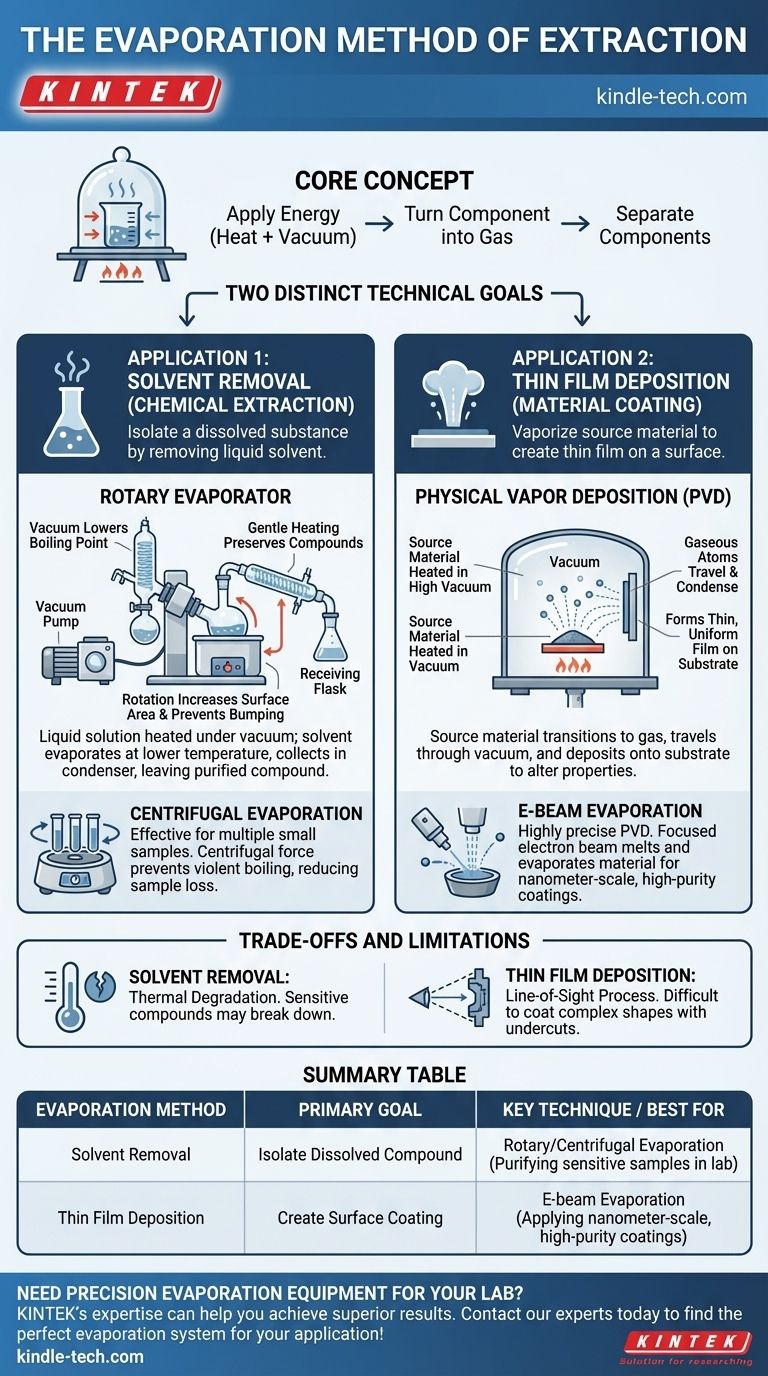
At its core, the evaporation method of extraction is a process that separates components by turning one of them into a gas. This is achieved by applying energy, typically heat, often within a vacuum to lower the material's boiling point. However, the term applies to two fundamentally different technical goals: removing a liquid solvent to isolate a dissolved substance, and vaporizing a source material to create a thin film on a surface.
The term "evaporation extraction" is context-dependent, referring to two distinct processes. The first is a chemical lab technique for gently removing a liquid solvent to leave behind a purified substance. The second is a materials science technique for creating ultra-thin, high-purity coatings by vaporizing a solid source material onto a substrate.

The Two Primary Applications of Evaporation
The key to understanding this method is to first identify the goal. Are you trying to get rid of a liquid to keep what's dissolved in it, or are you trying to move a material from one place to another by turning it into a gas?
Application 1: Solvent Removal (Chemical Extraction)
This is the classic laboratory method for isolating a compound. The goal is to gently remove a liquid solvent, leaving behind the desired non-volatile substance (the solute).
How It Works: Rotary Evaporation
A solution is placed in a rotating flask that is heated gently in a water bath. A vacuum is applied, which lowers the solvent's boiling point, allowing it to evaporate at a much lower temperature than normal.
This gentle heating helps preserve temperature-sensitive compounds. The rotation increases the surface area of the liquid and prevents violent boiling, or "bumping." The resulting solvent vapor travels into a condenser, where it cools back into a liquid and collects in a separate flask, leaving the purified compound behind.
A Variation: Centrifugal Evaporation
This method also uses a vacuum to lower the solvent's boiling point but uses centrifugal force instead of rotation in a flask. This is highly effective for processing many small samples at once.
The process forces the solvent to boil from the surface downwards, which dramatically reduces the risk of sample loss or cross-contamination between samples.
Application 2: Thin Film Deposition (Material Coating)
In materials science and manufacturing, evaporation is used to create incredibly thin, high-purity coatings. The goal here is not to discard the vapor, but to use it as the final product.
The principle is simple and can be compared to steam from a hot bath condensing on a cold ceiling. A source material is heated in a vacuum chamber until it evaporates, and the resulting gas travels and deposits onto a target object, called a substrate.
How It Works: Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
This is the general category for thin film coating via evaporation. A source material is heated in a high vacuum, causing it to transition into a gaseous phase.
These gaseous atoms or molecules travel through the vacuum chamber and condense on the cooler substrate, forming a thin, uniform film that alters the substrate's physical properties.
A Key Example: E-Beam Evaporation
This is a highly precise form of PVD. Instead of a simple heater, a focused beam of electrons bombards the source material in a water-cooled crucible.
The intense energy from the electron beam causes the material to melt and evaporate. This produces a very pure vapor that creates high-purity coatings with a thickness controlled at the nanometer scale (typically 5 to 250 nm).
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, both applications of evaporation have specific constraints that determine their use.
For Solvent Removal
The primary challenge is thermal degradation. Even with a vacuum, some compounds are too sensitive for any amount of heat and may break down. The efficiency also depends heavily on the solvent's boiling point and the stability of the vacuum.
For Thin Film Deposition
This is a "line-of-sight" process. The evaporated material travels in a straight line, making it difficult to coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with undercuts. Furthermore, the properties of the final film are highly sensitive to the purity of the vacuum and the source material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge effectively, you must match the technique to your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is isolating a temperature-sensitive compound from a liquid solution: You need a solvent removal technique like rotary or centrifugal evaporation to gently boil off the liquid without damaging your product.
- If your primary focus is creating an ultra-thin, high-purity coating on a surface: You need a thin film deposition technique like PVD, and more specifically e-beam evaporation for the highest precision and purity.
Understanding the distinction between removing a solvent and depositing a material is the key to mastering evaporation as a technical tool.
Summary Table:
| Evaporation Method | Primary Goal | Key Technique | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solvent Removal | Isolate a dissolved compound | Rotary/Centrifugal Evaporation | Purifying temperature-sensitive samples in a lab |
| Thin Film Deposition | Create a coating on a surface | E-beam Evaporation (PVD) | Applying nanometer-scale, high-purity coatings |
Need precision evaporation equipment for your lab? Whether you're purifying compounds or depositing thin films, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment can help you achieve superior results. Our solutions are designed for reliability and precision. Contact our experts today to find the perfect evaporation system for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of PECVD deposition? Achieve High-Quality Films at Low Temperatures
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is plasma activated chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition


















