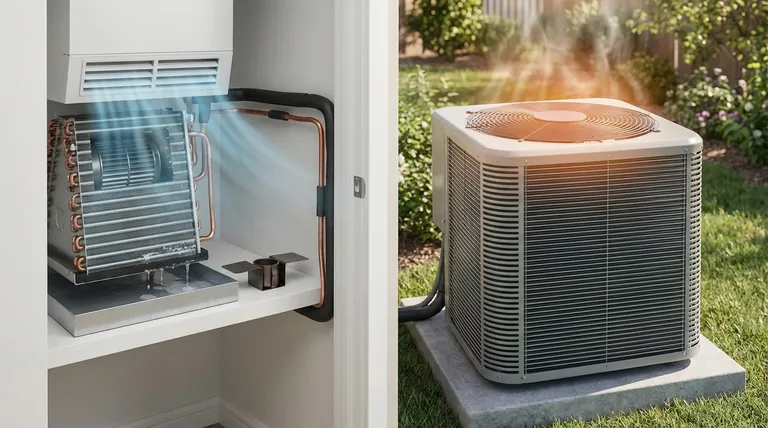
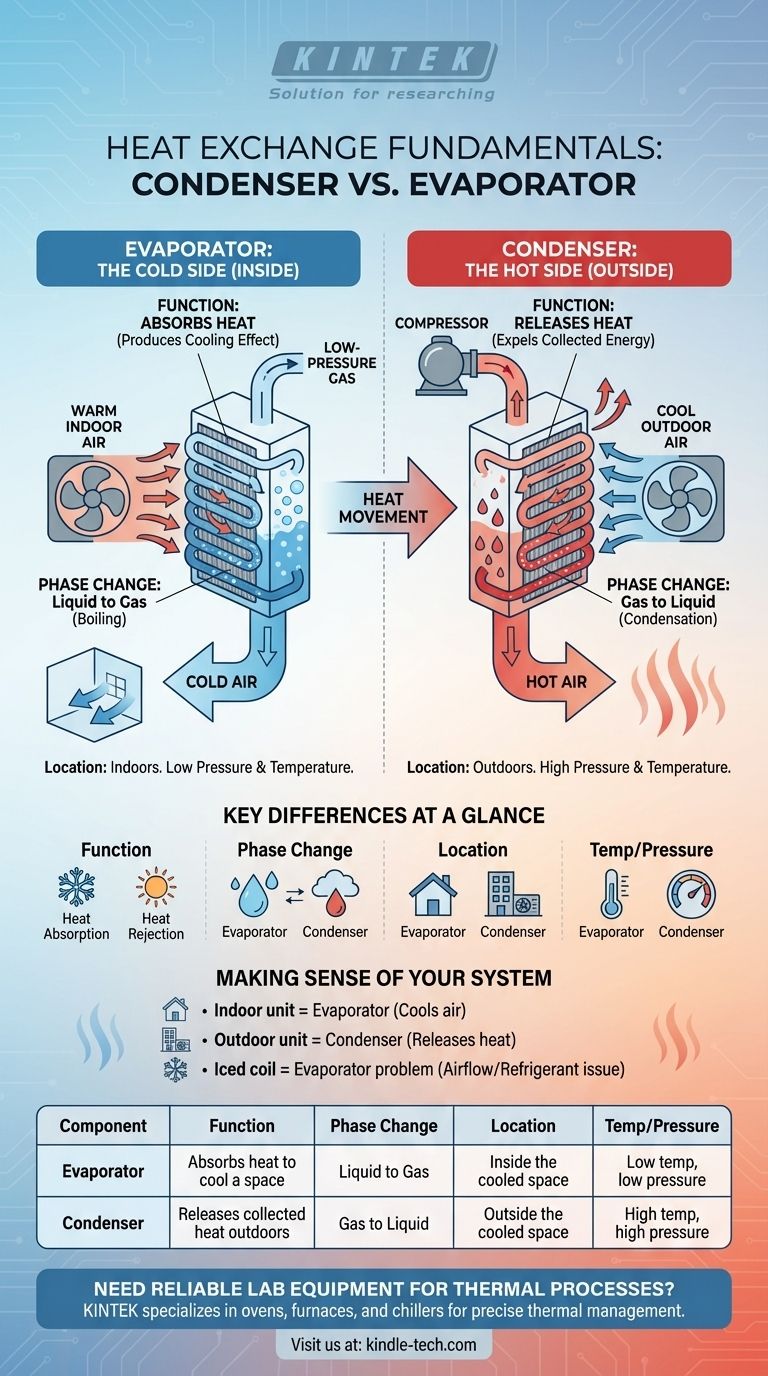
At their core, a condenser and an evaporator perform opposite functions that are essential for moving heat. The evaporator absorbs heat from the space you want to cool, while the condenser releases that collected heat into the outside environment. They are two sides of the same coin in any refrigeration or air conditioning system.
The simplest way to understand the difference is by function and location: The evaporator is the "cold side" inside your home or refrigerator that absorbs heat, while the condenser is the "hot side" outside that rejects heat.

The Core Function: Moving Heat
To understand these components, you must first grasp that air conditioners and refrigerators don't "create" cold. They are heat pumps—machines designed to move heat from one place to another.
The magic ingredient that carries this heat is a chemical compound called a refrigerant. The condenser and evaporator are simply coils where the refrigerant changes its physical state to either absorb or release thermal energy.
The Evaporator: Where Cooling Happens
The evaporator's job is to absorb heat from the indoor space, which is what produces the cooling effect you feel.
The Principle: Absorbing Heat Through Boiling
The key principle is evaporation. When a liquid turns into a gas (boils), it must absorb a significant amount of energy from its surroundings. This is why rubbing alcohol feels cold on your skin—it's evaporating and pulling heat from your body to do so.
The Process
Inside the evaporator, a very cold, low-pressure liquid refrigerant flows through a series of coils. A fan blows the warm indoor air across these coils. The heat from the air is absorbed by the refrigerant, causing it to boil and turn into a gas.
The Result: Cold Air
Because the heat has been removed from the air and transferred into the refrigerant, the air leaving the evaporator coils is now cold. This is the chilled air that cools your room or refrigerator.
The Condenser: Where Heat is Released
The condenser's job is the exact opposite: to release the heat that the refrigerant collected in the evaporator.
The Principle: Releasing Heat Through Condensation
The governing principle here is condensation. When a gas turns back into a liquid, it releases the large amount of energy it absorbed during evaporation. Think of how a cold mirror fogs up in a steamy bathroom—the water vapor (gas) releases heat as it condenses into liquid water on the mirror's surface.
The Process
After leaving the evaporator, the refrigerant (now a gas) is sent to a compressor, which raises its pressure and temperature dramatically. This hot, high-pressure gas then flows into the condenser coils, which are located outside. A fan blows cooler ambient air across these coils.
The Result: Expelling Heat
The heat flows from the hot refrigerant gas to the cooler outdoor air. As the refrigerant loses its heat, it condenses back into a high-pressure liquid. This is why the air blowing from the outdoor unit of an AC system feels hot.
Understanding the Key Differences
While they look similar—both are typically finned coils—their roles and operating conditions are diametrically opposed.
Function
The evaporator's function is heat absorption. The condenser's function is heat rejection.
Phase Change
In the evaporator, the refrigerant changes from a liquid to a gas. In the condenser, the refrigerant changes from a gas to a liquid.
Location
The evaporator is always located inside the space being cooled (e.g., your home's indoor air handler, inside a refrigerator). The condenser is located outside that space (e.g., the outdoor AC unit, on the back or bottom of a refrigerator).
Temperature and Pressure
The evaporator operates at a low pressure and low temperature to allow the refrigerant to boil easily. The condenser operates at a high pressure and high temperature to allow the refrigerant to release its heat to the surroundings.
Making Sense of Your System
Applying this knowledge allows you to quickly identify components and understand the state of your system.
- If you see the unit inside your home or building: You are looking at the evaporator, which is responsible for absorbing heat and cooling your air.
- If you see the unit outside your home: You are looking at the condenser, which is responsible for releasing that collected heat outdoors.
- If you are diagnosing a problem like an iced-over coil: This typically happens on the evaporator and indicates a problem with airflow or low refrigerant, preventing proper heat absorption.
By understanding this fundamental exchange of heat, you can better diagnose and maintain any cooling system.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Phase Change | Location | Temperature/Pressure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evaporator | Absorbs heat to cool a space | Liquid to Gas | Inside the cooled space | Low temperature, low pressure |
| Condenser | Releases collected heat outdoors | Gas to Liquid | Outside the cooled space | High temperature, high pressure |
Need reliable lab equipment for temperature control or thermal processes? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including ovens, furnaces, and chillers designed for precise, efficient thermal management. Our solutions help laboratories maintain optimal conditions for experiments and storage. Contact us today to find the perfect equipment for your laboratory's cooling and heating needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Vacuum Cold Trap Chiller Indirect Cold Trap Chiller
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- 304 316 Stainless Steel Vacuum Ball Valve Stop Valve for High Vacuum Systems
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Non-Standard Insulator Customization
People Also Ask
- What is the widely used boat made of in thermal evaporation? Choosing the Right Material for High-Purity Deposition
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What temperature does evaporation occur? Unlock the Secrets to Controlling the Rate of Evaporation
- How does a molybdenum evaporation source function in H2S for MoS2 synthesis? Master Reactive Film Deposition
- How is deposition time calculated? Mastering the Clock for Strategic Legal Advantage



















