The capacity of an autoclave refers to the volume of its internal pressure chamber, where sterilization occurs. While large industrial and medical units can range from 100 to 3,000 liters, smaller tabletop and vertical models are also widely used for laboratory and clinical applications, with capacities starting much lower.
The term "capacity" is more than just a volume measurement; it dictates the autoclave's physical design, its intended application, and its overall operational efficiency. The choice between a small vertical unit and a large horizontal one depends entirely on the volume and type of materials you need to sterilize.

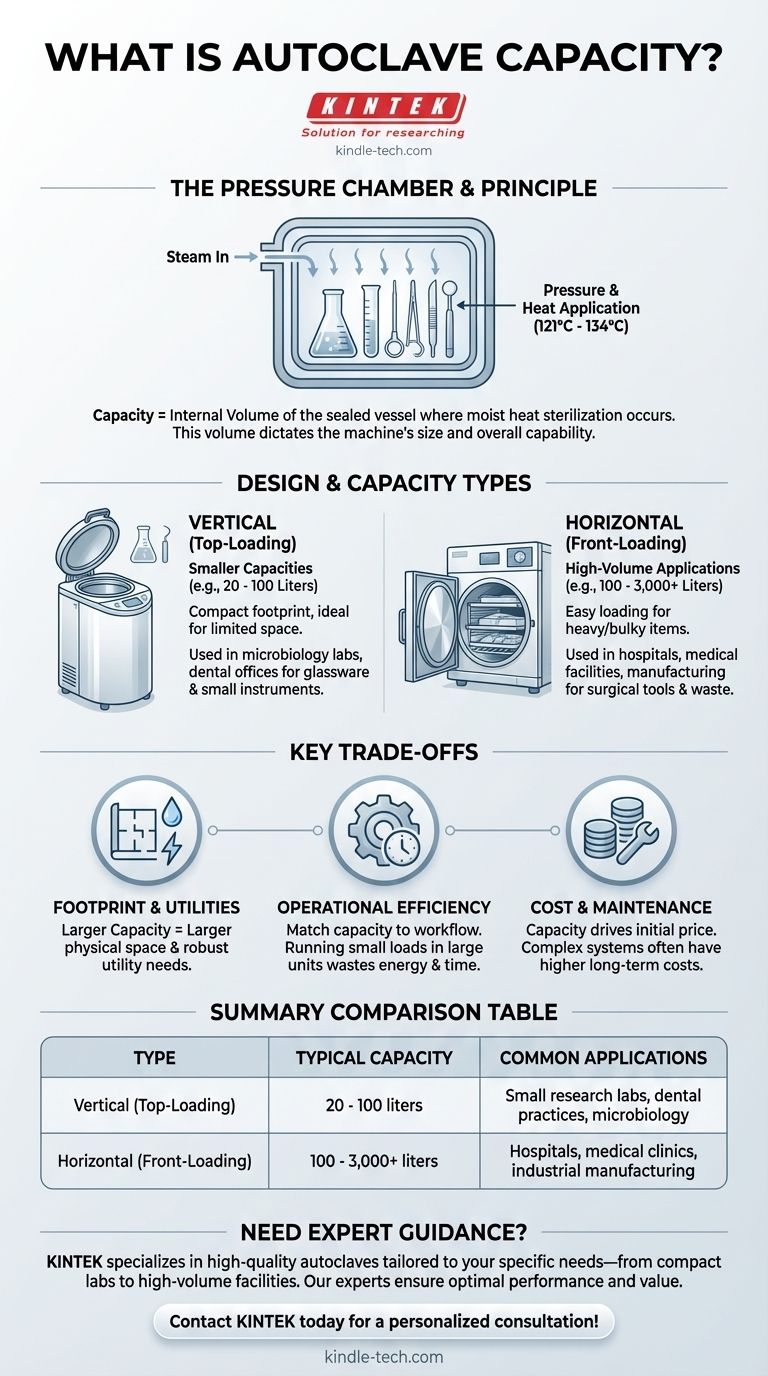
What Defines Autoclave Capacity
The Core Component: The Pressure Chamber
The capacity of an autoclave is determined by the internal volume of its pressure chamber. This is the sealed vessel where steam, pressure, and high temperature are applied to sterilize materials.
This chamber consists of an inner wall that holds the items and an outer wall or jacket that helps maintain temperature and pressure. The size of this chamber is the single most important factor in the machine's overall size and capability.
The Principle of Operation
An autoclave operates on the principle of moist heat sterilization. An electrical heater boils water to create high-pressure steam inside the chamber.
This combination of steam and pressure (typically reaching 121°C to 134°C) effectively penetrates materials to kill microbes, bacteria, and viruses. The chamber must be large enough to accommodate the items while allowing for proper steam circulation.
How Autoclave Design Relates to Capacity
Vertical Autoclaves: Smaller, Top-Loading Units
Vertical autoclaves are loaded from the top and are typically designed for smaller capacities. Their compact, upright design makes them ideal for environments with limited space.
These units are frequently used in microbiology labs, research facilities, and dental offices for sterilizing glassware, laboratory containers, and smaller instruments.
Horizontal Autoclaves: Larger, Front-Loading Units
Horizontal autoclaves feature a front-opening door, similar to a large oven, and are built for high-volume applications. Their design allows for easier loading and unloading of heavy or bulky items.
You will find these large-capacity units in hospitals for sterilizing surgical instruments, in medical facilities for processing biohazardous waste, and in manufacturing settings.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Footprint and Utility Needs
A larger capacity directly translates to a larger physical footprint. High-capacity horizontal autoclaves require significant dedicated space and more robust utility connections for electricity and water.
Operational Efficiency
Using a large autoclave for small, frequent loads is highly inefficient. It wastes energy, water, and time. Matching the capacity to your typical workflow is critical for cost-effective operation.
Cost and Maintenance
Capacity is a primary driver of an autoclave's initial purchase price. Larger and more complex horizontal systems are significantly more expensive and often have higher long-term maintenance costs than smaller vertical units.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct capacity is a foundational decision that impacts everything from workflow to operating budget.
- If your primary focus is a small research lab or dental practice: A smaller, top-loading vertical autoclave provides sufficient capacity for instruments and media in a space-efficient design.
- If your primary focus is a hospital or high-volume medical clinic: A large, front-loading horizontal autoclave is necessary to handle the throughput of surgical tools and medical waste safely.
- If your primary focus is industrial manufacturing or large-scale waste decontamination: Your choice will be a high-capacity horizontal unit specifically sized to match your production batch requirements.
Ultimately, choosing the right autoclave capacity is a strategic decision that directly impacts your operational efficiency and sterilization success.
Summary Table:
| Autoclave Type | Typical Capacity Range | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical (Top-Loading) | 20 - 100 liters | Small research labs, dental practices, microbiology |
| Horizontal (Front-Loading) | 100 - 3,000+ liters | Hospitals, medical clinics, industrial manufacturing |
Need expert guidance selecting the perfect autoclave for your laboratory?
Choosing the right capacity is crucial for your workflow efficiency and budget. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including autoclaves tailored to your specific needs—whether you run a compact research lab or a high-volume medical facility.
Our experts will help you assess your requirements to ensure you get a solution that offers optimal performance and value.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and enhance your sterilization process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- What extreme conditions does a laboratory autoclave simulate? Testing Wear Resistance of Nuclear Fuel Cladding
- What is the size of a laboratory autoclave? A Guide to Choosing the Right Capacity
- What is the efficiency of an autoclave? Achieving Total Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What are the settings for autoclave sterilization? Ensure Reliable Sterility with Proper Parameters
- What method of sterilization is autoclaving? The Definitive Guide to Moist Heat Sterilization
- Is an autoclave a medical device? Understanding Regulatory Classification and Intended Use
- What are the 4 parameters of the autoclave process? Master the Key to Guaranteed Sterilization
- Are all autoclaves the same? Understanding the Critical Differences for Sterilization Success



















