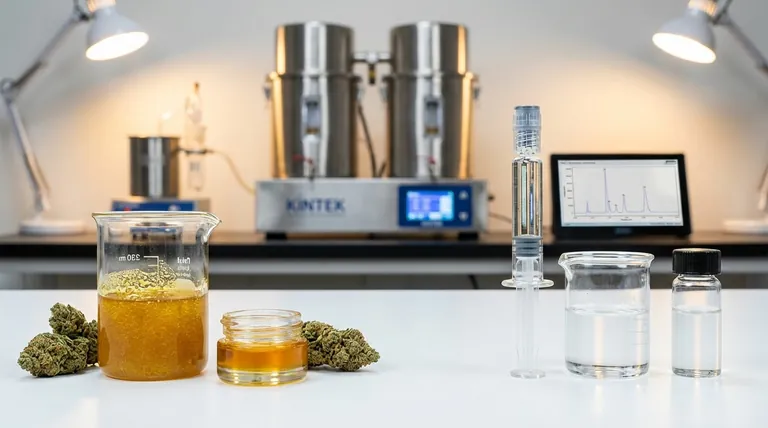
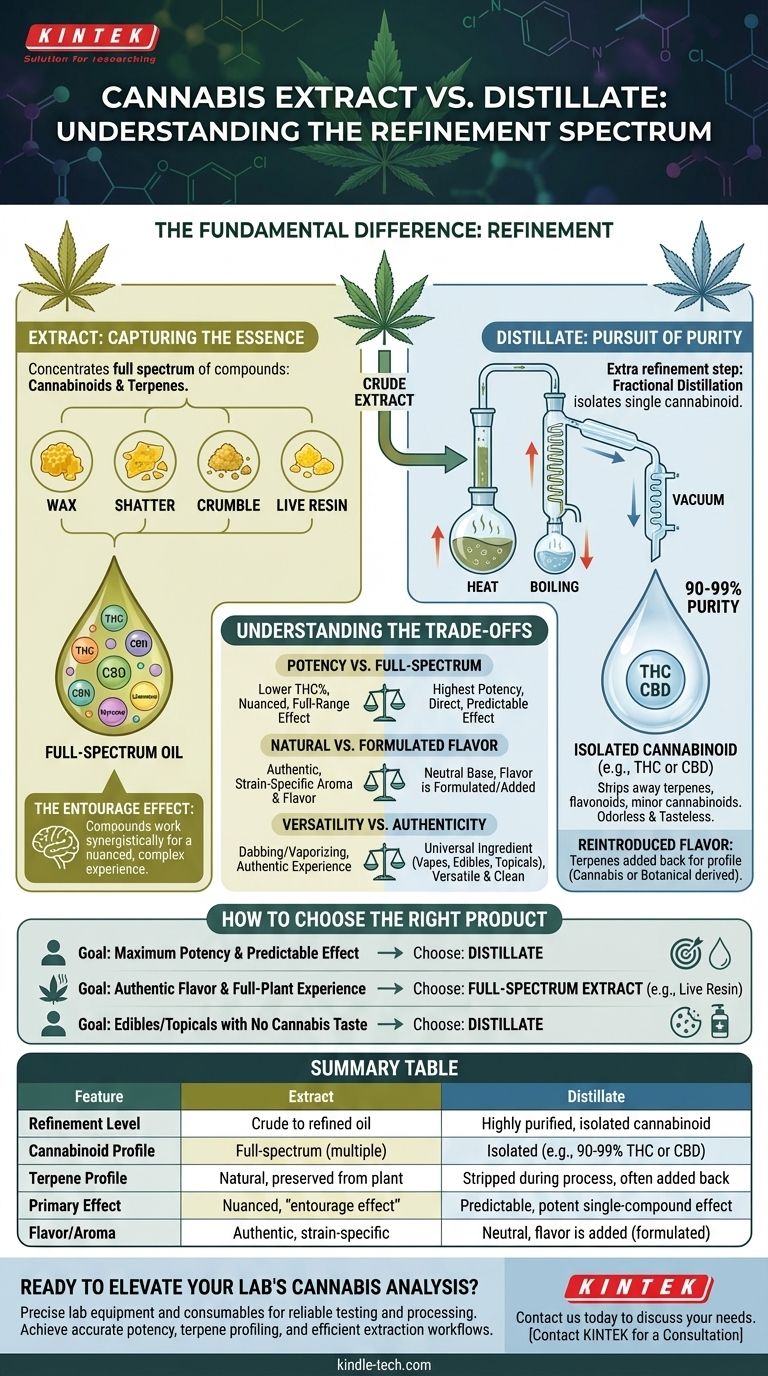
The fundamental difference is one of refinement. All cannabis distillates are extracts, but not all extracts are distillates. An extract is any oil that concentrates compounds from the cannabis plant, while a distillate is a highly refined extract that has been purified to isolate a single cannabinoid, such as THC or CBD.
The core choice between an extract and a distillate comes down to a trade-off: Extracts prioritize preserving the full, natural spectrum of the plant's compounds for a nuanced effect, while distillates prioritize maximizing the potency and purity of a single compound for a predictable effect.

Understanding "Extract" as a Broad Category
The Goal of Extraction: Capture the Plant's Essence
The primary goal of extraction is to pull the desirable compounds—cannabinoids (like THC and CBD) and terpenes (which provide aroma and flavor)—out of the raw plant material.
This process concentrates these compounds into a much more potent and versatile form than the original flower.
Common Forms of Extracts
Extraction can be done using various solvents like CO2, ethanol, or hydrocarbons (butane/propane). The specific method used results in different consistencies and products you may recognize.
These include wax, shatter, crumble, budder, and live resin. Each retains a significant portion of the source plant's original chemical profile.
The Power of the "Entourage Effect"
Extracts are often called "full-spectrum" because they contain a wide range of cannabinoids and terpenes. The theory of the entourage effect suggests that these compounds work together synergistically to produce a more complex and nuanced experience than any single compound could alone.
Defining Distillate: The Pursuit of Purity
The Process: An Extra Step of Refinement
Creating a distillate involves taking a crude cannabis extract and putting it through an additional process called fractional distillation.
This process uses precisely controlled heat and vacuum pressure to separate the various compounds based on their unique boiling points. The goal is to isolate one specific cannabinoid, most commonly THC or CBD.
The Result: An Isolated Cannabinoid
The final product is a thick, translucent oil that is almost entirely pure. Cannabis distillates often test at 90-99% purity for the target cannabinoid.
Crucially, this process strips away virtually everything else, including terpenes, flavonoids, and minor cannabinoids, leaving behind an odorless and tasteless product.
Reintroducing Flavor and Effect
Because pure distillate has no flavor, manufacturers often add terpenes back into the final product.
These can be cannabis-derived terpenes (from the original plant or others) to mimic a specific strain, or botanical-derived terpenes (from other plants) to create unique flavor profiles like blueberry or citrus.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Potency vs. a Full-Spectrum Experience
A distillate offers the highest potency of a single cannabinoid, delivering a very direct and predictable effect. There is no ambiguity about what you are consuming.
An extract offers a lower overall THC percentage but provides the full range of compounds that work in concert. Many users find this "entourage effect" results in a more satisfying and well-rounded experience that is truer to the source strain.
Natural Flavor vs. Formulated Flavor
The best extracts, particularly live resin (made from flash-frozen plants), are celebrated for their authentic and powerful aroma and flavor profiles. They taste and smell exactly like the plant they came from.
Distillates are a blank canvas. Their flavor is entirely dependent on the quality and source of the terpenes that are added back in after distillation. This can be a benefit for some products, like edibles, where a neutral base is desired.
Versatility vs. Authenticity
Distillate is extremely versatile. Its purity and lack of flavor make it the perfect base for vape cartridges, edibles, and topicals because it can be easily measured and formulated without introducing a "weedy" taste.
Extracts are typically consumed through dabbing or specialized vaporizers. Their strong flavors and varied consistencies make them less suitable as a universal ingredient but highly sought after for a more authentic consumption experience.
How to Choose the Right Product for You
Your choice should be guided by the experience you are seeking.
- If your primary focus is maximum potency and a highly predictable effect: Distillate is the most direct and efficient option available.
- If your primary focus is authentic flavor and a nuanced, full-plant experience: A full-spectrum extract like live resin or live rosin will deliver the authentic profile you're looking for.
- If your primary focus is creating edibles or topicals without a cannabis taste: Distillate provides a potent, clean, and flavorless cannabinoid base to build upon.
Ultimately, understanding the journey from plant to product empowers you to select the precise experience you want to have.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Extract | Distillate |
|---|---|---|
| Refinement Level | Crude to refined oil | Highly purified, isolated cannabinoid |
| Cannabinoid Profile | Full-spectrum (multiple cannabinoids) | Isolated (e.g., 90-99% THC or CBD) |
| Terpene Profile | Natural, preserved from plant | Stripped during process, often added back |
| Primary Effect | Nuanced, "entourage effect" | Predictable, potent single-compound effect |
| Flavor/Aroma | Authentic, strain-specific | Neutral, flavor is added (formulated) |
Ready to Elevate Your Lab's Cannabis Analysis?
Understanding the nuances between extracts and distillates is crucial for quality control and product development. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables you need for reliable cannabis testing and processing.
We help our laboratory partners achieve accurate potency measurements, terpene profiling, and efficient extraction workflows. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can support your specific needs and ensure the highest standards in your cannabis research and production.
Contact KINTEK for a Consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
People Also Ask
- What is the process of batch annealing? Achieve Maximum Softness for Deep-Drawn Metals
- What are the advantages and limitations of heat treatment? Tailor Material Properties for Peak Performance
- Why is a laboratory magnetic stirrer required for benzoic acid esters? Boost Reaction Speed & Yield with High RPM
- What is the primary function of a vacuum pump? Remove Gas Molecules to Create a Controlled Vacuum
- What is benefit of sintering? Achieve Superior Material Performance & Complex Part Manufacturing
- What is the role of a magnetic stirrer in Zn-Based Zeolite prep? Maximize Ion Exchange and Homogeneity
- What is the difference between sintering and powder metallurgy? Sintering is a Key Step Within the Process
- What is heat treatment in simple terms? A Guide to Transforming Material Properties

