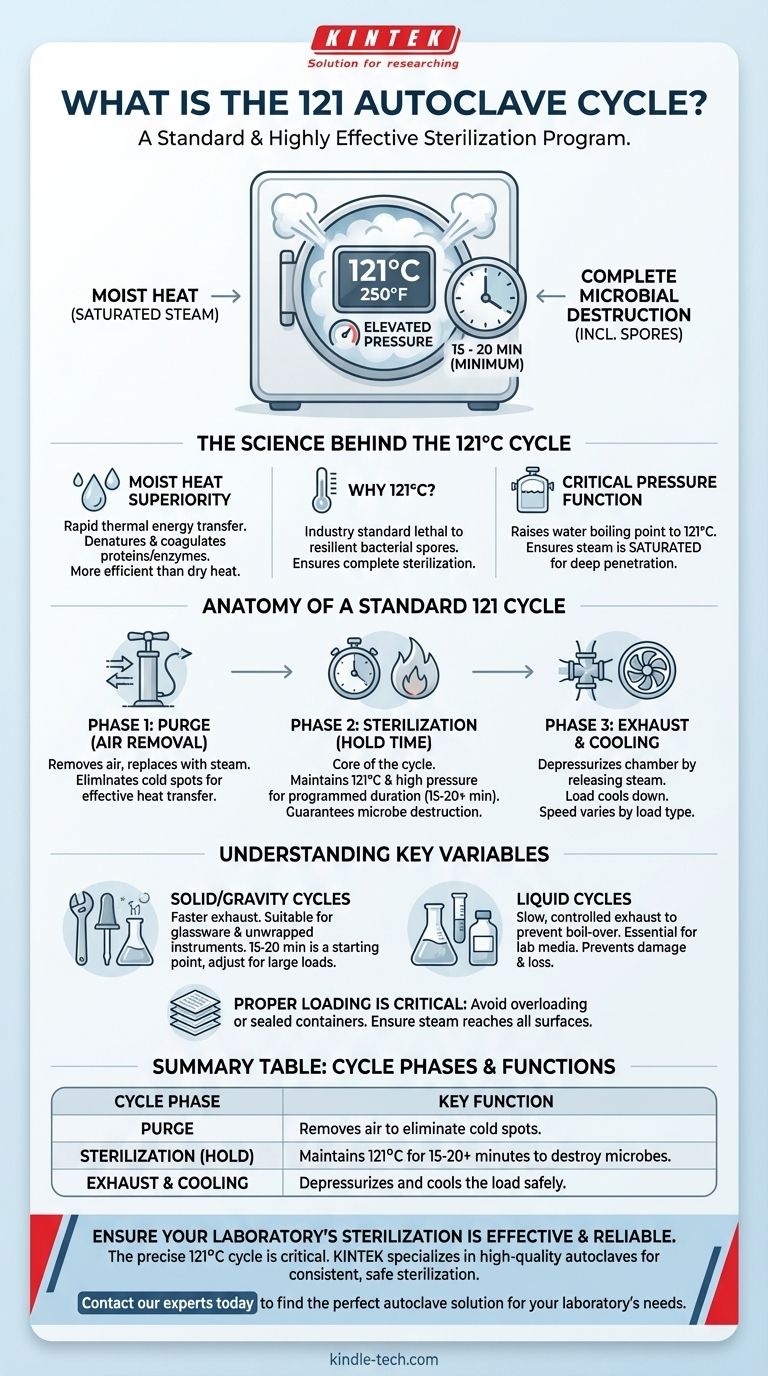
In simple terms, the "121 cycle" is a standard and highly effective sterilization program for an autoclave. It uses saturated steam heated to 121° Celsius (250° F) under pressure for a minimum of 15 to 20 minutes to destroy all forms of microbial life, including heat-resistant bacteria and spores.
The effectiveness of the 121 cycle does not come from temperature alone. It is the precise combination of moist heat (steam), elevated pressure, and sufficient time that enables the complete penetration and destruction of microorganisms, making it a cornerstone of modern sterilization.
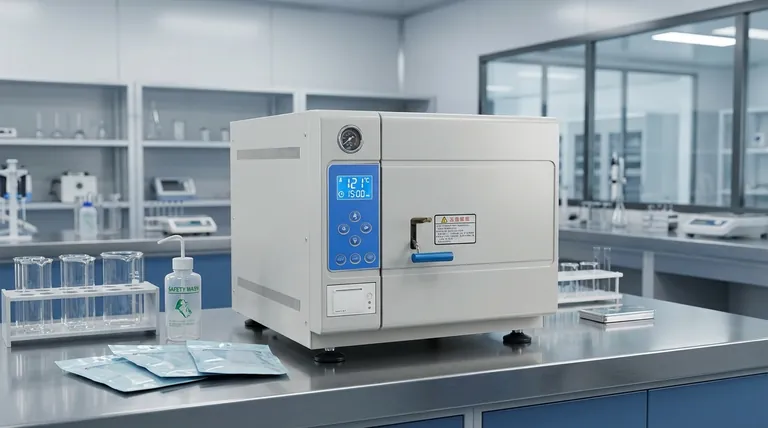

The Science Behind the 121°C Cycle
To truly understand the 121 cycle, you must look beyond the numbers and grasp the scientific principles that make it so reliable. It is a carefully orchestrated process where each element plays a critical role.
The Superiority of Moist Heat
Moist heat, in the form of saturated steam, is a far more efficient agent for sterilization than dry heat. Steam rapidly transfers thermal energy to microorganisms.
This intense energy transfer irreversibly denatures and coagulates essential proteins and enzymes, effectively destroying the cellular structures required for microbes to live and reproduce.
Why 121 Degrees Celsius?
This specific temperature is the established industry standard because it is proven to be lethal to even the most resilient bacterial spores.
While lower temperatures can kill many bacteria, 121°C provides the necessary thermal energy to guarantee the destruction of thermophiles and spores, ensuring a complete sterilization outcome.
The Critical Function of Pressure
Water boils at 100°C at normal atmospheric pressure. To reach the target temperature of 121°C, the pressure inside the autoclave chamber must be increased.
This elevated pressure serves two functions: it raises the boiling point of water to 121°C, and it ensures the steam becomes saturated, allowing it to fully penetrate the load and eliminate any insulating air pockets.
Anatomy of a Standard 121 Cycle
A typical 121 cycle is not just a single heating phase. It consists of several distinct stages designed to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Phase 1: Purge (Air Removal)
Before sterilization can begin, all air must be removed from the chamber. Air is a poor conductor of heat and its presence creates cold spots, which would lead to sterilization failure. The autoclave purges this air and replaces it with steam.
Phase 2: Sterilization (Hold Time)
This is the core of the cycle. The chamber is maintained at a constant temperature of 121°C and high pressure for the programmed duration—typically 15 to 20 minutes. This "hold time" is what guarantees the complete destruction of all microbes.
Phase 3: Exhaust and Cooling
Once the hold time is complete, the chamber is depressurized by releasing the steam. The load then begins to cool down. The speed of this phase can vary significantly depending on whether the load contains liquids or just solid goods.
Understanding the Key Variables
Relying on a single "20-minute" rule for all situations is a common and critical mistake. Effective sterilization requires you to consider the nature of the load.
The "15-20 Minute" Rule Isn't Absolute
The standard 15-20 minute hold time is a guideline for small, simple loads. As the reference material notes, the time must be adjusted based on the size and density of the load.
A large, dense bag of biological waste or a tightly packed set of instruments requires a significantly longer hold time to ensure steam penetrates to its very center.
Liquid vs. Solid Cycles
Sterilizing liquids (like microbiological media) requires a dedicated "liquid cycle." These cycles use a much slower, more controlled exhaust phase.
A rapid pressure drop would cause the superheated liquids to boil over violently, creating a mess, causing loss of volume, and potentially cracking glassware. Solid or "gravity" cycles can exhaust much faster.
The Importance of Proper Loading
How you place items in the autoclave is critical. Overloading the chamber or using sealed containers prevents steam from reaching all surfaces. This creates air pockets and guarantees that items will not be properly sterilized.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To use an autoclave effectively, match the cycle parameters to the specific load you are sterilizing.
- If your primary focus is routine sterilization of glassware or unwrapped instruments: The standard 121°C cycle for 15-20 minutes is a reliable starting point for average-sized loads.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing liquids like lab media: Always use a dedicated liquid cycle at 121°C to prevent boil-over during the exhaust phase.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing large, dense, or porous loads: You must validate a longer hold time to ensure heat and steam fully penetrate the entire load.
Understanding the principles of the 121 cycle transforms the autoclave from a simple machine into a precision tool for guaranteed sterilization.
Summary Table:
| Cycle Phase | Key Function |
|---|---|
| Purge | Removes air to eliminate cold spots. |
| Sterilization (Hold) | Maintains 121°C for 15-20+ minutes to destroy microbes. |
| Exhaust & Cooling | Depressurizes and cools the load safely. |
Ensure your laboratory's sterilization is effective and reliable. The precise 121°C cycle is critical for destroying all microbial life, but proper equipment and usage are key. KINTEK specializes in high-quality autoclaves and lab equipment designed for consistent, safe sterilization.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect autoclave solution for your laboratory's specific needs, from routine glassware to sensitive liquid media.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 16L 24L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the size of a laboratory autoclave? A Guide to Choosing the Right Capacity
- How does an autoclave sterilize instruments supplies and equipment? A Guide to High-Pressure Steam Sterilization
- What is an autoclave laboratory equipment? The Ultimate Guide to Steam Sterilization
- What are the safety concerns when autoclaving? A Guide to Preventing Burns, Explosions, and Biohazards
- Why is it important to autoclave the prepared reagents before using? Ensure Sterility and Reliable Results



















