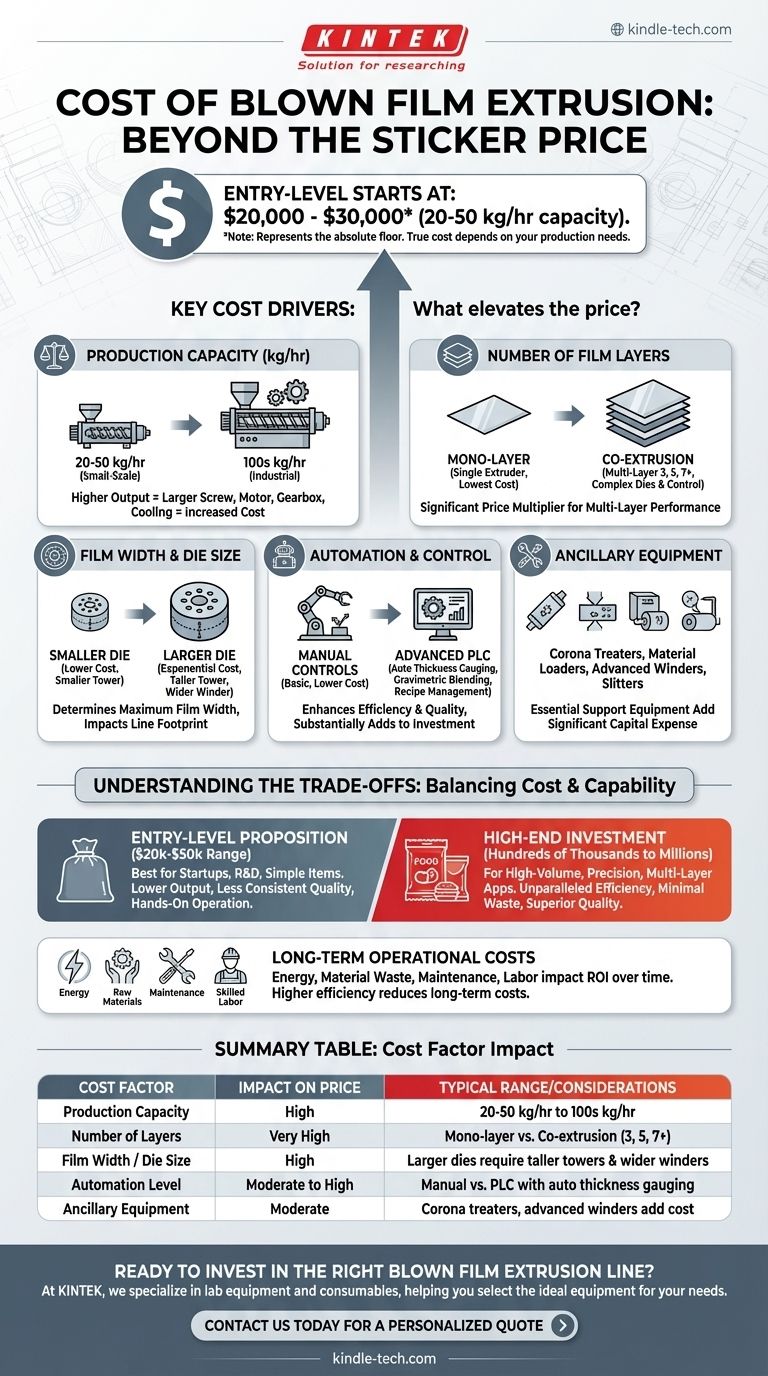
To put it directly, the cost of a blown film extrusion line varies enormously. A very basic, entry-level machine with a low production capacity (around 20-50 kg/hr) can start in the $20,000 to $30,000 range. However, this figure represents the absolute floor and is not indicative of the cost for most industrial or high-quality applications.
The sticker price of the extrusion machine is only a fraction of the total investment. The true cost is dictated by your specific production requirements—such as output, film layers, and automation—which can easily elevate the price into the six or even seven-figure range.
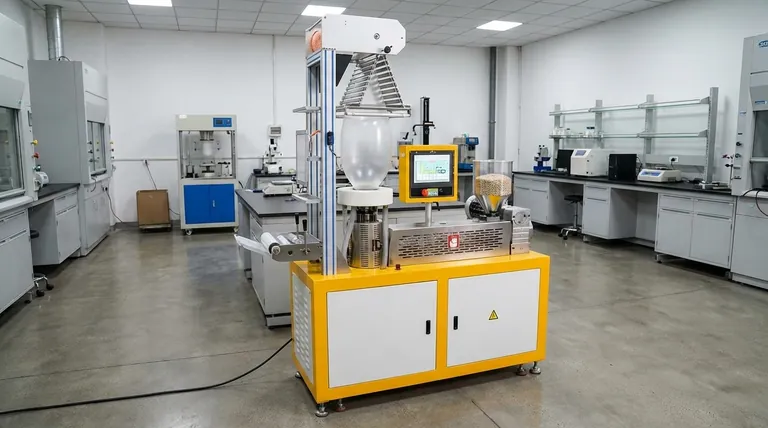

Beyond the Base Price: Key Cost Drivers
Understanding what influences the price of a blown film line is critical to making a sound investment. The final cost is a sum of its components and capabilities, each tailored to a specific production goal.
Production Capacity (kg/hr)
The most fundamental cost factor is output. The 20-50 kg/hr capacity of an entry-level machine is suitable for very small-scale work.
Increasing capacity requires a larger extruder screw, a more powerful motor and gearbox, and a more robust cooling system (especially the air ring). Each of these upgrades adds significant cost.
Number of Film Layers
This is one of the most significant price multipliers. A mono-layer line uses a single extruder and is the simplest and cheapest configuration.
Co-extrusion lines, which produce multi-layer films (e.g., 3, 5, or 7 layers), require multiple extruders, a highly complex and expensive feedblock and die, and sophisticated control systems to manage each layer. This technology is essential for modern packaging films with barrier properties.
Film Width and Die Size
The maximum width of the film you can produce is determined by the diameter of the circular die.
A larger die is exponentially more expensive to manufacture with the precision required. It also necessitates a larger air ring, a taller tower structure, and a wider winder at the end of the line, all of which increase the overall footprint and cost.
Automation and Control Systems
The level of automation directly impacts both the initial price and the long-term operational efficiency.
Base models may have simple manual controls. Advanced lines use PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems that offer features like automatic thickness gauging and control, gravimetric blending and dosing for raw materials, and recipe management. These systems reduce waste and labor costs but add substantially to the initial investment.
Ancillary Equipment
A blown film line does not operate in a vacuum. The total project cost must include essential support equipment.
This includes material loaders and blenders, corona treaters (to prepare the film surface for printing), post-extrusion slitters, and advanced winding systems. Each of these can be a significant capital expense on its own.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The vast price range exists because different machines are built to solve different problems. Choosing the right one involves balancing upfront cost with long-term performance and capability.
The Entry-Level Proposition
A machine in the $20,000-$50,000 range is best suited for startups, R&D labs, or producing simple, non-critical items like basic trash bags.
The trade-off is clear: you accept lower output, less consistent film quality, limited material compatibility, and the need for more hands-on operator intervention.
The High-End Investment
Lines costing hundreds of thousands or even millions of dollars are built for high-volume, high-precision applications. These are common in food packaging, medical films, and agricultural films.
The high initial investment buys unparalleled efficiency, minimal material waste, superior and consistent film quality, and the ability to produce complex multi-layer structures that command a higher market price.
Long-Term Operational Costs
Beyond the machine's price, you must budget for ongoing operational costs.
Energy consumption is a major factor, as are raw material costs, routine maintenance, and the need for skilled labor. A more expensive and efficient machine often has a lower cost-per-kilogram of film produced, delivering a better return on investment over time.
Making the Right Investment for Your Goal
Your application dictates your budget. Focus first on the film you need to produce, not the price of the machine.
- If your primary focus is starting a small-scale operation or testing materials: An entry-level mono-layer machine is a viable entry point, but be prepared for its operational limitations.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality packaging or technical films: Budget for a multi-layer co-extrusion line, as this capability is non-negotiable for modern performance films.
- If your primary focus is maximizing long-term profitability and efficiency: Invest in automation features like gravimetric control and advanced winding, as they will reduce material waste and labor costs significantly over the machine's life.
Ultimately, defining your product requirements and production goals is the most critical step in determining the true cost of your blown film extrusion investment.
Summary Table:
| Cost Factor | Impact on Price | Typical Range/Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Production Capacity | High | 20-50 kg/hr (entry-level) to 100s of kg/hr (industrial) |
| Number of Layers | Very High | Mono-layer (low cost) vs. Co-extrusion (3, 5, 7+ layers) |
| Film Width / Die Size | High | Larger dies require taller towers & wider winders |
| Automation Level | Moderate to High | Manual controls vs. PLC with auto thickness gauging |
| Ancillary Equipment | Moderate | Corona treaters, advanced winders, material blenders add cost |
Ready to invest in the right blown film extrusion line for your needs? At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with precision and expertise. Whether you're starting small with an entry-level system or scaling up to a high-capacity, multi-layer line, our team can help you select the ideal equipment to maximize your ROI and production efficiency. Contact us today to discuss your project and get a personalized quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab Blown Film Extrusion Three Layer Co-Extrusion Film Blowing Machine
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Powerful Plastic Crusher Machine
- Touchscreen Automatic Vacuum Heat Press
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the process of extrusion blowing? A Guide to Efficient Hollow Plastic Part Production
- What does a blown film machine do? Transform Plastic Pellets into Versatile Film
- Why are high-pressure hydraulic presses necessary for UHMWPE? Mastering Zero-Flow Material Processing
- What is the process of double extrusion? Create Integrated Multi-Material Components
- How does extrusion work step by step? A Guide to the Continuous Manufacturing Process



















