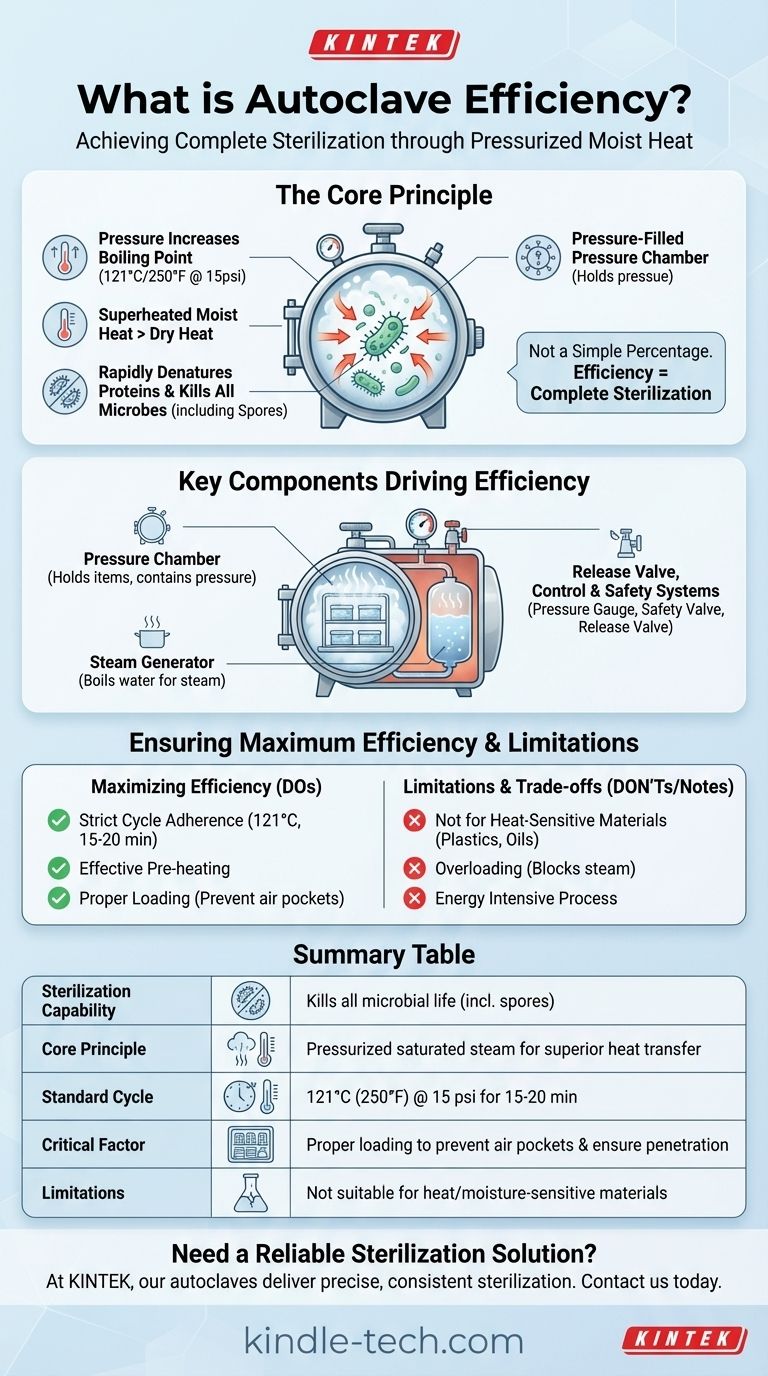
An autoclave's efficiency is not measured as a simple percentage, but by its unparalleled ability to achieve complete sterilization. It reliably kills all forms of microbial life, including highly resistant bacterial spores, by using high-pressure saturated steam at a typical cycle of 121°C (250°F) for 15-20 minutes.
The core of an autoclave's efficiency lies in a simple principle of physics: pressure increases the boiling point of water. This creates superheated, moisture-laden steam that transfers heat far more effectively than dry air, rapidly penetrating and destroying microorganisms.

The Core Principle: Why Moist Heat Under Pressure Excels
To understand an autoclave's efficiency, you must first understand why it is the gold standard for sterilization in medical and laboratory settings. It’s not just about heat, but a specific kind of heat.
Overcoming the Limits of Boiling Water
At standard atmospheric pressure, water boils at 100°C (212°F). While this temperature can kill many active bacteria, it is not sufficient to reliably destroy hardy bacterial spores. Simply boiling instruments does not guarantee sterilization.
The Power of High Pressure
An autoclave is a sealed pressure chamber. By increasing the internal pressure, it forces water to boil at a much higher temperature. For example, at a pressure of 15 pounds per square inch (psi) above atmospheric pressure, the boiling point of water rises to 121°C (250°F).
How Saturated Steam Kills Microbes
This superheated steam is the key. Unlike the dry heat of an oven, this moist heat is incredibly effective at transferring thermal energy into microorganisms. The moisture rapidly denatures and coagulates the essential proteins within bacteria, viruses, and spores, killing them quickly and completely.
Key Components Driving Autoclave Efficiency
Several critical components work in concert to create and maintain the precise conditions needed for this process to be both effective and repeatable.
The Pressure Chamber and Lid
This is the main vessel that holds the items to be sterilized. Its robust construction, along with a tightly sealing lid or door, is essential for containing the high pressure required to achieve sterilization temperatures. Many designs use an outer jacket or coiled pipes to circulate steam, heating the chamber walls quickly and evenly.
The Steam Generator
Often an integrated electrical heater, the steam generator's function is to boil water and produce the saturated steam. An efficient generator brings the autoclave up to temperature and pressure quickly, reducing overall cycle time.
Control and Safety Systems
The process is not left to chance. An autoclave's efficiency is guaranteed by its controls.
- Pressure Gauge: Displays the internal pressure, allowing the operator to confirm the correct conditions are met.
- Safety Valve: A critical feature that automatically releases pressure if it exceeds a safe level, preventing malfunction.
- Pressure Release Valve: Allows for the controlled release of steam and pressure at the end of the sterilization cycle.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, an autoclave is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is crucial for proper use.
Not Suitable for All Materials
The combination of high heat and moisture can damage or destroy certain materials. Heat-sensitive plastics, oils, powders, and corrosive substances should not be autoclaved.
The Critical Role of Proper Loading
Efficiency is easily compromised by improper loading. If items are packed too tightly or wrapped in materials that block steam, air pockets can form. These pockets prevent steam from reaching every surface, leading to incomplete sterilization.
Energy and Water Consumption
An autoclave cycle requires a significant amount of electrical energy to heat the water and water to produce the steam. While the process itself is efficient at killing microbes, it is an energy-intensive operation.
Ensuring Maximum Efficiency in Your Process
Applying these principles correctly ensures that every cycle is successful. Your goal dictates which aspect of efficiency you prioritize.
- If your primary focus is guaranteed sterilization: Strictly adhere to validated time and temperature cycles, such as 121°C for at least 15 minutes, to ensure the destruction of even the most resistant spores.
- If your primary focus is operational speed: Ensure your autoclave has an effective pre-heating function and avoid overloading the chamber, as larger loads require longer times to reach target temperature.
- If your primary focus is preventing damage: Confirm that every item is designated as "autoclavable" and use appropriate bags or wraps that permit steam penetration without trapping condensation.
By mastering its principles of operation, the autoclave becomes an exceptionally reliable and predictable tool for achieving total sterilization.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | How It Defines Autoclave Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Sterilization Capability | Kills all microbial life, including highly resistant spores. |
| Core Principle | Uses pressurized saturated steam for superior heat transfer. |
| Standard Cycle | 121°C (250°F) at 15 psi for 15-20 minutes. |
| Critical Factor | Proper loading to prevent air pockets and ensure steam penetration. |
| Limitations | Not suitable for heat-sensitive or moisture-sensitive materials. |
Need a reliable sterilization solution for your lab?
At KINTEK, we understand that your laboratory's efficiency and safety depend on dependable equipment. Our range of high-performance autoclaves is designed to deliver the precise, consistent sterilization you need to protect your research and ensure compliance.
We specialize in providing lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific workflow. Let our experts help you select the perfect autoclave to guarantee complete sterilization, prevent damage to sensitive materials, and optimize your operational speed.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory's sterilization needs and discover the right autoclave for you.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Desktop Fast High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 16L 24L for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the design requirements for a corrosion-resistant autoclave? Expert Solutions for Scheelite Leaching
- What lab supplies should be autoclaved? A Guide to Safe Sterilization and Decontamination
- What is incubator sterilization? Essential Guide to Contamination Control for Labs
- What is the function of a high-pressure Autoclave in the alkaline leaching process of scheelite? Maximize Tungsten Yield
- Can you sterilize without autoclave? Yes, and Here's How to Choose the Right Method
- What are the advantages of using a large-capacity autoclave for the secondary curing of calcium silicate specimens?
- Why is an autoclave the most effective sterilizer? Unlock the Power of Pressurized Steam for Guaranteed Sterility
- What are the different sterilization methods for a microbiology lab? Ensure Reliable and Safe Experiments



















