallons of a single color, most commonly black. Draining, cleaning, and refilling a tank to change colors is a major undertaking. Consequently, facilities rarely offer more than one or two color options.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right coating depends entirely on your project's material, volume, and performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum corrosion protection for high-volume steel parts: E-coating is the undisputed industry standard and should be your first consideration, especially as a primer.
- If your primary focus is a cosmetic topcoat with many color options or UV resistance: Consider powder coating or liquid spray painting over an E-coat primer or as a standalone process.
- If your primary focus is coating a non-conductive material like plastic or wood: E-coating is not a viable option; you must explore other finishing methods.
- If your primary focus is a low-volume or one-off project: The high setup costs and complexity of E-coating make processes like spray painting or powder coating far more practical.
Ultimately, E-coating serves as the foundational protective layer for millions of products, delivering performance where it matters most.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Electrodeposition Process | Ensures uniform coating on all surfaces, including complex geometries and internal cavities. |
| Exceptional Corrosion Resistance | Creates a pinhole-free barrier, ideal for harsh environments. |
| High Transfer Efficiency (>95%) | Minimizes paint waste, making it cost-effective for high-volume production. |
| Strong Adhesion | Provides a durable finish resistant to chipping and peeling. |
| Primary Use as a Primer | Serves as an excellent base layer for additional topcoats (e.g., powder coating). |
Need a Reliable Coating Solution for Your Metal Parts?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables tailored to your finishing needs. Whether you're in automotive, aerospace, or industrial manufacturing, our expertise ensures you achieve durable, corrosion-resistant results.
Let us help you optimize your coating process—contact our experts today for a customized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Customizable CO2 Reduction Flow Cell for NRR ORR and CO2RR Research
- Evaporation Crucible for Organic Matter
- Iridium Dioxide IrO2 for Water Electrolysis
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between RDE and RRDE? Unlock Advanced Electrochemical Reaction Analysis
- What are the specifications of the Platinum-Titanium Functional Electrode? Maximize Electrochemical Performance
- What is the difference between ring disk electrode and rotating disk electrode? Unlock Deeper Electrochemical Insights
- What is the rotating ring disk electrode method? Unlock Real-Time Reaction Analysis
- How should a platinum wire/rod electrode be cleaned before use? A Guide to Reliable Electrochemical Data



















