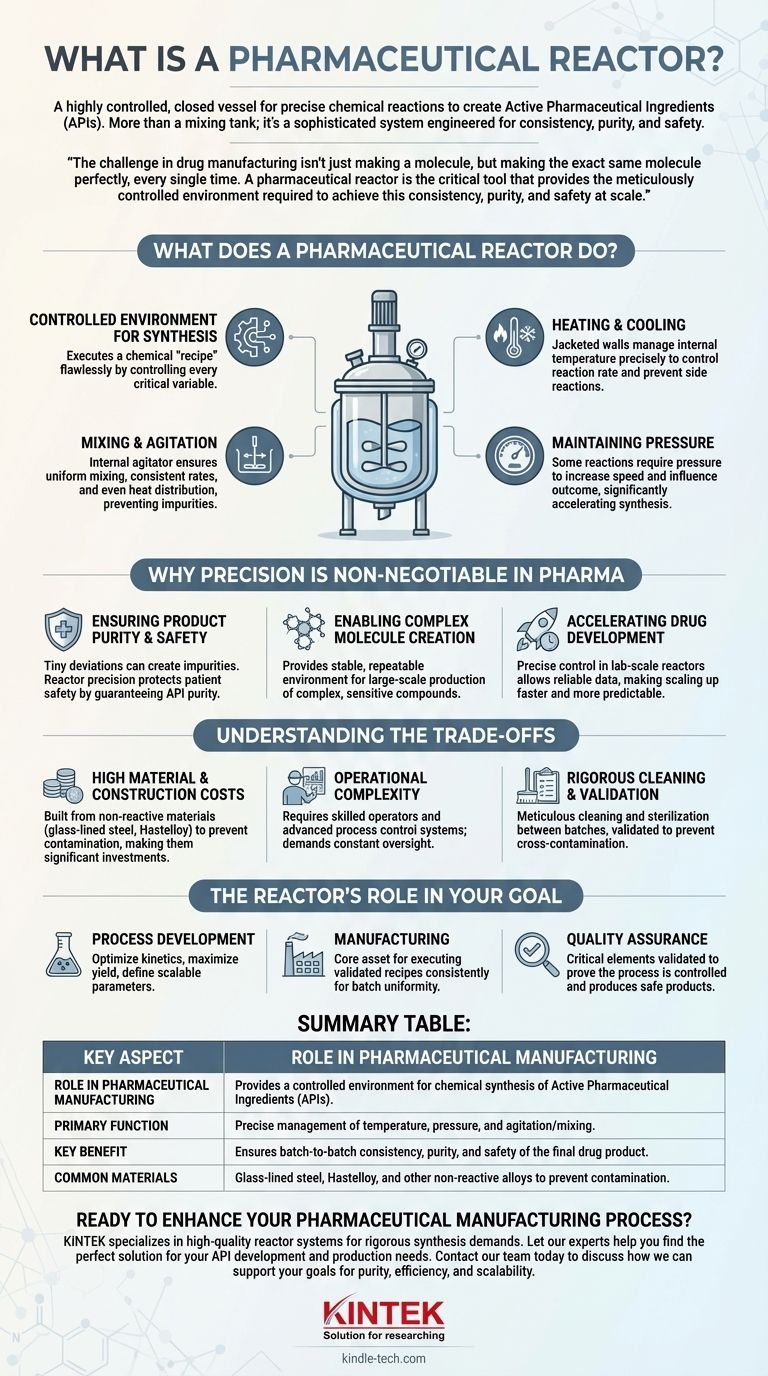
In essence, a pharmaceutical reactor is a highly controlled, closed vessel where the precise chemical reactions needed to create an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API)—the core component of a drug—take place. It is far more than a simple mixing tank; it is a sophisticated system engineered to manage temperature, pressure, and mixing with extreme accuracy, ensuring the final product is both safe and effective.
The challenge in drug manufacturing isn't just making a molecule, but making the exact same molecule perfectly, every single time. A pharmaceutical reactor is the critical tool that provides the meticulously controlled environment required to achieve this consistency, purity, and safety at scale.

What Does a Pharmaceutical Reactor Actually Do?
A reactor serves as the heart of the chemical synthesis process. Its design allows operators to create and maintain the ideal conditions for a specific chemical reaction to proceed efficiently and predictably.
A Controlled Environment for Synthesis
Think of a reactor not as a container, but as a self-contained, programmable environment. Its purpose is to execute a chemical "recipe" flawlessly by controlling every critical variable.
Key Functions: Heating and Cooling
Many chemical reactions either release heat (exothermic) or absorb it (endothermic). A reactor's jacketed walls allow a heating or cooling fluid to circulate, precisely managing the internal temperature to prevent unwanted side reactions or ensure the reaction proceeds at the optimal rate.
Mixing and Agitation
An internal agitator, or stirrer, is crucial. It ensures that all reactants are uniformly mixed, which promotes consistent reaction rates and even heat distribution. Without proper agitation, "hot spots" could form, leading to impurities and a lower-quality product.
Maintaining Pressure
Some reactions are best performed under pressure to increase their speed and influence the outcome. High-pressure reactors, as noted in drug development, can significantly accelerate the synthesis of complex molecules, reducing the time from lab to market.
Why Precision is Non-Negotiable in Pharma
While reactors are used in many industries, the standards for pharmaceutical applications are exceptionally high. In this context, the reactor's primary job is to eliminate variability.
Ensuring Product Purity and Safety
Even a tiny deviation in temperature or mixing speed can create unwanted byproducts or impurities in the final drug. A pharmaceutical-grade reactor's precision is a primary line of defense in protecting patient safety by guaranteeing the purity of the API.
Enabling Complex Molecule Creation
Modern medicines are often highly complex molecules that can only be synthesized under very specific conditions. The reactor provides the stable, repeatable environment that makes large-scale production of these sensitive compounds possible.
Accelerating Drug Development
During research and development, scientists use lab-scale reactors to test and optimize reaction conditions. The ability to control these variables precisely allows for reliable data and makes scaling up the process to full production more predictable and faster.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The precision required of pharmaceutical reactors comes with specific challenges and considerations. They are highly specialized pieces of equipment, not commodity items.
High Material and Construction Costs
To prevent contamination and corrosion, pharmaceutical reactors are built from non-reactive materials like glass-lined steel or specialized alloys like Hastelloy. This, combined with the sophisticated engineering, makes them a significant capital investment.
Operational Complexity
These systems require skilled operators and advanced process control systems (PCS) to manage the reaction parameters. They are not "set it and forget it" devices; they are part of a complex, validated manufacturing process that demands constant oversight.
Rigorous Cleaning and Validation
Between batches, a reactor must be meticulously cleaned and sterilized to prevent any cross-contamination. This cleaning process itself must be validated to prove its effectiveness, adding time and operational cost to the overall production cycle.
The Reactor's Role in Your Goal
How you view a reactor depends entirely on your function within the pharmaceutical industry.
- If your primary focus is Process Development: The reactor is your instrument for optimizing reaction kinetics, maximizing yield, and defining the scalable parameters for production.
- If your primary focus is Manufacturing: The reactor is the core production asset for executing validated recipes consistently to ensure batch-to-batch uniformity and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is Quality Assurance: The reactor and its control system are critical elements you must validate to prove the manufacturing process is under control and capable of producing a safe and pure product.
Ultimately, the reactor transforms chemical potential into life-saving medicine through precise, repeatable control.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Role in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Provides a controlled environment for chemical synthesis of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs). |
| Critical Controls | Precise management of temperature, pressure, and agitation/mixing. |
| Key Benefit | Ensures batch-to-batch consistency, purity, and safety of the final drug product. |
| Common Materials | Glass-lined steel, Hastelloy, and other non-reactive alloys to prevent contamination. |
Ready to enhance your pharmaceutical manufacturing process? The precision and reliability of your reactor are paramount to producing safe, effective drugs. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including reactor systems designed for the rigorous demands of pharmaceutical synthesis. Let our experts help you find the perfect solution for your API development and production needs.
Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your goals for purity, efficiency, and scalability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP for Small Workpiece Production 400Mpa
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
People Also Ask
- How does a cold isostatic press contribute to the formation of TZC molybdenum alloy green bodies? Key Densification Tips
- What advantages does CIP equipment offer for W-TiC composites? Achieve High-Density, Defect-Free Materials
- Why is a cold isostatic press (CIP) required after Li/Li3PS4-LiI/Li battery assembly? Optimize Your Solid-State Interface
- What advantages does a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP) offer for solid-state batteries? Superior Density & Uniformity
- How does a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP) contribute to the fabrication of HE-O-MIEC and LLZTO? Expert Densification Guide



















